Human Cytomegalovirus Immediate Early 1 Protein Causes Loss of SOX2 from Neural Progenitor Cells by Trapping Unphosphorylated STAT3 in the Nucleus
- PMID: 29950413
- PMCID: PMC6096794
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.00340-18
Human Cytomegalovirus Immediate Early 1 Protein Causes Loss of SOX2 from Neural Progenitor Cells by Trapping Unphosphorylated STAT3 in the Nucleus
Abstract
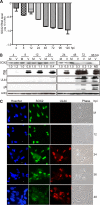
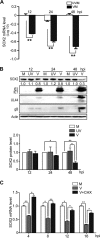
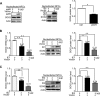
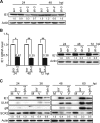
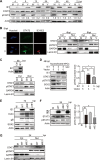
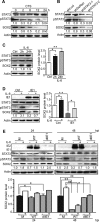
The mechanisms underlying neurodevelopmental damage caused by virus infections remain poorly defined. Congenital human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) infection is the leading cause of fetal brain development disorders. Previous work has linked HCMV infection to perturbations of neural cell fate, including premature differentiation of neural progenitor cells (NPCs). Here, we show that HCMV infection of NPCs results in loss of the SOX2 protein, a key pluripotency-associated transcription factor. SOX2 depletion maps to the HCMV major immediate early (IE) transcription unit and is individually mediated by the IE1 and IE2 proteins. IE1 causes SOX2 downregulation by promoting the nuclear accumulation and inhibiting the phosphorylation of STAT3, a transcriptional activator of SOX2 expression. Deranged signaling resulting in depletion of a critical stem cell protein is an unanticipated mechanism by which the viral major IE proteins may contribute to brain development disorders caused by congenital HCMV infection.IMPORTANCE Human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) infections are a leading cause of brain damage, hearing loss, and other neurological disabilities in children. We report that the HCMV proteins known as IE1 and IE2 target expression of human SOX2, a central pluripotency-associated transcription factor that governs neural progenitor cell (NPC) fate and is required for normal brain development. Both during HCMV infection and when expressed alone, IE1 causes the loss of SOX2 from NPCs. IE1 mediates SOX2 depletion by targeting STAT3, a critical upstream regulator of SOX2 expression. Our findings reveal an unanticipated mechanism by which a common virus may cause damage to the developing nervous system and suggest novel targets for medical intervention.
Keywords: HCMV; IE1; SOX2; STAT3; neural progenitor cells.
Copyright © 2018 American Society for Microbiology.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Human cytomegalovirus IE1 downregulates Hes1 in neural progenitor cells as a potential E3 ubiquitin ligase.PLoS Pathog. 2017 Jul 27;13(7):e1006542. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1006542. eCollection 2017 Jul. PLoS Pathog. 2017. PMID: 28750047 Free PMC article.
-
Human Cytomegalovirus Infection Dysregulates the Localization and Stability of NICD1 and Jag1 in Neural Progenitor Cells.J Virol. 2015 Jul;89(13):6792-804. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00351-15. Epub 2015 Apr 22. J Virol. 2015. PMID: 25903338 Free PMC article.
-
Human Cytomegalovirus IE2 Protein Disturbs Brain Development by the Dysregulation of Neural Stem Cell Maintenance and the Polarization of Migrating Neurons.J Virol. 2017 Aug 10;91(17):e00799-17. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00799-17. Print 2017 Sep 1. J Virol. 2017. PMID: 28615204 Free PMC article.
-
Bright and Early: Inhibiting Human Cytomegalovirus by Targeting Major Immediate-Early Gene Expression or Protein Function.Viruses. 2020 Jan 16;12(1):110. doi: 10.3390/v12010110. Viruses. 2020. PMID: 31963209 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Human Cytomegalovirus Infection and Neurocognitive and Neuropsychiatric Health.Pathogens. 2024 May 16;13(5):417. doi: 10.3390/pathogens13050417. Pathogens. 2024. PMID: 38787269 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A congenital CMV infection model for follow-up studies of neurodevelopmental disorders, neuroimaging abnormalities, and treatment.JCI Insight. 2022 Jan 11;7(1):e152551. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.152551. JCI Insight. 2022. PMID: 35014624 Free PMC article.
-
Human Cytomegalovirus Disruption of Calcium Signaling in Neural Progenitor Cells and Organoids.J Virol. 2019 Aug 13;93(17):e00954-19. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00954-19. Print 2019 Sep 1. J Virol. 2019. PMID: 31217241 Free PMC article.
-
Hearing Loss Caused by HCMV Infection through Regulating the Wnt and Notch Signaling Pathways.Viruses. 2021 Apr 6;13(4):623. doi: 10.3390/v13040623. Viruses. 2021. PMID: 33917368 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Human cytomegalovirus infection impairs neural differentiation via repressing sterol regulatory element binding protein 2-mediated cholesterol biosynthesis.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2024 Jul 6;81(1):289. doi: 10.1007/s00018-024-05278-0. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2024. PMID: 38970696 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of the STAT3 Signaling Pathway by the RNA-Dependent RNA Polymerase Protein of Arenavirus.Viruses. 2021 May 25;13(6):976. doi: 10.3390/v13060976. Viruses. 2021. PMID: 34070281 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Stagno S, Pass RF, Cloud G, Britt WJ, Henderson RE, Walton PD, Veren DA, Page F, Alford CA. 1986. Primary cytomegalovirus infection in pregnancy. Incidence, transmission to fetus, and clinical outcome. JAMA 256:1904–1908. - PubMed
-
- Conboy TJ, Pass RF, Stagno S, Britt WJ, Alford CA, McFarland CE, Boll TJ. 1986. Intellectual development in school-aged children with asymptomatic congenital cytomegalovirus infection. Pediatrics 77:801–806. - PubMed
-
- Pass RF, Stagno S, Myers GJ, Alford CA. 1980. Outcome of symptomatic congenital cytomegalovirus infection: results of long-term longitudinal follow-up. Pediatrics 66:758–762. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

