COPII-dependent ER export in animal cells: adaptation and control for diverse cargo
- PMID: 29916038
- PMCID: PMC6096569
- DOI: 10.1007/s00418-018-1689-2
COPII-dependent ER export in animal cells: adaptation and control for diverse cargo
Abstract
The export of newly synthesized proteins from the endoplasmic reticulum is fundamental to the ongoing maintenance of cell and tissue structure and function. After co-translational translocation into the ER, proteins destined for downstream intracellular compartments or secretion from the cell are sorted and packaged into transport vesicles by the COPII coat protein complex. The fundamental discovery and characterization of the pathway has now been augmented by a greater understanding of the role of COPII in diverse aspects of cell function. We now have a deep understanding of how COPII contributes to the trafficking of diverse cargoes including extracellular matrix molecules, developmental signalling proteins, and key metabolic factors such as lipoproteins. Structural and functional studies have shown that the COPII coat is both highly flexible and subject to multiple modes of regulation. This has led to new discoveries defining roles of COPII in development, autophagy, and tissue organization. Many of these newly emerging features of the canonical COPII pathway are placed in a context of procollagen secretion because of the fundamental interest in how a coat complex that typically generates 80-nm transport vesicles can package a cargo reported to be over 300 nm. Here we review the current understanding of COPII and assess the current consensus on its role in packaging diverse cargo proteins.
Keywords: COPII; Endoplasmic reticulum; Golgi, procollagen; Vesicle.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
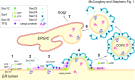

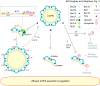
Similar articles
-
Vesicle-mediated export from the ER: COPII coat function and regulation.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013 Nov;1833(11):2464-72. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2013.02.003. Epub 2013 Feb 15. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013. PMID: 23419775 Free PMC article. Review.
-
COPII - a flexible vesicle formation system.Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2013 Aug;25(4):420-7. doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2013.04.005. Epub 2013 May 20. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 23702145 Free PMC article.
-
COPII coat assembly and selective export from the endoplasmic reticulum.J Biochem. 2004 Dec;136(6):755-60. doi: 10.1093/jb/mvh184. J Biochem. 2004. PMID: 15671485 Review.
-
COPII-coated vesicles: flexible enough for large cargo?Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2005 Aug;17(4):345-52. doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2005.06.004. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2005. PMID: 15975775 Review.
-
COPII collar defines the boundary between ER and ER exit site and does not coat cargo containers.J Cell Biol. 2021 Jun 7;220(6):e201907224. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201907224. J Cell Biol. 2021. PMID: 33852719 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Tango1 coordinates the formation of endoplasmic reticulum/Golgi docking sites to mediate secretory granule formation.J Biol Chem. 2019 Dec 20;294(51):19498-19510. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA119.011063. Epub 2019 Nov 5. J Biol Chem. 2019. PMID: 31690624 Free PMC article.
-
TRK-Fused Gene (TFG), a protein involved in protein secretion pathways, is an essential component of the antiviral innate immune response.PLoS Pathog. 2021 Jan 7;17(1):e1009111. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1009111. eCollection 2021 Jan. PLoS Pathog. 2021. PMID: 33411856 Free PMC article.
-
Splicing variation of BMP2K balances abundance of COPII assemblies and autophagic degradation in erythroid cells.Elife. 2020 Aug 14;9:e58504. doi: 10.7554/eLife.58504. Elife. 2020. PMID: 32795391 Free PMC article.
-
COPII cage assembly factor Sec13 integrates information flow regulating endomembrane function in response to human variation.Sci Rep. 2024 May 3;14(1):10160. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-60687-2. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38698045 Free PMC article.
-
Cargo receptor Surf4 regulates endoplasmic reticulum export of proinsulin in pancreatic β-cells.Commun Biol. 2022 May 13;5(1):458. doi: 10.1038/s42003-022-03417-6. Commun Biol. 2022. PMID: 35562580 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Amodio G, Venditti R, De Matteis MA, Moltedo O, Pignataro P, Remondelli P. Endoplasmic reticulum stress reduces COPII vesicle formation and modifies Sec23a cycling at ERESs. FEBS Lett. 2013;587:3261–3266. - PubMed
-
- Antonny B, Madden D, Hamamoto S, Orci L, Schekman R. Dynamics of the COPII coat with GTP and stable analogues. Nat Cell Biol. 2001;3:531–537. - PubMed
-
- Appenzeller-Herzog C, Hauri HP. The ER–Golgi intermediate compartment (ERGIC): in search of its identity and function. J Cell Sci. 2006;119:2173–2183. - PubMed
-
- Arimitsu N, et al. p125/Sec23-interacting protein (Sec23ip) is required for spermiogenesis. FEBS Lett. 2011;585:2171–2176. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

