Effects of vitamin C and E on toxic action of alcohol on partial hepatectomy-induced liver regeneration in rats
- PMID: 30087544
- PMCID: PMC6064813
- DOI: 10.3164/jcbn.17-96
Effects of vitamin C and E on toxic action of alcohol on partial hepatectomy-induced liver regeneration in rats
Abstract
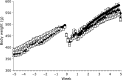
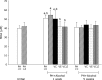
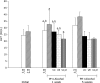
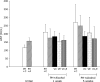
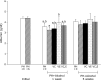
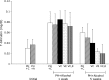
The purpose of this study was to investigate the influence of vitamins C and E on the toxic action of alcohol in rat liver regeneration. Male Sprague-Dawley rats subjected to 70% partial hepatectomy were divided into five groups (Groups 1 to 5). Rats in Groups 2 to 5 were only provided alcohol for drinking. Additionally, vitamin C, vitamin E, and vitamin C in combination with vitamin E were administered to Groups 3, 4, and 5, respectively. Alcohol inhibits liver regeneration, resulting in an increase in free radicals produced by alcohol metabolism and thus causing cellular damage and altering liver function. During liver regeneration, vitamins C and E significantly ameliorated liver injury from alcohol administration by reducing hepatic lipid peroxidation. Vitamins C and E protect against liver injury and dysfunction, attenuate lipid peroxidation, and thus may be more effective in combination than either vitamin alone against alcohol-mediated toxic effects during liver regeneration.
Keywords: alcohol; antioxidant; liver regeneration; oxidative stress; partial hepatectomy.
Conflict of interest statement
We have not received any financial support or other benefits from commercial sources for the work reported in the manuscript. None of the authors have financial interests that could create a potential conflict of interest or the appearance of a conflict of interest with regard to this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Protective effect of some vitamins against the toxic action of ethanol on liver regeneration induced by partial hepatectomy in rats.World J Gastroenterol. 2008 Feb 14;14(6):899-907. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.899. World J Gastroenterol. 2008. PMID: 18240347 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of antioxidant vitamins on glutathione depletion and lipid peroxidation induced by restraint stress in the rat liver.Drugs R D. 2005;6(3):157-65. doi: 10.2165/00126839-200506030-00004. Drugs R D. 2005. PMID: 15869319
-
Effect of vitamin E deficiency on inhibition of liver regeneration by long-term administration of alcohol.Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 1996 Feb;20(1 Suppl):47A-50A. doi: 10.1111/j.1530-0277.1996.tb01728.x. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 1996. PMID: 8659689
-
Relationship between glutathione and polyamine metabolism after partial hepatectomy in alcohol-treated rats.Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 1998 May;22(S3 Pt 1):125S-128S. doi: 10.1111/acer.1998.22.s3_part1.125s. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 1998. PMID: 9622388
-
Role of oxidative stress and antioxidant therapy in alcoholic and nonalcoholic liver diseases.Adv Pharmacol. 1997;38:601-28. doi: 10.1016/s1054-3589(08)61001-7. Adv Pharmacol. 1997. PMID: 8895826 Review.
Cited by
-
Plasma quercetin metabolites are affected by intestinal microbiota of human microbiota-associated mice fed with a quercetin-containing diet.J Clin Biochem Nutr. 2019 Nov;65(3):232-239. doi: 10.3164/jcbn.19-45. Epub 2019 Oct 10. J Clin Biochem Nutr. 2019. PMID: 31777425 Free PMC article.
-
Differential Effect of Antioxidants Glutathione and Vitamin C on the Hepatic Injuries Induced by Plasmodium berghei ANKA Infection.Biomed Res Int. 2021 Sep 4;2021:9694508. doi: 10.1155/2021/9694508. eCollection 2021. Biomed Res Int. 2021. PMID: 34527745 Free PMC article.
-
The Use of Chitosan-Coated Nanovesicles in Repairing Alcohol-Induced Damage of Liver Cells in Mice.Medicina (Kaunas). 2022 Jun 5;58(6):762. doi: 10.3390/medicina58060762. Medicina (Kaunas). 2022. PMID: 35744025 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kune GA, Vitetta L. Alcohol consumption and the etiology of colorectal cancer: a review of the scientific evidence from 1957 to 1991. Nutr Cancer. 1992;18:97–111. - PubMed
-
- Kurose I, Higuchi H, Kato S, Miura S, Ishii H. Ethanol-induced oxidative stress in the liver. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 1996;20 (1 Suppl):77A–85A. - PubMed
-
- Badger TM, Huang J, Ronis M. Induction of cytochrome P450 2E1 during chronic ethanol exposure occurs via transcription of the CYP 2E1 gene when blood alcohol concentration are high. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1993;190:780–785. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

