Rapid Response Fluorescence Probe Enabled In Vivo Diagnosis and Assessing Treatment Response of Hypochlorous Acid-Mediated Rheumatoid Arthritis
- PMID: 30128246
- PMCID: PMC6096987
- DOI: 10.1002/advs.201800397
Rapid Response Fluorescence Probe Enabled In Vivo Diagnosis and Assessing Treatment Response of Hypochlorous Acid-Mediated Rheumatoid Arthritis
Abstract
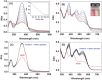
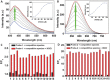
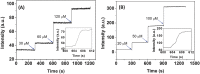
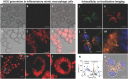
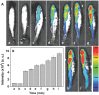
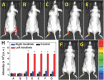
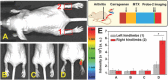
Diagnosis and early assessment of the treatment response of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) necessitates a reliable bioanalytical method for rapid, sensitive, and specific detection of the hypochlorous acid (HOCl) biomarker in inflammatory diseases. Herein, two fluorescence probes, Probe-1 and Probe-2 are developed for quantitative monitoring and visualization of inflammatory response-related HOCl levels in vitro and in vivo. In the presence of HOCl, fluorescence "OFF-ON" response is obtained for both the probes as a result of specific HOCl-triggered C=N bond cleavage reaction. Probe-1 and Probe-2 feature rapid response (<4 s), a high degree of sensitivity and selectivity toward HOCl, which allow them to be used for quantification of HOCl in a simulated physiological condition. Using Probe-2 as the probe, fluorescence imaging and flow cytometry analysis of HOCl levels in lysosome of inflammatory mimic cells, visualization of HOCl generation in endotoxin-induced inflammation of adult zebrafish and RA of mice are possible. Probe-2 exhibits high effectiveness for early assessment of the treatment response of HOCl-mediated RA in mice with an antiarthritic drug, methotrexate (MTX). The results demonstrate that Probe-2 is a powerful tool for future studies on diagnosis and monitoring treatment efficiency in a broad range of inflammatory diseases, including RA.
Keywords: fluorescence probes; hypochlorous acid; inflammatory diseases; rheumatoid arthritis; treatment response.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Quinoline-based fluorescent probe for the detection and monitoring of hypochlorous acid in a rheumatoid arthritis model.RSC Adv. 2021 Sep 24;11(50):31656-31662. doi: 10.1039/d1ra06224g. eCollection 2021 Sep 21. RSC Adv. 2021. PMID: 35496887 Free PMC article.
-
Dual-Channel/Localization Single-Molecule Fluorescence Probe for Monitoring ATP and HOCl in Early Diagnosis and Therapy of Rheumatoid Arthritis.Anal Chem. 2024 Apr 9;96(14):5428-5436. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.3c05342. Epub 2024 Mar 29. Anal Chem. 2024. PMID: 38551643
-
Responsive Fluorescence Probe for Selective and Sensitive Detection of Hypochlorous Acid in Live Cells and Animals.Chem Asian J. 2018 Sep 17;13(18):2611-2618. doi: 10.1002/asia.201800957. Epub 2018 Aug 6. Chem Asian J. 2018. PMID: 29963750
-
Recent development of synthetic probes for detection of hypochlorous acid/hypochlorite.Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc. 2020 Oct 15;240:118545. doi: 10.1016/j.saa.2020.118545. Epub 2020 May 31. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc. 2020. PMID: 32521447 Review.
-
Research Progress of Small Molecule Fluorescent Probes for Detecting Hypochlorite.Sensors (Basel). 2021 Sep 22;21(19):6326. doi: 10.3390/s21196326. Sensors (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34640646 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Practical Implementation of Artificial Intelligence-Based Deep Learning and Cloud Computing on the Application of Traditional Medicine and Western Medicine in the Diagnosis and Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Dec 23;12:765435. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.765435. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 35002704 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rutin-modified silver nanoparticles as a chromogenic probe for the selective detection of Fe3+ in aqueous medium.RSC Adv. 2019 Sep 23;9(51):30007-30011. doi: 10.1039/c9ra06653e. eCollection 2019 Sep 18. RSC Adv. 2019. PMID: 35531525 Free PMC article.
-
Sequential detection of hypochlorous acid and sulfur dioxide derivatives by a red-emitting fluorescent probe and bioimaging applications in vitro and in vivo.RSC Adv. 2022 May 26;12(25):15861-15869. doi: 10.1039/d2ra01048h. eCollection 2022 May 23. RSC Adv. 2022. PMID: 35733666 Free PMC article.
-
Quinoline-based fluorescent probe for the detection and monitoring of hypochlorous acid in a rheumatoid arthritis model.RSC Adv. 2021 Sep 24;11(50):31656-31662. doi: 10.1039/d1ra06224g. eCollection 2021 Sep 21. RSC Adv. 2021. PMID: 35496887 Free PMC article.
-
An Anthracene Carboxamide-Based Fluorescent Probe for Rapid and Sensitive Detection of Mitochondrial Hypochlorite in Living Cells.Biosensors (Basel). 2023 Sep 12;13(9):883. doi: 10.3390/bios13090883. Biosensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37754117 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Joo Y.‐B., Park K.‐S., N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, e27. - PubMed
-
- Brand D. D., Latham K. A., Rosloniec E. F., Nat. Protoc. 2007, 2, 1269. - PubMed
-
- Herman S., Zurgil N., Deutsch M., Inflammation Res. 2005, 54, 273. - PubMed
-
- Firestein G. S., Paine M. M., Boyle D. L., Arthritis Rheum. 1994, 37, 193. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
