Small molecule targeting the Rac1-NOX2 interaction prevents collagen-related peptide and thrombin-induced reactive oxygen species generation and platelet activation
- PMID: 30007118
- PMCID: PMC6472274
- DOI: 10.1111/jth.14240
Small molecule targeting the Rac1-NOX2 interaction prevents collagen-related peptide and thrombin-induced reactive oxygen species generation and platelet activation
Abstract
Essentials Reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation by NOX2 plays a critical role in platelet activation. Rac1 regulation of NOX2 is important for ROS generation. Small molecule inhibitor of the Rac1-p67phox interaction prevents platelet activation. Pharmacologic targeting of Rac1-NOX2 axis can be a viable approach for antithrombotic therapy.
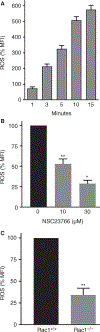
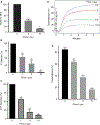
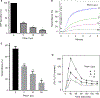
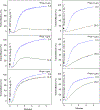
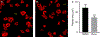
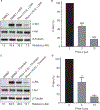
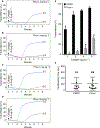
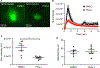
Summary: Background Platelets from patients with X-linked chronic granulomatous disease or mice deficient in nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (phosphate) (NAD(P)H) oxidase isoform NOX2 exhibit diminished reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation and platelet activation. Binding of Rac1 GTPase to p67phox plays a critical role in NOX2 activation by facilitating the assembly of the NOX2 enzyme complex. Objective We tested the hypothesis that Phox-I, a rationally designed small molecule inhibitor of Rac-p67phox interaction, may serve as an antithrombosis agent by suppressing ROS production and platelet activation. Results Collagen-related peptide (CRP) induced ROS generation in a time-dependent manner. Platelets from Rac1-/- mice or human platelets treated with NSC23766, a specific Rac inhibitor, produced significantly less ROS in response to CRP. Treatment of platelets with Phox-I inhibited diverse CRP-induced responses, including: (i) ROS generation; (ii) release of P-selectin; (iii) secretion of ATP; (iv) platelet aggregation; and (v) phosphorylation of Akt. Similarly, incubation of platelets with Phox-I inhibited thrombin-induced: (i) secretion of ATP; (ii) platelet aggregation; (iii) rise in cytosolic calcium; and (iv) phosphorylation of Akt. In mouse models, intraperitoneal administration of Phox-I inhibited: (i) collagen-induced platelet aggregation without affecting the tail bleeding time and (ii) in vivo platelet adhesion/accumulation at the laser injury sites on the saphenous vein without affecting the time for complete cessation of blood loss. Conclusions Small molecule targeting of the Rac1-p67phox interaction may present an antithrombosis regimen by preventing GPVI- and non-GPVI-mediated NOX2 activation, ROS generation and platelet function without affecting the bleeding time.
Keywords: NADPH oxidase; Rac1 GTP-binding protein; platelet activation; reactive oxygen species; thrombosis.
© 2018 International Society on Thrombosis and Haemostasis.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure of Conflict of Interests
The authors state that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Differential Roles of the NADPH-Oxidase 1 and 2 in Platelet Activation and Thrombosis.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2016 May;36(5):846-54. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.116.307308. Epub 2016 Mar 17. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2016. PMID: 26988594 Free PMC article.
-
The role of Nox1 and Nox2 in GPVI-dependent platelet activation and thrombus formation.Redox Biol. 2014 Jan 13;2:178-86. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2013.12.023. eCollection 2014. Redox Biol. 2014. PMID: 24494191 Free PMC article.
-
Gene targeting implicates Cdc42 GTPase in GPVI and non-GPVI mediated platelet filopodia formation, secretion and aggregation.PLoS One. 2011;6(7):e22117. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0022117. Epub 2011 Jul 18. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21789221 Free PMC article.
-
NADPH oxidase 2 (NOX2): A key target of oxidative stress-mediated platelet activation and thrombosis.Trends Cardiovasc Med. 2018 Oct;28(7):429-434. doi: 10.1016/j.tcm.2018.03.001. Epub 2018 Mar 26. Trends Cardiovasc Med. 2018. PMID: 29661712 Review.
-
NADPH Oxidase-2 and Atherothrombosis: Insight From Chronic Granulomatous Disease.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2017 Feb;37(2):218-225. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.116.308351. Epub 2016 Dec 8. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2017. PMID: 27932349 Review.
Cited by
-
Rac GTPase Signaling in Immune-Mediated Mechanisms of Atherosclerosis.Cells. 2021 Oct 20;10(11):2808. doi: 10.3390/cells10112808. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34831028 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rho GTPase regulation of reactive oxygen species generation and signalling in platelet function and disease.Small GTPases. 2021 Sep-Nov;12(5-6):440-457. doi: 10.1080/21541248.2021.1878001. Epub 2021 Apr 12. Small GTPases. 2021. PMID: 33459160 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structure-Activity Relationship Analysis of Rhosin, a RhoA GTPase Inhibitor, Reveals a New Class of Antiplatelet Agents.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Feb 19;24(4):4167. doi: 10.3390/ijms24044167. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36835579 Free PMC article.
-
Shear and Integrin Outside-In Signaling Activate NADPH-Oxidase 2 to Promote Platelet Activation.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2021 May 5;41(5):1638-1653. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.120.315773. Epub 2021 Mar 11. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2021. PMID: 33691478 Free PMC article.
-
Rho GTPase Signaling in Platelet Regulation and Implication for Antiplatelet Therapies.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jan 28;24(3):2519. doi: 10.3390/ijms24032519. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36768837 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Krotz F, Sohn HY, Pohl U. Reactive oxygen species: players in the platelet game. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2004; 24: 1988–96. - PubMed
-
- Begonja AJ, Gambaryan S, Geiger J, Aktas B, Pozgajova M, Nieswandt B, Walter U. Platelet NAD(P)H-oxidase-generated ROS production regulates alphaIIbbeta3-integrin activation independent of the NO/cGMP pathway. Blood 2005; 106: 2757–60. - PubMed
-
- Violi F, Pignatelli P. Platelet NOX, a novel target for antithrombotic treatment. Thromb Haemost 2014; 111: 817–23. - PubMed
-
- Bedard K, Krause KH. The NOX family of ROS-generating NADPH oxidases: physiology and pathophysiology. Physiol Rev 2007; 87: 245–313. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

