Mesenchymal stromal cells attenuate sevoflurane-induced apoptosis in human neuroglioma H4 cells
- PMID: 30021512
- PMCID: PMC6052698
- DOI: 10.1186/s12871-018-0553-1
Mesenchymal stromal cells attenuate sevoflurane-induced apoptosis in human neuroglioma H4 cells
Abstract
Background: Inhalation of sevoflurane can induce neuronal apoptosis, cognitive impairment and abnormal behaviors. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) can secret neurotrophic factors and cytokines to protect from oxidative stress-related neuronal apoptosis. However, whether MSCs can protect from sevoflurane-induced neuronal apoptosis and the potential mechanisms are unclear.
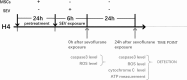
Methods: A non-contact co-culture of MSCs with human neuroglioma H4 cells (H4 cells) was built. H4 cells were co-cultured with MSCs or without MSCs (control) for 24 h. The co-cultured H4 cells were exposed to 4% sevoflurane for 6 h. The levels of caspase-3, reactive oxygen species (ROS), adenosine triphosphate (ATP), and the release of cytochrome C were determined by Western blot and fluorescence assay.
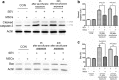
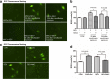
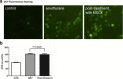
Results: Sevoflurane exposure significantly elevated the levels of cleaved caspase 3 and Bax in H4 cells. However, these phenomena were significantly offset by the co-culture with MSCs in H4 cells. Co-culture with MSCs before, but not after, sevoflurane exposure, significantly attenuated sevoflurane-induced ROS production in H4 cells. MSCs prevented sevoflurane-mediated release of cytochrome C from the mitochondria and production of ATP in H4 cells.
Conclusions: Our study indicated that soluble factors secreted by MSCs attenuated the sevoflurane-induced oxidative stress and apoptosis of neuronal cells by preserving their mitochondrial function.
Keywords: Apoptosis, mitochondrial dysfunction; Mesenchymal stem cells; Reactive oxygen species; Sevoflurane.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
All experimental protocols were approved by the Animal Care and Use of Shanghai Ninth People’s Hospital Affiliated to Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine Committee.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Glucose may attenuate isoflurane-induced caspase-3 activation in H4 human neuroglioma cells.Anesth Analg. 2014 Dec;119(6):1373-80. doi: 10.1213/ANE.0000000000000383. Anesth Analg. 2014. PMID: 25068691
-
PARKIN overexpression in human mesenchymal stromal cells from Wharton's jelly suppresses 6-hydroxydopamine-induced apoptosis: Potential therapeutic strategy in Parkinson's disease.Cytotherapy. 2018 Jan;20(1):45-61. doi: 10.1016/j.jcyt.2017.09.011. Epub 2017 Nov 2. Cytotherapy. 2018. PMID: 29079356
-
Mesenchymal stem cells alleviate oxidative stress-induced mitochondrial dysfunction in the airways.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2018 May;141(5):1634-1645.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2017.08.017. Epub 2017 Sep 11. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2018. PMID: 28911970
-
CsA attenuates compression-induced nucleus pulposus mesenchymal stem cells apoptosis via alleviating mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress.Life Sci. 2018 Jul 15;205:26-37. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2018.05.014. Epub 2018 May 8. Life Sci. 2018. PMID: 29746847
-
2,5-hexanedione induced apoptosis in mesenchymal stem cells from rat bone marrow via mitochondria-dependent caspase-3 pathway.Ind Health. 2015;53(3):222-35. doi: 10.2486/indhealth.2014-0182. Epub 2015 Jan 29. Ind Health. 2015. PMID: 25739802 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The emerging antioxidant paradigm of mesenchymal stem cell therapy.Stem Cells Transl Med. 2020 Sep;9(9):985-1006. doi: 10.1002/sctm.19-0446. Epub 2020 Jun 4. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2020. PMID: 32497410 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Involvement of Mitochondrial Dynamics and Mitophagy in Sevoflurane-Induced Cell Toxicity.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021 Feb 26;2021:6685468. doi: 10.1155/2021/6685468. eCollection 2021. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021. Retraction in: Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2023 Aug 2;2023:9760436. doi: 10.1155/2023/9760436 PMID: 33728028 Free PMC article. Retracted. Review.
-
LncRNA Riken Attenuated Sevoflurane-Induced Neuroinflammation by Regulating the MicroRNA-101a/MKP-1/JNK Pathway.Neurotox Res. 2022 Feb;40(1):186-197. doi: 10.1007/s12640-021-00443-w. Epub 2021 Nov 26. Neurotox Res. 2022. PMID: 34826047
-
Sevoflurane-induced POCD-associated exosomes delivered miR-584-5p regulates the growth of human microglia HMC3 cells through targeting BDNF.Aging (Albany NY). 2022 Nov 30;14(24):9890-9907. doi: 10.18632/aging.204398. Epub 2022 Nov 30. Aging (Albany NY). 2022. PMID: 36455873 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Qiao Y, Feng H, Zhao T, Yan H, Zhang H, Zhao X. Postoperative cognitive dysfunction after inhalational anesthesia in elderly patients undergoing major surgery: the influence of anesthetic technique, cerebral injury and systemic inflammation. BMC Anesthesiol. 2015;15:154. doi: 10.1186/s12871-015-0130-9. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

