Structural relationship between the putative hair cell mechanotransduction channel TMC1 and TMEM16 proteins
- PMID: 30063209
- PMCID: PMC6067890
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.38433
Structural relationship between the putative hair cell mechanotransduction channel TMC1 and TMEM16 proteins
Abstract
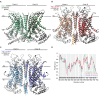
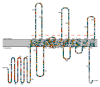
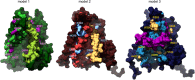
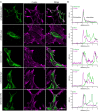
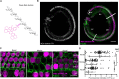
The hair cell mechanotransduction (MET) channel complex is essential for hearing, yet it's molecular identity and structure remain elusive. The transmembrane channel-like 1 (TMC1) protein localizes to the site of the MET channel, interacts with the tip-link responsible for mechanical gating, and genetic alterations in TMC1 alter MET channel properties and cause deafness, supporting the hypothesis that TMC1 forms the MET channel. We generated a model of TMC1 based on X-ray and cryo-EM structures of TMEM16 proteins, revealing the presence of a large cavity near the protein-lipid interface that also harbors the Beethoven mutation, suggesting that it could function as a permeation pathway. We also find that hair cells are permeable to 3 kDa dextrans, and that dextran permeation requires TMC1/2 proteins and functional MET channels, supporting the presence of a large permeation pathway and the hypothesis that TMC1 is a pore forming subunit of the MET channel complex.
Keywords: Ca2+-activated Cl- channel; deafness; ion channel pore; ion permeation; lipid scramblase; mechanosensation; molecular biophysics; mouse; structural biology.
Conflict of interest statement
AB, CF No competing interests declared, KS Reviewing editor, eLife
Figures



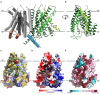

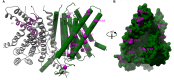
Similar articles
-
New Tmc1 Deafness Mutations Impact Mechanotransduction in Auditory Hair Cells.J Neurosci. 2021 May 19;41(20):4378-4391. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2537-20.2021. Epub 2021 Apr 6. J Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 33824189 Free PMC article.
-
Tmc1 Point Mutation Affects Ca2+ Sensitivity and Block by Dihydrostreptomycin of the Mechanoelectrical Transducer Current of Mouse Outer Hair Cells.J Neurosci. 2016 Jan 13;36(2):336-49. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2439-15.2016. J Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 26758827 Free PMC article.
-
A Tmc1 mutation reduces calcium permeability and expression of mechanoelectrical transduction channels in cochlear hair cells.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019 Oct 8;116(41):20743-20749. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1908058116. Epub 2019 Sep 23. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019. PMID: 31548403 Free PMC article.
-
Is TMC1 the Hair Cell Mechanotransducer Channel?Biophys J. 2016 Jul 12;111(1):3-9. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2016.05.032. Biophys J. 2016. PMID: 27410728 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transmembrane channel-like (TMC) genes are required for auditory and vestibular mechanosensation.Pflugers Arch. 2015 Jan;467(1):85-94. doi: 10.1007/s00424-014-1582-3. Epub 2014 Jul 31. Pflugers Arch. 2015. PMID: 25074487 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
New Tmc1 Deafness Mutations Impact Mechanotransduction in Auditory Hair Cells.J Neurosci. 2021 May 19;41(20):4378-4391. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2537-20.2021. Epub 2021 Apr 6. J Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 33824189 Free PMC article.
-
Distinct functions of TMC channels: a comparative overview.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2019 Nov;76(21):4221-4232. doi: 10.1007/s00018-019-03214-1. Epub 2019 Oct 4. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2019. PMID: 31584127 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hair cell maturation is differentially regulated along the tonotopic axis of the mammalian cochlea.J Physiol. 2020 Jan;598(1):151-170. doi: 10.1113/JP279012. Epub 2019 Dec 21. J Physiol. 2020. PMID: 31661723 Free PMC article.
-
Aminoglycoside- and Cisplatin-Induced Ototoxicity: Mechanisms and Otoprotective Strategies.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2019 Nov 1;9(11):a033548. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a033548. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2019. PMID: 30559254 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The speed of the hair cell mechanotransducer channel revealed by fluctuation analysis.J Gen Physiol. 2021 Oct 4;153(10):e202112959. doi: 10.1085/jgp.202112959. Epub 2021 Aug 19. J Gen Physiol. 2021. PMID: 34411238 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ahmed ZM, Goodyear R, Riazuddin S, Lagziel A, Legan PK, Behra M, Burgess SM, Lilley KS, Wilcox ER, Riazuddin S, Griffith AJ, Frolenkov GI, Belyantseva IA, Richardson GP, Friedman TB. The tip-link antigen, a protein associated with the transduction complex of sensory hair cells, is protocadherin-15. Journal of Neuroscience. 2006;26:7022–7034. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1163-06.2006. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

