rSjP40 suppresses hepatic stellate cell activation by promoting microRNA-155 expression and inhibiting STAT5 and FOXO3a expression
- PMID: 30091834
- PMCID: PMC6201359
- DOI: 10.1111/jcmm.13819
rSjP40 suppresses hepatic stellate cell activation by promoting microRNA-155 expression and inhibiting STAT5 and FOXO3a expression
Abstract
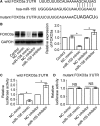
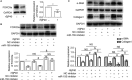
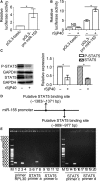
Activation of hepatic stellate cells (HSCs) is the central event of the evolution of hepatic fibrosis. Schistosomiasis is one of the pathogenic factors which could induce hepatic fibrosis. Previous studies have shown that recombinant Schistosoma japonicum egg antigen P40 (rSjP40) can inhibit the activation and proliferation of HSCs. MicroRNA-155 is one of the multifunctional noncoding RNA, which is involved in a series of important biological processes including cell development, proliferation, differentiation and apoptosis. Here, we try to observe the role of microRNA-155 in rSjP40-inhibited HSC activation and explore its potential mechanisms. We found that microRNA-155 was raised in rSjP40-treated HSCs, and further studies have shown that rSjP40 enhanced microRNA-155 expression by inhibiting STAT5 transcription. Up-regulated microRNA-155 can down-regulate the expression of FOXO3a and then participate in rSjP40-inhibited expression of α-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA) and collagen I. Furthermore, we observed microRNA-155 inhibitor could partially restore the down-regulation of FOXO3a, α-SMA and collagen I expression in LX-2 cells induced by rSjP40. Therefore, our research provides further insight into the mechanism by which rSjP40 could inhibit HSC activation via miR-155.
Keywords: Schistosoma japonicum; hepatic fibrosis; hepatic stellate cells; microRNA-155; rSjP40.
© 2018 The Authors. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd and Foundation for Cellular and Molecular Medicine.
Figures

Similar articles
-
ATF3 is involved in rSjP40-mediated inhibition of HSCs activation in Schistosoma japonicum-infected mice.J Cell Mol Med. 2024 Jun;28(12):e18458. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.18458. J Cell Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 39031798 Free PMC article.
-
rSjp40 inhibits activated hepatic stellate cells by promoting nuclear translocation of YB1 and inducing BMP-7/Smad1/5/8 pathway.Parasit Vectors. 2019 May 31;12(1):279. doi: 10.1186/s13071-019-3539-z. Parasit Vectors. 2019. PMID: 31151477 Free PMC article.
-
The role of let-7b in the inhibition of hepatic stellate cell activation by rSjP40.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2021 Jun 23;15(6):e0009472. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0009472. eCollection 2021 Jun. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2021. PMID: 34161325 Free PMC article.
-
microRNA-146a is involved in rSjP40-inhibited activation of LX-2 cells by targeting Smad4 expression.J Cell Biochem. 2018 Nov;119(11):9249-9253. doi: 10.1002/jcb.27193. Epub 2018 Jun 28. J Cell Biochem. 2018. PMID: 29953648
-
Role of microRNAs in Hepatic Stellate Cells and Hepatic Fibrosis: An Update.Curr Pharm Des. 2021;27(27):3000-3011. doi: 10.2174/1381612826666201023143542. Curr Pharm Des. 2021. PMID: 33100194 Review.
Cited by
-
Hallmarks of Aging in the Liver.Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2019 Aug 7;17:1151-1161. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2019.07.021. eCollection 2019. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2019. PMID: 31462971 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ATF3 is involved in rSjP40-mediated inhibition of HSCs activation in Schistosoma japonicum-infected mice.J Cell Mol Med. 2024 Jun;28(12):e18458. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.18458. J Cell Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 39031798 Free PMC article.
-
The role of microRNAs in the pathogenesis, grading and treatment of hepatic fibrosis in schistosomiasis.Parasit Vectors. 2019 Dec 30;12(1):611. doi: 10.1186/s13071-019-3866-0. Parasit Vectors. 2019. PMID: 31888743 Free PMC article. Review.
-
rSjp40 inhibits activated hepatic stellate cells by promoting nuclear translocation of YB1 and inducing BMP-7/Smad1/5/8 pathway.Parasit Vectors. 2019 May 31;12(1):279. doi: 10.1186/s13071-019-3539-z. Parasit Vectors. 2019. PMID: 31151477 Free PMC article.
-
Pathology and molecular mechanisms of Schistosoma japonicum-associated liver fibrosis.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022 Oct 28;12:1035765. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.1035765. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36389166 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Anthony B, Mathieson W, de Castro‐Borges W, Allen J. Schistosoma mansoni: egg‐induced downregulation of hepatic stellate cell activation and fibrogenesis. Exp Parasitol. 2010;124(4):409‐420. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

