Distinctive Roles for Type I and Type II Interferons and Interferon Regulatory Factors in the Host Cell Defense against Varicella-Zoster Virus
- PMID: 30089701
- PMCID: PMC6189497
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.01151-18
Distinctive Roles for Type I and Type II Interferons and Interferon Regulatory Factors in the Host Cell Defense against Varicella-Zoster Virus
Abstract
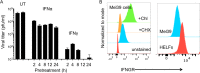
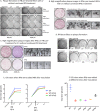
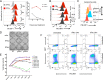
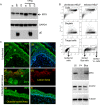
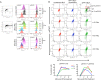
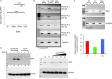
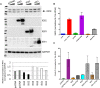
Both type I and type II interferons (IFNs) have been implicated in the host defense against varicella-zoster virus (VZV), a common human herpesvirus that causes varicella and zoster. The purpose of this study was to compare their contributions to the control of VZV replication, to identify the signaling pathways that are critical for mediating their antiviral activity, and to define the mechanisms by which the virus counteracts their effects. Gamma interferon (IFN-γ) was much more potent than IFN-α in blocking VZV infection, which was associated with a differential induction of the interferon regulatory factor (IRF) proteins IRF1 and IRF9, respectively. These observations account for the clinical experience that while the formation of VZV skin lesions is initially controlled by local immunity, adaptive virus-specific T cell responses are required to prevent life-threatening VZV infections.IMPORTANCE While both type I and type II IFNs are involved in the control of herpesvirus infections in the human host, to our knowledge, their relative contributions to the restriction of viral replication and spread have not been assessed. We report that IFN-γ has more potent activity than IFN-α against VZV. Findings from this comparative analysis show that the IFN-α-IRF9 axis functions as a first line of defense to delay the onset of viral replication and spread, whereas the IFN-γ-IRF1 axis has the capacity to block the infectious process. Our findings underscore the importance of IRFs in IFN regulation of herpesvirus infection and account for the clinical experience of the initial control of VZV skin infection attributable to IFN-α production, together with the requirement for induction of adaptive IFN-γ-producing VZV-specific T cells to resolve the infection.
Keywords: IRF1 mediates the inhibitory effects of interferon gamma on VZV; IRF9 mediates the action of interferon alpha on VZV; VZV innate immune control; interferon alpha delays onset of VZV spread; interferon gamma abrogates VZV replication.
Copyright © 2018 American Society for Microbiology.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Modulation of major histocompatibility class II protein expression by varicella-zoster virus.J Virol. 2000 Feb;74(4):1900-7. doi: 10.1128/jvi.74.4.1900-1907.2000. J Virol. 2000. PMID: 10644363 Free PMC article.
-
Varicella Viruses Inhibit Interferon-Stimulated JAK-STAT Signaling through Multiple Mechanisms.PLoS Pathog. 2015 May 14;11(5):e1004901. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1004901. eCollection 2015 May. PLoS Pathog. 2015. PMID: 25973608 Free PMC article.
-
Interferon Gamma Inhibits Varicella-Zoster Virus Replication in a Cell Line-Dependent Manner.J Virol. 2019 May 29;93(12):e00257-19. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00257-19. Print 2019 Jun 15. J Virol. 2019. PMID: 30918075 Free PMC article.
-
The emerging role of interferon regulatory factor 9 in the antiviral host response and beyond.Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2016 Jun;29:35-43. doi: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2016.03.002. Epub 2016 Mar 4. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2016. PMID: 26987614 Review.
-
Immunobiology of Varicella-Zoster Virus Infection.J Infect Dis. 2018 Sep 22;218(suppl_2):S68-S74. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiy403. J Infect Dis. 2018. PMID: 30247598 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Human IRF1 governs macrophagic IFN-γ immunity to mycobacteria.Cell. 2023 Feb 2;186(3):621-645.e33. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2022.12.038. Cell. 2023. PMID: 36736301 Free PMC article.
-
Skin Viral Infections: Host Antiviral Innate Immunity and Viral Immune Evasion.Front Immunol. 2020 Nov 6;11:593901. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.593901. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 33240281 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lack of strong innate immune reactivity renders macrophages alone unable to control productive Varicella-Zoster Virus infection in an isogenic human iPSC-derived neuronal co-culture model.Front Immunol. 2023 May 23;14:1177245. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1177245. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37287975 Free PMC article.
-
Tofacitinib downregulates antiviral immune defence in keratinocytes and reduces T cell activation.Arthritis Res Ther. 2021 May 21;23(1):144. doi: 10.1186/s13075-021-02509-8. Arthritis Res Ther. 2021. PMID: 34020693 Free PMC article.
-
Functional paralysis of human natural killer cells by alphaherpesviruses.PLoS Pathog. 2019 Jun 13;15(6):e1007784. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1007784. eCollection 2019 Jun. PLoS Pathog. 2019. PMID: 31194857 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

