LIN28 Selectively Modulates a Subclass of Let-7 MicroRNAs
- PMID: 30029005
- PMCID: PMC6238216
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2018.06.029
LIN28 Selectively Modulates a Subclass of Let-7 MicroRNAs
Abstract
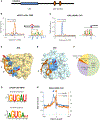
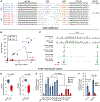
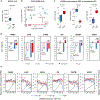
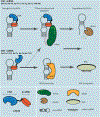
LIN28 is a bipartite RNA-binding protein that post-transcriptionally inhibits the biogenesis of let-7 microRNAs to regulate development and influence disease states. However, the mechanisms of let-7 suppression remain poorly understood because LIN28 recognition depends on coordinated targeting by both the zinc knuckle domain (ZKD), which binds a GGAG-like element in the precursor, and the cold shock domain (CSD), whose binding sites have not been systematically characterized. By leveraging single-nucleotide-resolution mapping of LIN28 binding sites in vivo, we determined that the CSD recognizes a (U)GAU motif. This motif partitions the let-7 microRNAs into two subclasses, precursors with both CSD and ZKD binding sites (CSD+) and precursors with ZKD but no CSD binding sites (CSD-). LIN28 in vivo recognition-and subsequent 3' uridylation and degradation-of CSD+ precursors is more efficient, leading to their stronger suppression in LIN28-activated cells and cancers. Thus, CSD binding sites amplify the regulatory effects of LIN28.
Keywords: CLIP; LIN28; bipartite binding; cancer; cold shock domain; let-7 microRNA biogenesis; selective suppression; stem cell.
Copyright © 2018 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Lin28 cold-shock domain remodels pre-let-7 microRNA.Nucleic Acids Res. 2012 Aug;40(15):7492-506. doi: 10.1093/nar/gks355. Epub 2012 May 8. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012. PMID: 22570413 Free PMC article.
-
LIN28 Zinc Knuckle Domain Is Required and Sufficient to Induce let-7 Oligouridylation.Cell Rep. 2017 Mar 14;18(11):2664-2675. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2017.02.044. Cell Rep. 2017. PMID: 28297670
-
Recognition of the let-7g miRNA precursor by human Lin28B.FEBS Lett. 2012 Nov 16;586(22):3986-90. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2012.09.034. Epub 2012 Oct 11. FEBS Lett. 2012. PMID: 23063642
-
Mechanisms of Lin28-mediated miRNA and mRNA regulation--a structural and functional perspective.Int J Mol Sci. 2013 Aug 9;14(8):16532-53. doi: 10.3390/ijms140816532. Int J Mol Sci. 2013. PMID: 23939427 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A mirror of two faces: Lin28 as a master regulator of both miRNA and mRNA.Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2012 Jul-Aug;3(4):483-94. doi: 10.1002/wrna.1112. Epub 2012 Mar 29. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2012. PMID: 22467269 Review.
Cited by
-
The Battle for Survival: The Role of RNA Non-Canonical Tails in the Virus-Host Interaction.Metabolites. 2023 Sep 13;13(9):1009. doi: 10.3390/metabo13091009. Metabolites. 2023. PMID: 37755289 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Amelioration of Ductular Reaction by Stem Cell Derived Extracellular Vesicles in MDR2 Knockout Mice via Lethal-7 microRNA.Hepatology. 2019 Jun;69(6):2562-2578. doi: 10.1002/hep.30542. Epub 2019 Apr 12. Hepatology. 2019. PMID: 30723922 Free PMC article.
-
The Target MicroRNAs and Potential Underlying Mechanisms of Yiqi-Bushen-Tiaozhi Recipe against-Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis.Front Pharmacol. 2020 Nov 12;11:529553. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.529553. eCollection 2020. Front Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 33281601 Free PMC article.
-
The distinct roles of zinc finger CCHC-type (ZCCHC) superfamily proteins in the regulation of RNA metabolism.RNA Biol. 2021 Dec;18(12):2107-2126. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2021.1909320. Epub 2021 May 4. RNA Biol. 2021. PMID: 33787465 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RNA uridyl transferases TUT4/7 differentially regulate miRNA variants depending on the cancer cell type.RNA. 2022 Mar;28(3):353-370. doi: 10.1261/rna.078976.121. Epub 2021 Dec 23. RNA. 2022. PMID: 34949722 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bernstein E, Caudy AA, Hammond SM, and Hannon GJ (2001). Role for a bidentate ribonuclease in the initiation step of RNA interference. Nature 409, 363–366. - PubMed
-
- Cho J, Chang H, Kwon SC, Kim B, Kim Y, Choe J, Ha M, Kim YK, and Kim VN (2012). LIN28A is a suppressor of ER-associated translation in embryonic stem cells. Cell 151, 765–777. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

