Maltodextrin modified liposomes for drug delivery through the blood-brain barrier
- PMID: 30108846
- PMCID: PMC6071985
- DOI: 10.1039/c7md00045f
Maltodextrin modified liposomes for drug delivery through the blood-brain barrier
Abstract
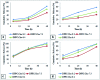
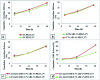
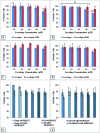
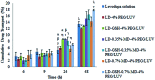
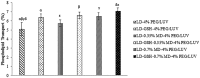
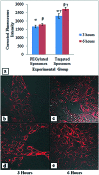
Central nervous system acting drugs, when administered intravenously, cannot show their effect in the brain due to the difficulty in crossing the blood-brain barrier (BBB). Levodopa is one of those drugs that are used to treat Parkinson's disease. In this study, a new liposomal levodopa delivery system that is modified with maltodextrin was developed in order to target and enhance transport through the BBB. An antioxidant, glutathione, was co-loaded in liposomes as a supportive agent and its effect on liposome stability and delivery was investigated. Glutathione co-loading had a positive effect on the viabilities of 3T3 and SH-SY5Y cells. Maltodextrin targeted liposomes showed high in vitro levodopa passage in the parallel artificial membrane permeability assay and had superior binding to MDCK cells. Results suggest that maltodextrin modification of liposomes is an effective way of targeting the BBB and the developed liposomal formulation would improve brain delivery of central nervous system agents.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Dual-targeting topotecan liposomes modified with tamoxifen and wheat germ agglutinin significantly improve drug transport across the blood-brain barrier and survival of brain tumor-bearing animals.Mol Pharm. 2009 May-Jun;6(3):905-17. doi: 10.1021/mp800218q. Mol Pharm. 2009. PMID: 19344115
-
Recent Advancements in Liposome-Based Strategies for Effective Drug Delivery to the Brain.Curr Med Chem. 2021;28(21):4152-4171. doi: 10.2174/0929867328666201218121728. Curr Med Chem. 2021. PMID: 33342401 Review.
-
Liposome-based targeting of dopamine to the brain: a novel approach for the treatment of Parkinson's disease.Mol Psychiatry. 2021 Jun;26(6):2626-2632. doi: 10.1038/s41380-020-0742-4. Epub 2020 May 5. Mol Psychiatry. 2021. PMID: 32372010
-
Liposome formulated with TAT-modified cholesterol for enhancing the brain delivery.Int J Pharm. 2011 Oct 31;419(1-2):85-95. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2011.07.021. Epub 2011 Jul 23. Int J Pharm. 2011. PMID: 21807083
-
Current advancements related to phytobioactive compounds based liposomal delivery for neurodegenerative diseases.Ageing Res Rev. 2023 Jan;83:101806. doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2022.101806. Epub 2022 Nov 23. Ageing Res Rev. 2023. PMID: 36427765 Review.
Cited by
-
Liposome Drug Delivery System across Endothelial Plasma Membrane: Role of Distance between Endothelial Cells and Blood Flow Rate.Molecules. 2020 Apr 18;25(8):1875. doi: 10.3390/molecules25081875. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 32325705 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Enhancing date seed phenolic bioaccessibility in soft cheese through a dehydrated liposome delivery system and its effect on testosterone-induced benign prostatic hyperplasia in rats.Front Nutr. 2023 Dec 18;10:1273299. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2023.1273299. eCollection 2023. Front Nutr. 2023. PMID: 38178973 Free PMC article.
-
An Overview of Nanotechnologies for Drug Delivery to the Brain.Pharmaceutics. 2022 Jan 19;14(2):224. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14020224. Pharmaceutics. 2022. PMID: 35213957 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Polyvinylpyrrolidone-Modified Taxifolin Liposomes Promote Liver Repair by Modulating Autophagy to Inhibit Activation of the TLR4/NF-κB Signaling Pathway.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022 Jun 1;10:860515. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2022.860515. eCollection 2022. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 35721857 Free PMC article.
-
The role of CD56bright NK cells in neurodegenerative disorders.J Neuroinflammation. 2024 Feb 13;21(1):48. doi: 10.1186/s12974-024-03040-8. J Neuroinflammation. 2024. PMID: 38350967 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Schapira A. H. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2009;30:41–47. - PubMed
-
- Jorg M., Kaczor A. A., Mak F. S., Lee K. C. K., Poso A., Miller N. D., Scammells P. J., Capuano B. Med. Chem. Commun. 2014;5:891–898.
-
- Chao O. Y., Mattern C., Silva A. M., Wessler J., Ruocco L. A., Nikolaus S., Huston J. P., Pum M. E. Brain Res. Bull. 2012;87:340–345. - PubMed
-
- Huang L., Deng M., He Y., Lu S., Ma R., Fang Y. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2016;43:634–643. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

