Vaccination with the Conserved Caveolin-1 Binding Motif in Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1 Glycoprotein gp41 Delays the Onset of Viral Infection and Provides Partial Protection in Simian/Human Immunodeficiency Virus-Challenged Cynomolgus Macaques
- PMID: 29976675
- PMCID: PMC6146716
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.00370-18
Vaccination with the Conserved Caveolin-1 Binding Motif in Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1 Glycoprotein gp41 Delays the Onset of Viral Infection and Provides Partial Protection in Simian/Human Immunodeficiency Virus-Challenged Cynomolgus Macaques
Abstract
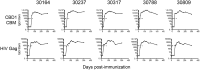
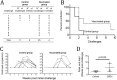
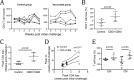
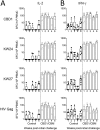
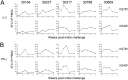
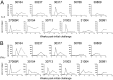
We have previously reported that the CBD1 peptide (SLEQIWNNMTWMQWDK), corresponding to the consensus caveolin-1 binding domain in human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) envelope glycoprotein gp41, elicits peptide-specific antibodies. Here, we have investigated the cellular immune response and the protective efficacy against a simian/human immunodeficiency virus (SHIV162P3) challenge. In addition to the CBD1 peptide, peptides overlapping the caveolin-binding-motif (CBM) (622IWNNMTWMQW631 or 622IWNNMTW628) were fused to a Gag-p24 T helper epitope for vaccination. All immunized cynomolgus macaques responded to a cocktail peptide immunization by inducing specific T cells and the production of high-titer CBD1/CBM peptide-specific antibodies. Six months after the fourth vaccine boost, six control and five vaccinated animals were challenged weekly by repeated exposure to SHIV162P3 via the mucosal rectal route. All control animals were infected after 1 to 3 challenges with SHIV, while among the five vaccinated monkeys, three became infected after a delay compared to control; one was infected after the eighth viral challenge, and one remained uninfected even after the ninth SHIV challenge. Immunized animals maintained a CD4 T cell count, and their central memory CD4 T cells were less depleted than in the control group. Furthermore, SHIV challenge stimulates antigen-specific memory T cell response in vaccinated macaques. Our results indicate that peptides derived from the CBM region can be immunogenic and provide protection against SHIV infection in cynomolgus monkeys.IMPORTANCE In HIV-1-producing cells, gp41 exists in a complexed form with caveolin-1, an interaction most probably mediated by the caveolin-1 binding motif. This sequence is highly conserved in every single HIV-1 isolate, thus suggesting that there is constant selective pressure to preserve this sequence for a specific function in the HIV infectious cycle. Consequently, the CBM sequence may represent the "Achilles' heel" of HIV-1 in the development of an efficient vaccine. Our results demonstrate that macaques immunized with the CBM-based peptides displayed a delay in the onset of viral infection and CD4 depletion, as well as a significant induction of antigen-specific memory T cell response, which is essential for the control of HIV/SIV infections. Finally, as HIV-infected individuals lack anti-CBM immune responses, CBM-based vaccines could have applications as a therapeutic vaccine in AIDS patients.
Keywords: AIDS; B cell; CD4; HIV; IgG; SIV; TH1; Th1; gp41; human immunodeficiency virus; immunization; macaque; memory T cells; simian immunodeficiency virus; vaccine.
Copyright © 2018 American Society for Microbiology.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Protection against chronic infection and AIDS by an HIV envelope peptide-cocktail vaccine in a pathogenic SHIV-rhesus model.Vaccine. 2001 Dec 12;20(5-6):813-25. doi: 10.1016/s0264-410x(01)00408-x. Vaccine. 2001. PMID: 11738745
-
Selective induction of cell-mediated immunity and protection of rhesus macaques from chronic SHIV(KU2) infection by prophylactic vaccination with a conserved HIV-1 envelope peptide-cocktail.Virology. 2008 Jan 5;370(1):130-41. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2007.08.022. Epub 2007 Oct 24. Virology. 2008. PMID: 17920095 Free PMC article.
-
The CBD1 peptide corresponding to the caveolin-1 binding domain of HIV-1 glycoprotein gp41 elicits neutralizing antibodies in cynomolgus macaques when administered with the tetanus T helper epitope.Mol Immunol. 2009 Feb;46(4):705-12. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2008.10.001. Epub 2008 Nov 17. Mol Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19010547
-
Protection of neonatal macaques against experimental SHIV infection by human neutralizing monoclonal antibodies.Transfus Clin Biol. 2001 Aug;8(4):350-8. doi: 10.1016/s1246-7820(01)00187-2. Transfus Clin Biol. 2001. PMID: 11642027 Review.
-
Understanding the basis of CD4(+) T-cell depletion in macaques infected by a simian-human immunodeficiency virus.Vaccine. 2002 May 6;20(15):1934-7. doi: 10.1016/s0264-410x(02)00072-5. Vaccine. 2002. PMID: 11983249 Review.
Cited by
-
New GMP manufacturing processes to obtain thermostable HIV-1 gp41 virosomes under solid forms for various mucosal vaccination routes.NPJ Vaccines. 2020 May 18;5(1):41. doi: 10.1038/s41541-020-0190-9. eCollection 2020. NPJ Vaccines. 2020. PMID: 32435515 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Estaquier JM, Idziorek T, De Bels F, Barré-Sinoussi F, Hurtrel B, Aubertin A-M, Venet A, Mehtali M, Muchmore E, Michel P. 1994. Programmed cell death and AIDS: significance of T-cell apoptosis in pathogenic and nonpathogenic primate lentiviral infections. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 91:9431–9435. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Silvestri G, Sodora DL, Koup RA, Paiardini M, O'Neil SP, McClure HM, Staprans SI, Feinberg MB. 2003. Nonpathogenic SIV infection of sooty mangabeys is characterized by limited bystander immunopathology despite chronic high-level viremia. Immunity 18:441–452. doi:10.1016/S1074-7613(03)00060-8. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

