Enterolactone modulates the ERK/NF-κB/Snail signaling pathway in triple-negative breast cancer cell line MDA-MB-231 to revert the TGF-β-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition
- PMID: 29951338
- PMCID: PMC5994556
- DOI: 10.20892/j.issn.2095-3941.2018.0012
Enterolactone modulates the ERK/NF-κB/Snail signaling pathway in triple-negative breast cancer cell line MDA-MB-231 to revert the TGF-β-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition
Abstract
Objective: Triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) is highly metastatic, and there is an urgent unmet need to develop novel therapeutic strategies leading to the new drug discoveries against metastasis. The transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β) is known to promote the invasive and migratory potential of breast cancer cells through induction of epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) via the ERK/NF-κB/Snail signaling pathway, leading to breast cancer metastasis. Targeting this pathway to revert the EMT would be an attractive, novel therapeutic strategy to halt breast cancer metastasis.
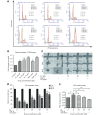
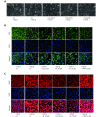
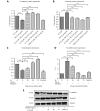
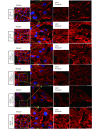
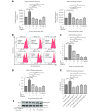
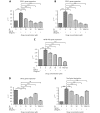
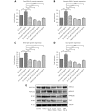
Methods: Effects of enterolactone (EL) on the cell cycle and apoptosis were investigated using flow cytometry and a cleaved caspase-3 enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), respectively. Effects of TGF-β induction and EL treatment on the functional malignancy of MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells were investigated using migration and chemo-invasion assays. The effects of EL on EMT markers and the ERK/NF-κB/Snail signaling pathway after TGF-β induction were studied using confocal microscopy, quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR), Western blot, and flow cytometry.
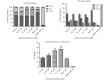
Results: Herein, we report that EL exhibits a significant antimetastatic effect on MDA-MB-231 cells by almost reverting the TGF-β-induced EMT in vitro. EL downregulates the mesenchymal markers N-cadherin and vimentin, and upregulates the epithelial markers E-cadherin and occludin. It represses actin stress fiber formation via inhibition of mitogen-activated protein kinase p-38 (MAPK-p38) and cluster of differentiation 44 (CD44). EL also suppresses ERK-1/2, NF-κB, and Snail at the mRNA and protein levels.
Conclusions: Briefly, EL was found to inhibit TGF-β-induced EMT by blocking the ERK/NF-κB/Snail signaling pathway, which is a promising target for breast cancer metastasis therapy.
Keywords: EMT; Enterolactone; breast cancer metastasis; invasion; migration.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Disulfiram inhibits TGF-β-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition and stem-like features in breast cancer via ERK/NF-κB/Snail pathway.Oncotarget. 2015 Dec 1;6(38):40907-19. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.5723. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 26517513 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of NF-κB by TOPK upregulates Snail/Slug expression in TGF-β1 signaling to induce epithelial-mesenchymal transition and invasion of breast cancer cells.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2020 Sep 10;530(1):122-129. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.07.015. Epub 2020 Jul 30. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2020. PMID: 32828273
-
Osthole inhibited TGF β-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) by suppressing NF-κB mediated Snail activation in lung cancer A549 cells.Cell Adh Migr. 2017 Sep 3;11(5-6):464-475. doi: 10.1080/19336918.2016.1259058. Epub 2017 Feb 2. Cell Adh Migr. 2017. PMID: 28146373 Free PMC article.
-
The novel role of Yin Yang 1 in the regulation of epithelial to mesenchymal transition in cancer via the dysregulated NF-κB/Snail/YY1/RKIP/PTEN Circuitry.Crit Rev Oncog. 2011;16(3-4):211-26. doi: 10.1615/critrevoncog.v16.i3-4.50. Crit Rev Oncog. 2011. PMID: 22248055 Review.
-
Targeted therapy approaches for epithelial-mesenchymal transition in triple negative breast cancer.Front Oncol. 2024 Oct 10;14:1431418. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1431418. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39450256 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
DCST1-AS1 Promotes TGF-β-Induced Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition and Enhances Chemoresistance in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cells via ANXA1.Front Oncol. 2020 Mar 12;10:280. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.00280. eCollection 2020. Front Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32226772 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Astaxanthin on the Proliferation and Migration of Breast Cancer Cells In Vitro.Antioxidants (Basel). 2018 Oct 4;7(10):135. doi: 10.3390/antiox7100135. Antioxidants (Basel). 2018. PMID: 30287735 Free PMC article.
-
LncRNA n339260 functions in hepatocellular carcinoma progression via regulation of miRNA30e-5p/TP53INP1 expression.J Gastroenterol. 2022 Oct;57(10):784-797. doi: 10.1007/s00535-022-01901-8. Epub 2022 Jul 8. J Gastroenterol. 2022. PMID: 35802258
-
Anticancer and antimetastatic potential of enterolactone: Clinical, preclinical and mechanistic perspectives.Eur J Pharmacol. 2019 Jun 5;852:107-124. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2019.02.022. Epub 2019 Feb 14. Eur J Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 30771348 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extracellular-Signal Regulated Kinase: A Central Molecule Driving Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition in Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Jun 13;20(12):2885. doi: 10.3390/ijms20122885. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31200510 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J, Lortet-Tieulent J, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 2015;65:87–108. - PubMed
-
- Hegde MV, Mali AV, Chandorkar SS. What is a cancer cell? Why does it metastasize? Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2013;14:3987–9. - PubMed
-
- Padua D, Massagué J. Roles of TGFβ in metastasis. Cell Res. 2009;19:89–102. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
