Quantification of radioactivity by planar gamma-camera images, a promoted method of absorbed dose in the thyroid after iodine-131 treatment
- PMID: 29977082
- PMCID: PMC6033874
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-018-28571-y
Quantification of radioactivity by planar gamma-camera images, a promoted method of absorbed dose in the thyroid after iodine-131 treatment
Abstract
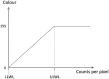
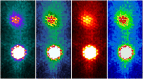
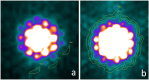
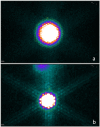
Iodine-131 (131I) is an essential and widely used radioisotope in thyroid diseases and animal experiments. Planar imaging has been considered the most popular method for 131I thyroid uptake radioactive activity quantification. The ROI defining section is essential and can affect the accuracy of quantitative results. However, a consistent method has not been proposed. In this study, a UC-ROI defining method based on ULWL setting and colour display grade was applied. Three steps were performed: image acquisition of five standard activity models and obtaining the exact value that the counts per radioactive activity contributes to the ROI; image acquisition of 20 rat thyroids and obtaining the counts of the ROI (thyroid); and calculating the rat thyroid radioactive activity and comparing these values with the true values. The accuracy of quantification activity of 131I in rat thyroid reached 2.62% ± 0.41%. The mean quantification within 5% could be achieved in 19 of 20 rat thyroids. No significant difference existed between calculated thyroid 131I activity and true values with a paired matched-test (t = -0.384, P = 0.706 > 0.05). The results indicated that with the UC-ROI defining method, more accurate thyroid uptake 131I radioactive activity quantification by SPECT planar imaging can be achieved in vivo rat study.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
GATE based Monte Carlo simulation of planar scintigraphy to estimate the nodular dose in radioiodine therapy for autonomous thyroid adenoma.Z Med Phys. 2011 Dec;21(4):290-300. doi: 10.1016/j.zemedi.2011.09.002. Epub 2011 Oct 7. Z Med Phys. 2011. PMID: 21983024
-
Reference-free thyroid uptake measurement.Nucl Med Commun. 2014 Apr;35(4):382-90. doi: 10.1097/MNM.0000000000000071. Nucl Med Commun. 2014. PMID: 24569705
-
[Thyroid uptake error in four different gamma camera systems].Nihon Hoshasen Gijutsu Gakkai Zasshi. 2004 Mar;60(3):387-92. doi: 10.6009/jjrt.kj00000922342. Nihon Hoshasen Gijutsu Gakkai Zasshi. 2004. PMID: 15131508 Japanese.
-
The continuing importance of thyroid scintigraphy in the era of high-resolution ultrasound.Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2002 Aug;29 Suppl 2:S425-38. doi: 10.1007/s00259-002-0811-8. Epub 2002 May 15. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2002. PMID: 12192542 Review.
-
[In vivo test of thyroid radioactive iodide uptake, pertechnetate 99m uptake and thyroid scintigraphy].Nihon Rinsho. 1997 Apr;55 Suppl 2:317-20. Nihon Rinsho. 1997. PMID: 9172537 Review. Japanese. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
In-situ x-ray fluorescence imaging of the endogenous iodine distribution in murine thyroids.Sci Rep. 2022 Feb 21;12(1):2903. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-06786-4. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35190621 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Buijs W, Siegel JA, Boerman OC, Corstens F. Absolute organ activity estimated by five different methods of background correction. Journal of Nuclear Medicine. 1998;39:2167–2172. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

