An open-label phase 1b study of obinutuzumab plus lenalidomide in relapsed/refractory follicular B-cell lymphoma
- PMID: 30068505
- PMCID: PMC6225348
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2018-05-853499
An open-label phase 1b study of obinutuzumab plus lenalidomide in relapsed/refractory follicular B-cell lymphoma
Abstract
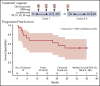
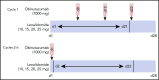
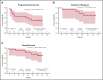
Obinutuzumab is a type II anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody that enhances antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity better than rituximab. Given promising results with lenalidomide and rituximab, this phase 1b study assessed the safety and efficacy of lenalidomide combined with obinutuzumab (GALEN). Patients age ≥18 years with relapsed or refractory (R/R) follicular lymphoma (FL) after rituximab-containing therapy received escalating doses (10 [n = 7], 15 [n = 3], 20 [n = 6], and 25 mg [n = 3]) of daily oral lenalidomide on days 1 to 21 of cycle 1 and on days 2 to 22 of cycles 2 to 6 (28-day cycles). Obinutuzumab 1000 mg IV was administered on days 8, 15, and 22 (cycle 1) and on day 1 (cycles 2-6). Dose was escalated in a 3 + 3 design based on dose-limiting toxicity (DLT) during cycle 1 to establish the maximum tolerated dose (MTD). We observed 164 adverse events (AEs), of which 139 were grade 1/2. The most common AEs were constipation (52.6%), neutropenia (47.4%), and asthenia (36.8%); 64.3% (9 of 14) of the grade 3/4 AEs were neutropenia/neutrophil decrease, but without any febrile neutropenia. Four DLTs occurred in 2 patients, all deemed unrelated to treatment. MTD was not reached. Twelve patients (63.2%) responded: 8 complete, 3 unconfirmed complete, and 1 partial response. Oral lenalidomide plus obinutuzumab is well tolerated and effective in R/R FL. The recommended dose of lenalidomide was established at 20 mg based on the risk of grade 3/4 neutropenia from cycle 2. This trial was registered at www.clinicaltrials.gov as #NCT01582776.
© 2018 by The American Society of Hematology.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: F.M. has received personal fees for consultancy, advisory boards, or scientific lectures from Gilead, Janssen, Celgene, Servier, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Roche, and Epizyme (outside the submitted work); S.L.G. received research grants, personal fees, and nonfinancial support from Celgene and Roche Genentech during the conduct of the study and has received grants, personal fees, and nonfinancial support from Celgene outside the submitted work; H.T. has received research grants and personal fees from Celgene, personal fees and nonfinancial support from Roche, and personal fees from Karyopharm, AstraZeneca, and Bristol-Myers Squibb outside the submitted work; C.T. has received consultancy fees or honoraria from Celgene, Bayer, AbbVie, and Janssen and research funding from Roche; C.M. has received research funding from Celgene and honoraria from Celgene and Bristol-Myers Squibb; K.T. has received research funding from Celgene and honoraria from Celgene and Roche; G.C. has received personal fees for consultancy and honoraria from Roche and Celgene and received personal fees for honoraria from Sanofi, Gilead, and Janssen during the conduct of the study; and R.H. has received consulting fees or honoraria from Bristol-Myers Squibb and Gilead. The remaining authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures

Comment in
-
Next-generation therapy for follicular lymphoma.Blood. 2018 Oct 4;132(14):1465-1467. doi: 10.1182/blood-2018-08-868117. Blood. 2018. PMID: 30287467 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Obinutuzumab combined with lenalidomide for relapsed or refractory follicular B-cell lymphoma (GALEN): a multicentre, single-arm, phase 2 study.Lancet Haematol. 2019 Aug;6(8):e429-e437. doi: 10.1016/S2352-3026(19)30089-4. Epub 2019 Jul 8. Lancet Haematol. 2019. PMID: 31296423 Clinical Trial.
