The Role of Inflammation and Inflammatory Mediators in the Development, Progression, Metastasis, and Chemoresistance of Epithelial Ovarian Cancer
- PMID: 30061485
- PMCID: PMC6116184
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers10080251
The Role of Inflammation and Inflammatory Mediators in the Development, Progression, Metastasis, and Chemoresistance of Epithelial Ovarian Cancer
Abstract
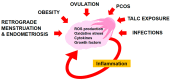
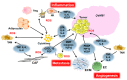
Inflammation plays a role in the initiation and development of many types of cancers, including epithelial ovarian cancer (EOC) and high grade serous ovarian cancer (HGSC), a type of EOC. There are connections between EOC and both peritoneal and ovulation-induced inflammation. Additionally, EOCs have an inflammatory component that contributes to their progression. At sites of inflammation, epithelial cells are exposed to increased levels of inflammatory mediators such as reactive oxygen species, cytokines, prostaglandins, and growth factors that contribute to increased cell division, and genetic and epigenetic changes. These exposure-induced changes promote excessive cell proliferation, increased survival, malignant transformation, and cancer development. Furthermore, the pro-inflammatory tumor microenvironment environment (TME) contributes to EOC metastasis and chemoresistance. In this review we will discuss the roles inflammation and inflammatory mediators play in the development, progression, metastasis, and chemoresistance of EOC.
Keywords: cytokines; epithelial ovarian cancer; growth factors; inflammation; reactive oxygen species.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
FOXM1 expression is significantly associated with chemotherapy resistance and adverse prognosis in non-serous epithelial ovarian cancer patients.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2017 May 8;36(1):63. doi: 10.1186/s13046-017-0536-y. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2017. PMID: 28482906 Free PMC article.
-
Etiopathogenesis of ovarian cancer. An inflamm-aging entity?Gynecol Oncol Rep. 2022 Jun 11;42:101018. doi: 10.1016/j.gore.2022.101018. eCollection 2022 Aug. Gynecol Oncol Rep. 2022. PMID: 35719320 Free PMC article. Review.
-
NSAID-activated gene 1 mediates pro-inflammatory signaling activation and paclitaxel chemoresistance in type I human epithelial ovarian cancer stem-like cells.Oncotarget. 2016 Nov 1;7(44):72148-72166. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.12355. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27708225 Free PMC article.
-
CYR61, a potential biomarker of tumor inflammatory response in epithelial ovarian cancer microenvironment of tumor progress.BMC Cancer. 2019 Nov 25;19(1):1140. doi: 10.1186/s12885-019-6321-x. BMC Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31766991 Free PMC article.
-
Chemokines driven ovarian cancer progression, metastasis and chemoresistance: Potential pharmacological targets for cancer therapy.Semin Cancer Biol. 2022 Nov;86(Pt 2):568-579. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2022.03.028. Epub 2022 Apr 1. Semin Cancer Biol. 2022. PMID: 35378273 Review.
Cited by
-
Hyperinsulinemia and Hypoadiponectinemia are Associated with Increased Risk for Occurrence of Ovarian Cancer in Non-diabetic Women of North Indian Population.Indian J Clin Biochem. 2021 Apr;36(2):221-227. doi: 10.1007/s12291-020-00891-9. Epub 2020 May 13. Indian J Clin Biochem. 2021. PMID: 33867714 Free PMC article.
-
Lifetime ovulatory years and ovarian cancer gene expression profiles.J Ovarian Res. 2022 May 13;15(1):59. doi: 10.1186/s13048-022-00995-1. J Ovarian Res. 2022. PMID: 35562768 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic Significance of Preoperative Inflammatory Biomarkers and Traditional Clinical Parameters in Patients with Spinal Metastasis from Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma: A Retrospective Study of 95 Patients in a Single Center.Cancer Manag Res. 2020 Jan 7;12:59-70. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S228570. eCollection 2020. Cancer Manag Res. 2020. PMID: 32021423 Free PMC article.
-
Regulatory role of the transforming growth factor-β signaling pathway in the drug resistance of gastrointestinal cancers.World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2021 Nov 15;13(11):1648-1667. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v13.i11.1648. World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34853641 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Stratification of ovarian cancer borderline from high-grade serous carcinoma patients by quantitative serum NMR spectroscopy of metabolites, lipoproteins, and inflammatory markers.Front Mol Biosci. 2023 Apr 19;10:1158330. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2023.1158330. eCollection 2023. Front Mol Biosci. 2023. PMID: 37168255 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Maiuri A.R., O’Hagan H.M. Interplay Between Inflammation and Epigenetic Changes in Cancer. Prog. Mol. Biol. Transl. Sci. 2016;144:69–117. - PubMed
-
- Clendenen T.V., Lundin E., Zeleniuch-Jacquotte A., Koenig K.L., Berrino F., Lukanova A., Lokshin A.E., Idahl A., Ohlson N., Hallmans G., et al. Circulating inflammation markers and risk of epithelial ovarian cancer. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2011;20:799–810. doi: 10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-10-1180. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chou C.H., Wei L.H., Kuo M.L., Huang Y.J., Lai K.P., Chen C.A., Hsieh C.Y. Up-regulation of interleukin-6 in human ovarian cancer cell via a Gi/PI3K-Akt/NF-κB pathway by lysophosphatidic acid, an ovarian cancer-activating factor. Carcinogenesis. 2005;26:45–52. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgh301. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

