Liver X Receptors Suppress Activity of Cholesterol and Fatty Acid Synthesis Pathways To Oppose Gammaherpesvirus Replication
- PMID: 30018108
- PMCID: PMC6050960
- DOI: 10.1128/mBio.01115-18
Liver X Receptors Suppress Activity of Cholesterol and Fatty Acid Synthesis Pathways To Oppose Gammaherpesvirus Replication
Abstract
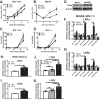
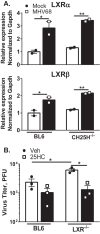
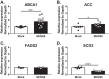
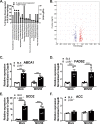
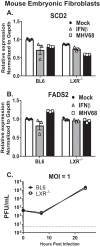
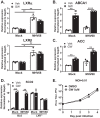
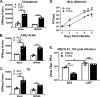
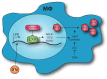
Gammaherpesviruses are oncogenic pathogens that persist in ~95% of the adult population. Cellular metabolic pathways have emerged as important regulators of many viral infections, including infections by gammaherpesviruses that require several lipid synthetic pathways for optimal replication. Liver X receptors (LXRs) are transcription factors that are critical regulators of cellular fatty acid and cholesterol synthesis pathways. Not surprisingly, LXRs are attractive therapeutic targets in cardiovascular disease. Here we describe an antiviral role for LXRs in the context of gammaherpesvirus infection of primary macrophages. We show that type I interferon increased LXR expression following infection. Surprisingly, there was not a corresponding induction of LXR target genes. Rather, LXRs suppressed the expression of target genes, leading to decreased fatty acid and cholesterol synthesis, two metabolic pathways that support gammaherpesvirus replication. This report defines LXR-mediated restriction of cholesterol and lipid synthesis as an intrinsic metabolic mechanism to restrict viral replication in innate immune cells.IMPORTANCE Fatty acid and cholesterol synthesis pathways of the host play important roles in diverse biological systems. Importantly, these two metabolic pathways are also usurped by a number of viruses to facilitate viral replication. In this report, we show that suppression of these pathways by liver X receptors in primary macrophages creates an intrinsic antiviral state that attenuates gammaherpesvirus replication by limiting viral access to the two metabolic pathways.
Keywords: cholesterol synthesis; fatty acid synthesis; gammaherpesvirus; liver X receptors; macrophages.
Copyright © 2018 Lange et al.
Figures
Similar articles
-
LXR Alpha Restricts Gammaherpesvirus Reactivation from Latently Infected Peritoneal Cells.J Virol. 2019 Mar 5;93(6):e02071-18. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02071-18. Print 2019 Mar 15. J Virol. 2019. PMID: 30602604 Free PMC article.
-
Low-Density Lipoprotein Receptor Suppresses the Endogenous Cholesterol Synthesis Pathway To Oppose Gammaherpesvirus Replication in Primary Macrophages.J Virol. 2021 Aug 10;95(17):e0064921. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00649-21. Epub 2021 Aug 10. J Virol. 2021. PMID: 34105999 Free PMC article.
-
Type I Interferon Counteracts Antiviral Effects of Statins in the Context of Gammaherpesvirus Infection.J Virol. 2016 Jan 6;90(7):3342-54. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02277-15. J Virol. 2016. PMID: 26739055 Free PMC article.
-
Liver X Receptors and their Agonists: Targeting for Cholesterol Homeostasis and Cardiovascular Diseases.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2017;22:41-64. doi: 10.21775/cimb.022.041. Epub 2016 Sep 27. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2017. PMID: 27669666 Review.
-
Getting the message direct manipulation of host mRNA accumulation during gammaherpesvirus lytic infection.Adv Virus Res. 2010;78:1-42. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-385032-4.00001-X. Adv Virus Res. 2010. PMID: 21040830 Review.
Cited by
-
LXR Alpha Restricts Gammaherpesvirus Reactivation from Latently Infected Peritoneal Cells.J Virol. 2019 Mar 5;93(6):e02071-18. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02071-18. Print 2019 Mar 15. J Virol. 2019. PMID: 30602604 Free PMC article.
-
Pseudorabies Virus Inhibits Expression of Liver X Receptors to Assist Viral Infection.Viruses. 2022 Mar 3;14(3):514. doi: 10.3390/v14030514. Viruses. 2022. PMID: 35336921 Free PMC article.
-
Conquering the Host: Determinants of Pathogenesis Learned from Murine Gammaherpesvirus 68.Annu Rev Virol. 2021 Sep 29;8(1):349-371. doi: 10.1146/annurev-virology-011921-082615. Annu Rev Virol. 2021. PMID: 34586873 Free PMC article.
-
Endosomal Cholesterol in Viral Infections - A Common Denominator?Front Physiol. 2021 Nov 11;12:750544. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2021.750544. eCollection 2021. Front Physiol. 2021. PMID: 34858206 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Liver X Receptor-Inducible Host E3 Ligase IDOL Targets a Human Cytomegalovirus Reactivation Determinant.J Virol. 2023 Jul 27;97(7):e0075823. doi: 10.1128/jvi.00758-23. Epub 2023 Jun 20. J Virol. 2023. PMID: 37338407 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

