Remote ischemic conditioning: a promising therapeutic intervention for multi-organ protection
- PMID: 30115811
- PMCID: PMC6128414
- DOI: 10.18632/aging.101527
Remote ischemic conditioning: a promising therapeutic intervention for multi-organ protection
Abstract
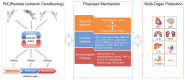
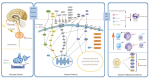
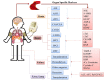
Despite decades of formidable exploration, multi-organ ischemia-reperfusion injury (IRI) encountered, particularly amongst elderly patients with clinical scenarios, such as age-related arteriosclerotic vascular disease, heart surgery and organ transplantation, is still an unsettled conundrum that besets clinicians. Remote ischemic conditioning (RIC), delivered via transient, repetitive noninvasive IR interventions to distant organs or tissues, is regarded as an innovative approach against IRI. Based on the available evidence, RIC holds the potential of affording protection to multiple organs or tissues, which include not only the heart and brain, but also others that are likely susceptible to IRI, such as the kidney, lung, liver and skin. Neuronal and humoral signaling pathways appear to play requisite roles in the mechanisms of RIC-related beneficial effects, and these pathways also display inseparable interactions with each other. So far, several hurdles lying ahead of clinical translation that remain to be settled, such as establishment of biomarkers, modification of RIC regimen, and deep understanding of underlying minutiae through which RIC exerts its powerful function. As this approach has garnered an increasing interest, herein, we aim to encapsulate an overview of the basic concept and postulated protective mechanisms of RIC, highlight the main findings from proof-of-concept clinical studies in various clinical scenarios, and also to discuss potential obstacles that remain to be conquered. More well designed and comprehensive experimental work or clinical trials are warranted in future research to confirm whether RIC could be utilized as a non-invasive, inexpensive and efficient adjunct therapeutic intervention method for multi-organ protection.
Keywords: age-related arteriosclerotic vascular disease; clinical translation; ischemia-reperfusion injury; multi-organ protection; remote ischemic conditioning.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



Similar articles
-
Remote ischemic preconditioning: a novel protective method from ischemia reperfusion injury--a review.J Surg Res. 2008 Dec;150(2):304-30. doi: 10.1016/j.jss.2007.12.747. Epub 2008 Jan 22. J Surg Res. 2008. PMID: 19040966 Review.
-
Protection of organs other than the heart by remote ischemic conditioning.J Cardiovasc Med (Hagerstown). 2013 Mar;14(3):193-205. doi: 10.2459/JCM.0b013e328359dd7b. J Cardiovasc Med (Hagerstown). 2013. PMID: 23079610 Review.
-
Remote Ischemic Conditioning and Renal Protection.J Cardiovasc Pharmacol Ther. 2017 Jul;22(4):321-329. doi: 10.1177/1074248417702480. Epub 2017 Apr 26. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol Ther. 2017. PMID: 28443376 Review.
-
Remote ischemic conditioning temporarily improves antioxidant defense.J Surg Res. 2016 Jan;200(1):105-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jss.2015.07.031. Epub 2015 Jul 22. J Surg Res. 2016. PMID: 26316445
-
No Effect of Remote Ischemic Conditioning Strategies on Recovery from Renal Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury and Protective Molecular Mediators.PLoS One. 2015 Dec 31;10(12):e0146109. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0146109. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26720280 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Effects of remote ischemic conditioning on microcirculatory alterations in patients with sepsis: a single-arm clinical trial.Ann Intensive Care. 2021 Apr 7;11(1):55. doi: 10.1186/s13613-021-00848-y. Ann Intensive Care. 2021. PMID: 33829305 Free PMC article.
-
The role of PAK1 in the sensitivity of kidney epithelial cells to ischemia-like conditions.Cell Cycle. 2019 Mar;18(5):596-604. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2019.1578149. Epub 2019 Feb 11. Cell Cycle. 2019. PMID: 30724698 Free PMC article.
-
Short-term remote ischemic conditioning may protect monkeys after ischemic stroke.Ann Clin Transl Neurol. 2019 Jan 15;6(2):310-323. doi: 10.1002/acn3.705. eCollection 2019 Feb. Ann Clin Transl Neurol. 2019. PMID: 30847363 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of remote ischemic conditioning on conditioned pain modulation and cardiac autonomic modulation in women with knee osteoarthritis: placebo-controlled randomized clinical trial protocol.Trials. 2023 Aug 7;24(1):502. doi: 10.1186/s13063-023-07527-2. Trials. 2023. PMID: 37550703 Free PMC article.
-
Nephroprotective effect of remote ischemic conditioning on type 2 diabetic rats.Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2024;27(10):1340-1345. doi: 10.22038/ijbms.2024.77896.16855. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2024. PMID: 39229583 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

