Metabolites as regulators of insulin sensitivity and metabolism
- PMID: 30104701
- PMCID: PMC6380503
- DOI: 10.1038/s41580-018-0044-8
Metabolites as regulators of insulin sensitivity and metabolism
Abstract
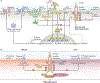
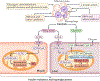
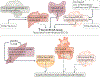
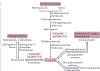
The cause of insulin resistance in obesity and type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is not limited to impaired insulin signalling but also involves the complex interplay of multiple metabolic pathways. The analysis of large data sets generated by metabolomics and lipidomics has shed new light on the roles of metabolites such as lipids, amino acids and bile acids in modulating insulin sensitivity. Metabolites can regulate insulin sensitivity directly by modulating components of the insulin signalling pathway, such as insulin receptor substrates (IRSs) and AKT, and indirectly by altering the flux of substrates through multiple metabolic pathways, including lipogenesis, lipid oxidation, protein synthesis and degradation and hepatic gluconeogenesis. Moreover, the post-translational modification of proteins by metabolites and lipids, including acetylation and palmitoylation, can alter protein function. Furthermore, the role of the microbiota in regulating substrate metabolism and insulin sensitivity is unfolding. In this Review, we discuss the emerging roles of metabolites in the pathogenesis of insulin resistance and T2DM. A comprehensive understanding of the metabolic adaptations involved in insulin resistance may enable the identification of novel targets for improving insulin sensitivity and preventing, and treating, T2DM.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests
B.B.K. is an inventor on patents related to the fatty acid esters of hydroxy fatty acids. The other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
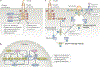
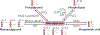
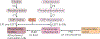
Similar articles
-
Metabolism and insulin signaling in common metabolic disorders and inherited insulin resistance.Dan Med J. 2014 Jul;61(7):B4890. Dan Med J. 2014. PMID: 25123125 Review.
-
Diabetes and branched-chain amino acids: What is the link?J Diabetes. 2018 May;10(5):350-352. doi: 10.1111/1753-0407.12645. Epub 2018 Feb 13. J Diabetes. 2018. PMID: 29369529
-
Pathway-selective insulin resistance and metabolic disease: the importance of nutrient flux.J Biol Chem. 2014 Jul 25;289(30):20462-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.R114.576355. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 24907277 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Unraveling the Regulation of Hepatic Metabolism by Insulin.Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2017 Jul;28(7):497-505. doi: 10.1016/j.tem.2017.03.003. Epub 2017 Apr 14. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2017. PMID: 28416361 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biochanin A improves hepatic steatosis and insulin resistance by regulating the hepatic lipid and glucose metabolic pathways in diet-induced obese mice.Mol Nutr Food Res. 2016 Sep;60(9):1944-55. doi: 10.1002/mnfr.201500689. Epub 2016 Jun 8. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2016. PMID: 27145114
Cited by
-
Untargeted metabolomics combined with pseudotargeted lipidomics revealed the metabolite profiles of blood-stasis syndrome in type 2 diabetes mellitus.Heliyon. 2024 Oct 18;10(20):e39554. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e39554. eCollection 2024 Oct 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39498030 Free PMC article.
-
A Bibliometric and Knowledge-Map Analysis of Macrophage Polarization in Insulin Resistance From 1999 to 2023.Immun Inflamm Dis. 2024 Oct;12(10):e70048. doi: 10.1002/iid3.70048. Immun Inflamm Dis. 2024. PMID: 39465505 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive analysis of the association between triglyceride-glucose index and coronary artery disease severity across different glucose metabolism states: a large-scale cross-sectional study from an Asian cohort.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2024 Jul 13;23(1):251. doi: 10.1186/s12933-024-02355-3. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2024. PMID: 39003471 Free PMC article.
-
Protein-Metabolite Interactions Shape Cellular Metabolism and Physiology.Methods Mol Biol. 2023;2554:1-10. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-2624-5_1. Methods Mol Biol. 2023. PMID: 36178616
-
Triglyceride-Glucose Index Linked to In-Hospital Mortality in Critically Ill Patients with Heart Disease.Rev Cardiovasc Med. 2022 Jul 21;23(8):263. doi: 10.31083/j.rcm2308263. eCollection 2022 Aug. Rev Cardiovasc Med. 2022. PMID: 39076642 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Taniguchi CM, Emanuelli B & Kahn CR Critical nodes in signalling pathways: insights into insulin action. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol 7, 85–96 (2006). - PubMed
-
- Martini M, De Santis MC, Braccini L, Gulluni F & Hirsch E PI3K/AKT signaling pathway and cancer: an updated review. Ann. Med 46, 372–383 (2014). - PubMed
-
- Wymann MP & Schneiter R Lipid signalling in disease. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol 9, 162–176 (2008). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

