Thrombopoietin knock-in augments platelet generation from human embryonic stem cells
- PMID: 30016991
- PMCID: PMC6050740
- DOI: 10.1186/s13287-018-0926-x
Thrombopoietin knock-in augments platelet generation from human embryonic stem cells
Abstract
Background: Refinement of therapeutic-scale platelet production in vitro will provide a new source for transfusion in patients undergoing chemotherapy or radiotherapy. However, procedures for cost-effective and scalable platelet generation remain to be established.
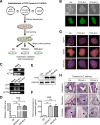
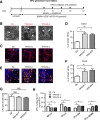
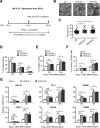
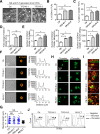
Methods: In this study, we established human embryonic stem cell (hESC) lines containing knock-in of thrombopoietin (TPO) via CRISPR/Cas9-mediated genome editing. The expression and secretion of TPO was detected by western blotting and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Then, we tested the potency for hematopoietic differentiation by coculturing the cells with mAGM-S3 cells and measured the generation of CD43+ and CD45+ hematopoietic progenitor cells (HPCs). The potency for megakaryocytic differentiation and platelet generation of TPO knock-in hESCs were further detected by measuring the expression of CD41a and CD42b. The morphology and function of platelets were analyzed with electronic microscopy and aggregation assay.
Results: The TPO gene was successfully inserted into the AAVS1 locus of the hESC genome and two cell lines with stable TPO expression and secretion were established. TPO knock-in exerts minimal effects on pluripotency but enhances early hematopoiesis and generation of more HPCs. More importantly, upon its knock-in, TPO augments megakaryocytic differentiation and platelet generation. In addition, the platelets derived from hESCs in vitro are functionally and morphologically comparable to those found in peripheral blood. Furthermore, TPO knock-in can partially replace the large quantities of extrinsic TPO necessary for megakaryocytic differentiation and platelet generation.
Conclusions: Our results demonstrate that autonomous production of cytokines in hESCs may become a powerful approach for cost-effective and large-scale platelet generation in translational medicine.
Keywords: Early hematopoiesis; Human embryonic stem cells; Knock-in; Platelets; Thrombopoietin.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The experiment on mice followed the internationally recognized guidelines. Meanwhile, ethical approval of animal research was signed by the Ethical Committee of the Institute of Hematology and Blood Diseases Hospital, Chinese Academy of Medical Science & Peking Union Medical College (approval no. KT2016011-EC-1).
Consent for publication
All authors consented to publication.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no financial competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Expression of the receptor MPL and proliferative effects of its ligand thrombopoietin on human leukemia cells.Leukemia. 1996 Feb;10(2):297-310. Leukemia. 1996. PMID: 8637239
-
Thrombopoietin: expression of its receptor MPL and proliferative effects on leukemic cells.Leukemia. 1996 Sep;10(9):1405-21. Leukemia. 1996. PMID: 8751457 Review.
-
Thrombopoietin: biology and clinical potentials.Int J Hematol. 1999 Dec;70(4):216-25. Int J Hematol. 1999. PMID: 10643146 Review.
-
Thrombopoietin: understanding and manipulating platelet production.Annu Rev Med. 1997;48:1-11. doi: 10.1146/annurev.med.48.1.1. Annu Rev Med. 1997. PMID: 9046940 Review.
-
Use of human leukemia-lymphoma cell lines in hematological research: effects of thrombopoietin on human leukemia cell lines.Hum Cell. 1996 Dec;9(4):309-16. Hum Cell. 1996. PMID: 9183663 Review.
Cited by
-
CAR-NK cells for cancer immunotherapy: from bench to bedside.Biomark Res. 2022 Mar 18;10(1):12. doi: 10.1186/s40364-022-00364-6. Biomark Res. 2022. PMID: 35303962 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem/stromal cells in patients with acute myeloid leukemia reveal transcriptome alterations and deficiency in cellular vitality.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021 Jun 26;12(1):365. doi: 10.1186/s13287-021-02444-0. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021. PMID: 34174939 Free PMC article.
-
Aquaporin 4 inhibition alleviates myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury by restraining cardiomyocyte pyroptosis.Bioengineered. 2021 Dec;12(1):9021-9030. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2021.1992332. Bioengineered. 2021. PMID: 34657556 Free PMC article.
-
Macrophages Derived From Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells: The Diversity of Protocols, Future Prospects, and Outstanding Questions.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Jun 2;9:640703. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.640703. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34150747 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In vitro Generation of Megakaryocytes and Platelets.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Aug 12;9:713434. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.713434. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34458269 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Feng Q, Shabrani N, Thon JN, Huo H, Thiel A, Machlus KR, Kim K, Brooks J, Li F, Luo C, Kimbrel EA, Wang J, Kim KS, Italiano J, J Cho SJL, Lanza R. Scalable generation of universal platelets from human induced pluripotent stem cells. Stem Cell Rep. 2014;3:817–831. doi: 10.1016/j.stemcr.2014.09.010. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Moreau T, AL Evans LV, Tijssen MR, Yan Y, MW Trotter D, Howard M, Colzani M, Arumugam WHW, Dalby A, Lampela R, Bouet G, Hobbs CM, Pask DC, Payne H, Ponomaryov T, Brill A, Soranzo N, Ouwehand WH, Pedersen RA, Ghevaert C. Large-scale production of megakaryocytes from human pluripotent stem cells by chemically defined forward programming. Nat Commun. 2016;7:11208. doi: 10.1038/ncomms11208. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Takayama N, Nishikii H, Usui J, Tsukui H, Sawaguchi A, Hiroyama T, Eto K, Nakauchi H. Generation of functional platelets from human embryonic stem cells in vitro via ES-sacs, VEGF-promoted structures that concentrate hematopoietic progenitors. Blood. 2008;111:5298–5306. doi: 10.1182/blood-2007-10-117622. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Nakamura S, Takayama N, Hirata S, Seo H, Endo H, Ochi K, Fujita K, Koike T, Harimoto K, Dohda T, Watanabe A, Okita K, Takahashi N, Sawaguchi A, Yamanaka S, Nakauchi H, Nishimura S, Eto K. Expandable megakaryocyte cell lines enable clinically applicable generation of platelets from human induced pluripotent stem cells. Cell Stem Cell. 2014;14:535–548. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2014.01.011. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

