The actin capping protein in Aspergillus nidulans enhances dynein function without significantly affecting Arp1 filament assembly
- PMID: 30061726
- PMCID: PMC6065395
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-018-29818-4
The actin capping protein in Aspergillus nidulans enhances dynein function without significantly affecting Arp1 filament assembly
Abstract
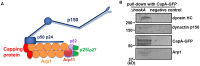
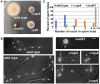
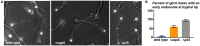
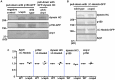
The minus-end-directed microtubule motor cytoplasmic dynein requires the dynactin complex for in vivo functions. The backbone of the vertebrate dynactin complex is the Arp1 (actin-related protein 1) mini-filament whose barbed end binds to the heterodimeric actin capping protein. However, it is unclear whether the capping protein is a dynactin component in lower eukaryotic organisms, especially because it does not appear to be a component of the budding yeast dynactin complex. Here our biochemical data show that the capping protein is a component of the dynactin complex in the filamentous fungus Aspergillus nidulans. Moreover, deletion of the gene encoding capping protein alpha (capA) results in a defect in both nuclear distribution and early-endosome transport, two dynein-mediated processes. However, the defect in either process is less severe than that exhibited by a dynein heavy chain mutant or the ∆p25 mutant of dynactin. In addition, loss of capping protein does not significantly affect the assembly of the dynactin Arp1 filament or the formation of the dynein-dynactin-∆C-HookA (Hook in A. nidulans) complex. These results suggest that fungal capping protein is not important for Arp1 filament assembly but its presence is required for enhancing dynein function in vivo.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
p25 of the dynactin complex plays a dual role in cargo binding and dynactin regulation.J Biol Chem. 2018 Oct 5;293(40):15606-15619. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.004000. Epub 2018 Aug 24. J Biol Chem. 2018. PMID: 30143531 Free PMC article.
-
The splicing-factor Prp40 affects dynein-dynactin function in Aspergillus nidulans.Mol Biol Cell. 2020 Jun 1;31(12):1289-1301. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E20-03-0166. Epub 2020 Apr 8. Mol Biol Cell. 2020. PMID: 32267207 Free PMC article.
-
The p25 subunit of the dynactin complex is required for dynein-early endosome interaction.J Cell Biol. 2011 Jun 27;193(7):1245-55. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201011022. J Cell Biol. 2011. PMID: 21708978 Free PMC article.
-
The role of the dynactin complex in intracellular motility.Int Rev Cytol. 1998;182:69-109. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)62168-3. Int Rev Cytol. 1998. PMID: 9522459 Review.
-
Cytoplasmic dynein and early endosome transport.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2015 Sep;72(17):3267-80. doi: 10.1007/s00018-015-1926-y. Epub 2015 May 23. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2015. PMID: 26001903 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
LIS1 regulates cargo-adapter-mediated activation of dynein by overcoming its autoinhibition in vivo.J Cell Biol. 2019 Nov 4;218(11):3630-3646. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201905178. Epub 2019 Sep 27. J Cell Biol. 2019. PMID: 31562232 Free PMC article.
-
Loss of Arp1, a putative actin-related protein, triggers filamentous and invasive growth and impairs pathogenicity in Candida albicans.Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2020 Dec 1;18:4002-4015. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2020.11.034. eCollection 2020. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2020. PMID: 33363697 Free PMC article.
-
VezA/vezatin facilitates proper assembly of the dynactin complex in vivo.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Apr 20:2024.04.19.590248. doi: 10.1101/2024.04.19.590248. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Cell Rep. 2024 Nov 26;43(11):114943. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2024.114943 PMID: 38659795 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Kinesin-1 autoinhibition facilitates the initiation of dynein cargo transport.J Cell Biol. 2023 Mar 6;222(3):e202205136. doi: 10.1083/jcb.202205136. Epub 2022 Dec 16. J Cell Biol. 2023. PMID: 36524956 Free PMC article.
-
p25 of the dynactin complex plays a dual role in cargo binding and dynactin regulation.J Biol Chem. 2018 Oct 5;293(40):15606-15619. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.004000. Epub 2018 Aug 24. J Biol Chem. 2018. PMID: 30143531 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

