The role of the baroreflex and parasympathetic nervous system in fructose-induced cardiac and metabolic alterations
- PMID: 30030527
- PMCID: PMC6054615
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-018-29336-3
The role of the baroreflex and parasympathetic nervous system in fructose-induced cardiac and metabolic alterations
Abstract
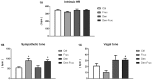
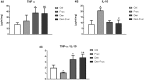
It is well-established that baroreflex sensitivity is essential for blood pressure control, and also plays a key role in the modulation of disease-induced metabolic alterations. In order to investigate the role of the baroreflex in the cardiometabolic and inflammatory derangements promoted by fructose overload, Wistar rats underwent sinoaortic denervation (SAD) or sham surgery and were studied 90 days after receiving tap water (Den and Ctrl) or a 10% fructose solution (Fruc and Den-Fruc). All experimental groups showed marked and similar degree of baroreflex impairment compared to Ctrl. As expected, fructose overload effectively induced metabolic syndrome; however, when it was associated with SAD, several alterations were attenuated. While Fruc rats displayed increased sympathetic modulation and tone and reduced vagal modulation compared to Ctrl animals, Den-Fruc rats showed greater vagal tone and modulation when compared to the Fruc group. Moreover, the Den-Fruc group showed augmented expression of β1 adrenergic receptors and TNF/IL-10 ratio and reduction of β2 in the left ventricle. The increase in vagal function was correlated with improved insulin sensitivity (r2 = 0.76), and decreased abdominal fat (r2 = -0.78) and β2 receptors (r2 = -0.85). Our results showed that: (1) chronic fructose overload induced severe baroreflex impairment, i.e. in a similar magnitude to that observed in SAD rats, which is accompanied by cardiometabolic dysfunctions; (2) the compensatory enhancement in parasympathetic function in SAD rats submitted to fructose intake may point out the possibility of use of approaches that improve vagal function as therapeutic target to attenuate fructose-induced cardiometabolic dysfunctions.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Baroreflex Impairment Precedes Cardiometabolic Dysfunction in an Experimental Model of Metabolic Syndrome: Role of Inflammation and Oxidative Stress.Sci Rep. 2018 Jun 5;8(1):8578. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-26816-4. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29872081 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiometabolic benefits of exercise training in an experimental model of metabolic syndrome and menopause.Menopause. 2012 May;19(5):562-8. doi: 10.1097/gme.0b013e3182358c9c. Menopause. 2012. PMID: 22157682
-
Preventive role of exercise training in autonomic, hemodynamic, and metabolic parameters in rats under high risk of metabolic syndrome development.J Appl Physiol (1985). 2013 Mar 15;114(6):786-91. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00586.2012. Epub 2013 Jan 17. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2013. PMID: 23329818
-
Baroreflexes and cardiovascular regulation in hypertension.J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1995;26 Suppl 2:S7-16. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1995. PMID: 8642810 Review.
-
Arterial baroreflex function in conscious rats.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2002 Aug;23(8):673-9. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2002. PMID: 12147187 Review.
Cited by
-
Impact of inhibition of the renin-angiotensin system on early cardiac and renal abnormalities in Sprague Dawley rats fed short-term high fructose plus high salt diet.Front Nutr. 2024 Aug 22;11:1436958. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2024.1436958. eCollection 2024. Front Nutr. 2024. PMID: 39238563 Free PMC article.
-
Chronic Consumption of Fructose Induces Behavioral Alterations by Increasing Orexin and Dopamine Levels in the Rat Brain.Nutrients. 2018 Nov 10;10(11):1722. doi: 10.3390/nu10111722. Nutrients. 2018. PMID: 30423806 Free PMC article.
-
Acute renal denervation normalizes aortic function and decreases blood pressure in spontaneously hypertensive rats.Sci Rep. 2020 Dec 11;10(1):21826. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-78674-8. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 33311525 Free PMC article.
-
A Novel Method for Baroreflex Sensitivity Estimation Using Modulated Gaussian Filter.Sensors (Basel). 2022 Jun 18;22(12):4618. doi: 10.3390/s22124618. Sensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35746400 Free PMC article.
-
Excessive Fructose Intake Impairs Baroreflex Sensitivity and Led to Elevated Blood Pressure in Rats.Nutrients. 2019 Oct 25;11(11):2581. doi: 10.3390/nu11112581. Nutrients. 2019. PMID: 31731536 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Girman CJ, et al. The metabolic syndrome and risk of major coronary events in the Scandinavian Simvastatin Survival Study (4S) and the Air Force/Texas Coronary Atherosclerosis Prevention Study (AFCAPS/TexCAPS) The American journal of cardiology. 2004;93:136–141. doi: 10.1016/j.amjcard.2003.09.028. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Richelsen, B. Sugar-sweetened beverages and cardio-metabolic disease risks. Current opinion in clinical nutrition and metabolic care, 10.1097/MCO.0b013e328361c53e (2013). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

