Inhibition of Parp1 by BMN673 Effectively Sensitizes Cells to Radiotherapy by Upsetting the Balance of Repair Pathways Processing DNA Double-Strand Breaks
- PMID: 29970481
- PMCID: PMC8195440
- DOI: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-17-0836
Inhibition of Parp1 by BMN673 Effectively Sensitizes Cells to Radiotherapy by Upsetting the Balance of Repair Pathways Processing DNA Double-Strand Breaks
Abstract
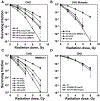
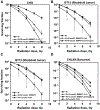
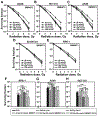
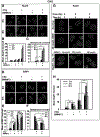
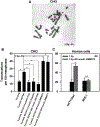
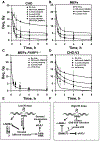
Parp inhibitors (Parpi) are commonly used as single agents for the management of tumors with homologous recombination repair (HRR) deficiencies, but combination with radiotherapy (RT) is not widely considered due to the modest radiosensitization typically observed. BMN673 is one of the most recently developed Parpi and has been shown to mediate strong cell sensitization to methylating agents. Here, we explore the mechanisms of BMN673 radiosensitization to killing, aiming to combine it with RT. We demonstrate markedly stronger radiosensitization by BMN673 at concentrations substantially lower (50 nmol/L) than olaparib (3 μmol/L) or AG14361 (0.4 μmol/L) and dramatically lower as compared with second-generation inhibitors such as PJ34 (5 μmol/L). Notably, BMN673 radiosensitization peaks after surprisingly short contact times (∼1 hour) and at pharmacologically achievable concentrations in vivo BMN673 exerts a complex set of effects on DNA double-strand break (DSB) processing, including inhibition of classic nonhomologous end-joining (cNHEJ) and alternative end-joining (altEJ) pathway at high doses of ionizing radiation (IR). BMN673 enhances resection at DSB and favors HRR and altEJ at low clinically relevant IR doses. The combined outcome of these effects is an abrogation in the inherent balance of DSB processing culminating in the formation of chromosomal translocations that underpin radiosensitization. Our observations pave the way to clinical trials exploring inherent benefits in combining BMN673 with RT for the treatment of various forms of cancer. Mol Cancer Ther; 17(10); 2206-16. ©2018 AACR.
©2018 American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure of Potential Conflicts of Interest
No potential conflicts of interest were disclosed.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Talazoparib enhances resection at DSBs and renders HR-proficient cancer cells susceptible to Polθ inhibition.Radiother Oncol. 2024 Nov;200:110475. doi: 10.1016/j.radonc.2024.110475. Epub 2024 Aug 13. Radiother Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39147034
-
Poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase inhibitors sensitize cancer cells to hypofractionated radiotherapy through altered selection of DNA double-strand break repair pathways.Int J Radiat Biol. 2022;98(7):1222-1234. doi: 10.1080/09553002.2022.2020357. Epub 2022 Jan 4. Int J Radiat Biol. 2022. PMID: 34919022
-
Selective radiosensitization of p53 mutant pancreatic cancer cells by combined inhibition of Chk1 and PARP1.Cell Cycle. 2011 Dec 15;10(24):4321-9. doi: 10.4161/cc.10.24.18661. Epub 2011 Dec 15. Cell Cycle. 2011. PMID: 22134241 Free PMC article.
-
BMN673 Is a PARP Inhibitor with Unique Radiosensitizing Properties: Mechanisms and Potential in Radiation Therapy.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Nov 16;14(22):5619. doi: 10.3390/cancers14225619. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36428712 Free PMC article. Review.
-
DNA double strand break repair inhibition as a cause of heat radiosensitization: re-evaluation considering backup pathways of NHEJ.Int J Hyperthermia. 2008 Feb;24(1):17-29. doi: 10.1080/02656730701784782. Int J Hyperthermia. 2008. PMID: 18214766 Review.
Cited by
-
PTEN Loss Enhances Error-Prone DSB Processing and Tumor Cell Radiosensitivity by Suppressing RAD51 Expression and Homologous Recombination.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Oct 25;23(21):12876. doi: 10.3390/ijms232112876. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36361678 Free PMC article.
-
Peptide receptor radionuclide therapy combinations for neuroendocrine tumours in ongoing clinical trials: status 2023.Theranostics. 2024 Jan 1;14(3):940-953. doi: 10.7150/thno.91268. eCollection 2024. Theranostics. 2024. PMID: 38250038 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 antagonizes DNA resection at double-strand breaks.Nat Commun. 2019 Jul 4;10(1):2954. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-10741-9. Nat Commun. 2019. PMID: 31273204 Free PMC article.
-
Radiotherapy as a tool to elicit clinically actionable signalling pathways in cancer.Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2022 Feb;19(2):114-131. doi: 10.1038/s41571-021-00579-w. Epub 2021 Nov 24. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2022. PMID: 34819622 Free PMC article. Review.
-
G2/M Checkpoint Abrogation With Selective Inhibitors Results in Increased Chromatid Breaks and Radiosensitization of 82-6 hTERT and RPE Human Cells.Front Public Health. 2021 May 28;9:675095. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2021.675095. eCollection 2021. Front Public Health. 2021. PMID: 34123995 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Farmer H, McCabe N, Lord CJ, Tutt AN, Johnson DA, Richardson TB, et al. Targeting the DNA repair defect in BRCA mutant cells as a therapeutic strategy. Nature 2005;434:917–21. - PubMed
-
- Bryant HE, Schultz N, Thomas HD, Parker KM, Flower D, Lopez E, et al. Specific killing of BRCA2-deficient tumours with inhibitors of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase. Nature 2005;434:913–7. - PubMed
-
- Fong PC, Boss DS, Yap TA, Tutt A, Wu P, Mergui-Roelvink M, et al. Inhibition of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase in tumors from BRCA mutation carriers. N Engl J Med 2009;361:123–34. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

