Novel influenza vaccine M2SR protects against drifted H1N1 and H3N2 influenza virus challenge in ferrets with pre-existing immunity
- PMID: 30007825
- PMCID: PMC6086587
- DOI: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2018.06.053
Novel influenza vaccine M2SR protects against drifted H1N1 and H3N2 influenza virus challenge in ferrets with pre-existing immunity
Abstract
Current influenza vaccines do not provide effective protection against heterologous influenza viruses. The ability of the novel M2SR influenza vaccine to protect against drifted influenza viruses was evaluated in naïve ferrets and in ferrets with pre-existing immunity to influenza. In naïve ferrets, M2SR provided similar protection against drifted challenge viruses as the comparator vaccine, FluMist®. However, in ferrets with pre-existing immunity, M2SR provided superior protection than FluMist in two model systems. In the first model, ferrets were infected with influenza A H1N1pdm and influenza B viruses to mimic the diverse influenza exposure in humans. The pre-infected ferrets, seropositive to H1N1pdm and influenza B but seronegative to H3N2, were then vaccinated with H3N2 M2SR or monovalent H3N2 FluMist virus (A/Brisbane/10/2007, clade 1) and challenged 6 weeks later with a drifted H3N2 virus (clade 3C.2a). Antibody titers to Brisbane/10/2007 were higher in M2SR vaccinated ferrets than in FluMist vaccinated ferrets in the pre-infected ferrets whereas the opposite was observed in naïve ferrets. After challenge with drifted H3N2 virus, M2SR provided superior protection than FluMist monovalent vaccine. In the second model, the impact of homologous pre-existing immunity upon vaccine-induced protection was evaluated. Ferrets, pre-infected with H1N1pdm virus, were vaccinated 90 days later with H1N1pdm M2SR or FluMist monovalent vaccine and challenged 6 weeks later with a pre-pandemic seasonal H1N1 virus, A/Brisbane/59/2007 (Bris59). While cross-reactive serum IgG antibodies against the Bris59 HA were detected after vaccination, anti-Bris59 hemagglutination inhibition antibodies were only detected post-challenge. M2SR provided better protection against Bris59 challenge than FluMist suggesting that homologous pre-existing immunity affected FluMist virus to a greater degree than M2SR. These results suggest that the single replication intranasal M2SR vaccine provides effective protection against drifted influenza A viruses not only in naïve ferrets but also in those with pre-existing immunity in contrast to FluMist viruses.
Keywords: Drifted; Hemagglutination inhibition; Heterosubtypic immunity; Intranasal; Live influenza; M2-deficient; Pre-existing immunity; Single replication.
Copyright © 2018. Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
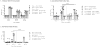

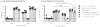
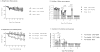
Similar articles
-
M2SR, a novel live influenza vaccine, protects mice and ferrets against highly pathogenic avian influenza.Vaccine. 2017 Jul 24;35(33):4177-4183. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2017.06.039. Epub 2017 Jun 28. Vaccine. 2017. PMID: 28668565 Free PMC article.
-
Intranasal M2SR (M2-Deficient Single Replication) H3N2 Influenza Vaccine Provides Enhanced Mucosal and Serum Antibodies in Adults.J Infect Dis. 2022 Dec 28;227(1):103-112. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiac433. J Infect Dis. 2022. PMID: 36350017 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Pandemic influenza 1918 H1N1 and 1968 H3N2 DNA vaccines induce cross-reactive immunity in ferrets against infection with viruses drifted for decades.Influenza Other Respir Viruses. 2011 Jan;5(1):13-23. doi: 10.1111/j.1750-2659.2010.00177.x. Epub 2010 Nov 3. Influenza Other Respir Viruses. 2011. PMID: 21138536 Free PMC article.
-
Recalling the Future: Immunological Memory Toward Unpredictable Influenza Viruses.Front Immunol. 2019 Jul 2;10:1400. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.01400. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31312199 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Influenza virus vaccine live intranasal--MedImmune vaccines: CAIV-T, influenza vaccine live intranasal.Drugs R D. 2003;4(5):312-9. doi: 10.2165/00126839-200304050-00007. Drugs R D. 2003. PMID: 12952502 Review.
Cited by
-
Immune Imprinting in the Influenza Ferret Model.Vaccines (Basel). 2020 Apr 8;8(2):173. doi: 10.3390/vaccines8020173. Vaccines (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32276530 Free PMC article. Review.
-
M2-Deficient Single-Replication Influenza Vaccine-Induced Immune Responses Associated With Protection Against Human Challenge With Highly Drifted H3N2 Influenza Strain.J Infect Dis. 2022 Aug 12;226(1):83-90. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiab374. J Infect Dis. 2022. PMID: 34323977 Free PMC article.
-
The Quest for a Truly Universal Influenza Vaccine.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2019 Oct 10;9:344. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2019.00344. eCollection 2019. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31649895 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparative models for human nasal infections and immunity.Dev Comp Immunol. 2019 Mar;92:212-222. doi: 10.1016/j.dci.2018.11.022. Epub 2018 Dec 1. Dev Comp Immunol. 2019. PMID: 30513304 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Animal Models for Influenza Research: Strengths and Weaknesses.Viruses. 2021 May 28;13(6):1011. doi: 10.3390/v13061011. Viruses. 2021. PMID: 34071367 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Belongia EA, et al. Effectiveness of inactivated influenza vaccines varied substantially with antigenic match from the 2004–2005 season to the 2006–2007 season. J Infect Dis. 2009;199(2):159–67. - PubMed
-
- Paules CI, et al. Chasing Seasonal Influenza - The Need for a Universal Influenza Vaccine. N Engl J Med. 2018;378(1):7–9. - PubMed
-
- Eick AA, et al. Comparison of the trivalent live attenuated vs. inactivated influenza vaccines among U.S. military service members. Vaccine. 2009;27(27):3568–75. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