-
Polatuzumab vedotin plus obinutuzumab and lenalidomide in patients with relapsed or refractory follicular lymphoma: a cohort of a multicentre, single-arm, phase 1b/2 study.Lancet Haematol. 2021 Dec;8(12):e891-e901. doi: 10.1016/S2352-3026(21)00311-2. Lancet Haematol. 2021. PMID: 34826412 Clinical Trial.
-
Safety and tolerability of idelalisib, lenalidomide, and rituximab in relapsed and refractory lymphoma: the Alliance for Clinical Trials in Oncology A051201 and A051202 phase 1 trials.Lancet Haematol. 2017 Apr;4(4):e176-e182. doi: 10.1016/S2352-3026(17)30028-5. Epub 2017 Mar 15. Lancet Haematol. 2017. PMID: 28314699 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
An Evidence-based Review of Anti-CD20 Antibody-containing Regimens for the Treatment of Patients With Relapsed or Refractory Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia, Diffuse Large B-cell Lymphoma, or Follicular Lymphoma.Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2018 Aug;18(8):508-518.e14. doi: 10.1016/j.clml.2018.05.009. Epub 2018 May 23. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2018. PMID: 29934061 Review.
-
The role of obinutuzumab in the management of follicular lymphoma.Future Oncol. 2019 Nov;15(31):3565-3578. doi: 10.2217/fon-2019-0193. Epub 2019 Sep 20. Future Oncol. 2019. PMID: 31538821 Review.
Cited by
-
Immunotherapy beyond cellular therapy in follicular lymphoma: A case of complete remission after failure of two CAR-T.Clin Case Rep. 2022 Apr 8;10(4):e05572. doi: 10.1002/ccr3.5572. eCollection 2022 Apr. Clin Case Rep. 2022. PMID: 35425600 Free PMC article.
-
Positron-emission tomography-based staging reduces the prognostic impact of early disease progression in patients with follicular lymphoma.Eur J Cancer. 2020 Feb;126:78-90. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2019.12.006. Epub 2020 Jan 8. Eur J Cancer. 2020. PMID: 31927165 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and safety of MIL62, a novel glycoengineered type Ⅱ anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody, combined with lenalidomide in patients with relapsed/refractory follicular lymphoma or marginal zone lymphoma: a multicentre, single-arm, phase 1b/2 trial.EClinicalMedicine. 2024 Jun 20;73:102702. doi: 10.1016/j.eclinm.2024.102702. eCollection 2024 Jul. EClinicalMedicine. 2024. PMID: 39007066 Free PMC article.
-
Unveiling the Role of the Tumor Microenvironment in the Treatment of Follicular Lymphoma.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Apr 26;14(9):2158. doi: 10.3390/cancers14092158. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35565286 Free PMC article. Review.
-
B cells in chronic graft-versus-host disease.Hum Immunol. 2019 Jun;80(6):393-399. doi: 10.1016/j.humimm.2019.03.003. Epub 2019 Mar 5. Hum Immunol. 2019. PMID: 30849450 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hernandez-Ilizaliturri FJ, Reddy N, Holkova B, Ottman E, Czuczman MS. Immunomodulatory drug CC-5013 or CC-4047 and rituximab enhance antitumor activity in a severe combined immunodeficient mouse lymphoma model. Clin Cancer Res. 2005;11(16):5984-5992. - PubMed
-
- Wu L, Adams M, Carter T, et al. . Lenalidomide enhances natural killer cell and monocyte-mediated antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity of rituximab-treated CD20+ tumor cells. Clin Cancer Res. 2008;14(14):4650-4657. - PubMed
-
- Reddy N, Hernandez-Ilizaliturri FJ, Deeb G, et al. . Immunomodulatory drugs stimulate natural killer-cell function, alter cytokine production by dendritic cells, and inhibit angiogenesis enhancing the anti-tumour activity of rituximab in vivo. Br J Haematol. 2008;140(1):36-45. - PubMed
-
- Zhang L, Qian Z, Cai Z, et al. . Synergistic antitumor effects of lenalidomide and rituximab on mantle cell lymphoma in vitro and in vivo. Am J Hematol. 2009;84(9):553-559. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

