Exosomes derived from human adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells alleviate atopic dermatitis
- PMID: 29996938
- PMCID: PMC6042362
- DOI: 10.1186/s13287-018-0939-5
Exosomes derived from human adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells alleviate atopic dermatitis
Abstract
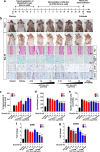
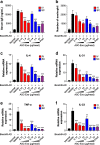
Exosomes are nano-sized vesicles (30-200 nm) constantly released by almost all cells. The ability of exosomes to travel between cells and deliver their cargo, which includes lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids, makes them an appealing cell-free therapy option to treat multiple diseases. Here, we investigated for the first time whether human adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes (ASC-exosomes) can ameliorate atopic dermatitis (AD) in an in vivo mouse model. When injected either intravenously (IV) or subcutaneously (SC) into NC/Nga mice treated with house dust mite antigens, ASC-exosomes were found to reduce pathological symptoms such as clinical score, the levels of serum IgE, the number of eosinophils in blood, and the infiltration of mast cells, CD86+, and CD206+ cells in skin lesions. ASC-exosomes also significantly reduced mRNA expression of various inflammatory cytokines such as interleukin (IL)-4, IL-23, IL-31, and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) in AD skin lesions of Nc/Nga mice. Taken together, these results suggest that ASC-exosomes can be a novel promising cell-free therapeutic modality for AD treatment.
Keywords: Adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells; Atopic dermatitis; Exosome; Inflammation.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval
The animal study was approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee and performed in accordance with the Animal Experimentation Policy.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
BSC and YWY are founders and stockholders of ExoCoBio Inc. All authors are employees of ExoCoBio Inc.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Exosomes from Human Adipose Tissue-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Promote Epidermal Barrier Repair by Inducing de Novo Synthesis of Ceramides in Atopic Dermatitis.Cells. 2020 Mar 10;9(3):680. doi: 10.3390/cells9030680. Cells. 2020. PMID: 32164386 Free PMC article.
-
Adipose tissue-derived exosomes alleviate particulate matter-induced inflammatory response and skin barrier damage in atopic dermatitis-like triple-cell model.PLoS One. 2024 Jan 19;19(1):e0292050. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0292050. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38241278 Free PMC article.
-
Exosomes derived from human adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells for the treatment of dupilumab-related facial redness in patients with atopic dermatitis: A report of two cases.J Cosmet Dermatol. 2022 Feb;21(2):844-849. doi: 10.1111/jocd.14153. Epub 2021 Apr 29. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2022. PMID: 33844417
-
Recent advance in mesenchymal stem cells therapy for atopic dermatitis.J Cell Biochem. 2023 Feb;124(2):181-187. doi: 10.1002/jcb.30365. Epub 2022 Dec 28. J Cell Biochem. 2023. PMID: 36576973 Review.
-
Exosomes as novel player in dermatologic field.Dermatol Ther. 2022 Nov;35(11):e15883. doi: 10.1111/dth.15883. Epub 2022 Oct 7. Dermatol Ther. 2022. PMID: 36183094 Review.
Cited by
-
Regenerative medicine strategies for hair growth and regeneration: A narrative review of literature.Regen Ther. 2022 Oct 31;21:527-539. doi: 10.1016/j.reth.2022.10.005. eCollection 2022 Dec. Regen Ther. 2022. PMID: 36382136 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Combination Treatment with Human Adipose Tissue Stem Cell-derived Exosomes and Fractional CO2 Laser for Acne Scars: A 12-week Prospective, Double-blind, Randomized, Split-face Study.Acta Derm Venereol. 2020 Nov 4;100(18):adv00310. doi: 10.2340/00015555-3666. Acta Derm Venereol. 2020. PMID: 33073298 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Exosomes From Adipose-Derived Stem Cells: The Emerging Roles and Applications in Tissue Regeneration of Plastic and Cosmetic Surgery.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020 Sep 10;8:574223. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.574223. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020. PMID: 33015067 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exosome-mediated macrophage regulation for inflammatory bowel disease repair: a potential target of gut inflammation.Am J Transl Res. 2023 Dec 15;15(12):6970-6987. eCollection 2023. Am J Transl Res. 2023. PMID: 38186999 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutic Application of Mesenchymal Stem Cells Derived Extracellular Vesicles for Immunomodulation.Front Immunol. 2019 Nov 15;10:2663. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.02663. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31849929 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

