Collagen peptide modified carboxymethyl cellulose as both antioxidant drug and carrier for drug delivery against retinal ischaemia/reperfusion injury
- PMID: 30030883
- PMCID: PMC6156360
- DOI: 10.1111/jcmm.13768
Collagen peptide modified carboxymethyl cellulose as both antioxidant drug and carrier for drug delivery against retinal ischaemia/reperfusion injury
Abstract
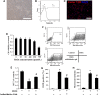
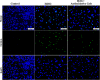
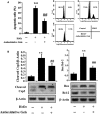
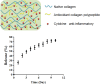
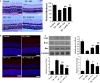
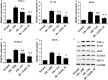
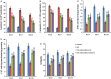
Oxidative stress can cause injury in retinal endothelial cells. Carboxymethyl cellulose modified with collagen peptide (CMCC) is of a distinct antioxidant capacity and potentially a good drug carrier. In this study, the protective effects of CMCC against H2 O2 -induced injury of primary retinal endothelial cells were investigated. In vitro, we demonstrated that CMCC significantly promoted viability of H2 O2 -treated cells, efficiently restrained cellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) production and cell apoptosis. Then, the CMCC was employed as both drug and anti-inflammatory drug carrier for treatment of retinal ischaemia/reperfusion (I/R) in rats. Animals were treated with CMCC or interleukin-10-loaded CMCC (IL-10@CMCC), respectively. In comparisons, the IL-10@CMCC treatment exhibited superior therapeutic effects, including better restoration of retinal structural thickness and less retinal apoptosis. Also, chemiluminescence demonstrated that transplantation of IL-10@CMCC markedly reduced the retinal oxidative stress level compared with CMCC alone and potently recovered the activities of typical antioxidant enzymes, SOD and CAT. Therefore, it could be concluded that CMCC provides a promising platform to enhance the drug-based therapy for I/R-related retinal injury.
Keywords: IL-10; antioxidant carrier; drug delivery; retinal ischaemia/reperfusion injury.
© 2018 The Authors. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd and Foundation for Cellular and Molecular Medicine.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Modification of carboxymethyl cellulose grafted with collagen peptide and its antioxidant activity.Carbohydr Polym. 2014 Nov 4;112:32-8. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2014.05.056. Epub 2014 May 29. Carbohydr Polym. 2014. PMID: 25129713
-
Hydrogen gas inhalation protects against cutaneous ischaemia/reperfusion injury in a mouse model of pressure ulcer.J Cell Mol Med. 2018 Sep;22(9):4243-4252. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.13704. Epub 2018 Jun 19. J Cell Mol Med. 2018. PMID: 29921037 Free PMC article.
-
Echinacoside protects retinal ganglion cells from ischemia/reperfusion-induced injury in the rat retina.Mol Vis. 2018 Nov 25;24:746-758. eCollection 2018. Mol Vis. 2018. PMID: 30581281 Free PMC article.
-
Salidroside protects retinal endothelial cells against hydrogen peroxide-induced injury via modulating oxidative status and apoptosis.Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2015;79(9):1406-13. doi: 10.1080/09168451.2015.1038212. Epub 2015 Apr 29. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2015. PMID: 25921655
-
Octreotide Protects the Mouse Retina against Ischemic Reperfusion Injury through Regulation of Antioxidation and Activation of NF-κB.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2015;2015:970156. doi: 10.1155/2015/970156. Epub 2015 Jun 14. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2015. PMID: 26175842 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Regulation of the Ocular Cell/Tissue Response by Implantable Biomaterials and Drug Delivery Systems.Bioengineering (Basel). 2020 Jun 30;7(3):65. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering7030065. Bioengineering (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32629806 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CD5L-induced activation of autophagy is associated with hepatoprotection in ischemic reperfusion injury via the CD36/ATG7 axis.Exp Ther Med. 2020 Apr;19(4):2588-2596. doi: 10.3892/etm.2020.8497. Epub 2020 Feb 7. Exp Ther Med. 2020. PMID: 32256738 Free PMC article.
-
Research progress of brain organoids in the field of diabetes.Mol Brain. 2024 Aug 6;17(1):53. doi: 10.1186/s13041-024-01123-4. Mol Brain. 2024. PMID: 39107846 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Retinal ischemia-reperfusion injury and pretreatment with Lycium barbarum glycopeptide.Int J Ophthalmol. 2024 Sep 18;17(9):1599-1605. doi: 10.18240/ijo.2024.09.04. eCollection 2024. Int J Ophthalmol. 2024. PMID: 39296572 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Progress on Cellulose-Based Ionic Compounds for Biomaterials.Adv Mater. 2021 Jul;33(28):e2000717. doi: 10.1002/adma.202000717. Epub 2020 Apr 9. Adv Mater. 2021. PMID: 32270900 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Stefansson E, Machemer R, de Juan E Jr, McCuen BW 2nd, Peterson J. Retinal oxygenation and laser treatment in patients with diabetic retinopathy. Am J Ophthalmol 1992;113:36‐38. - PubMed
-
- Levin LA. Models of neural injury. J Glaucoma. 2001;10:S19‐S21. - PubMed
-
- Osborne NN, Casson RJ, Wood JP, Chidlow G, Graham M, Melena J. Retinal ischemia: mechanisms of damage and potential therapeutic strategies. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2004;23:91‐147. - PubMed
-
- Szabo ME, Haines D, Garay E, et al. Antioxidant properties of calcium dobesilate in ischemic/reperfused diabetic rat retina. Eur J Pharmacol. 2001;428:277‐286. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

