Intercellular communications-redox interactions in radiation toxicity; potential targets for radiation mitigation
- PMID: 29911259
- PMCID: PMC6381372
- DOI: 10.1007/s12079-018-0473-3
Intercellular communications-redox interactions in radiation toxicity; potential targets for radiation mitigation
Abstract
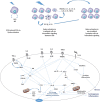
Nowadays, using ionizing radiation (IR) is necessary for clinical, agricultural, nuclear energy or industrial applications. Accidental exposure to IR after a radiation terror or disaster poses a threat to human. In contrast to the old dogma of radiation toxicity, several experiments during the last two recent decades have revealed that intercellular signaling and communications play a key role in this procedure. Elevated level of cytokines and other intercellular signals increase oxidative damage and inflammatory responses via reduction/oxidation interactions (redox system). Intercellular signals induce production of free radicals and inflammatory mediators by some intermediate enzymes such as cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2), nitric oxide synthase (NOS), NADPH oxidase, and also via triggering mitochondrial ROS. Furthermore, these signals facilitate cell to cell contact and increasing cell toxicity via cohort effect. Nitric oxide is a free radical with ability to act as an intercellular signal that induce DNA damage and changes in some signaling pathways in irradiated as well as non-irradiated adjacent cells. Targeting of these mediators by some anti-inflammatory agents or via antioxidants such as mitochondrial ROS scavengers opens a window to mitigate radiation toxicity after an accidental exposure. Experiments which have been done so far suggests that some cytokines such as IL-1β, TNF-α, TGF-β, IL-4 and IL-13 are some interesting targets that depend on irradiated organs and may help mitigate radiation toxicity. Moreover, animal experiments in recent years indicated that targeting of toll like receptors (TLRs) may be more useful for radioprotection and mitigation. In this review, we aimed to describe the role of intercellular interactions in oxidative injury, inflammation, cell death and killing effects of IR. Moreover, we described evidence on potential mitigation of radiation injury via targeting of these mediators.
Keywords: Bystander effect; Carcinogenesis; Cohort effect; Cytokines; Intracellular communication; Mitigation; Non-targeted effect; Radiation; Radiation disaster; Radiation toxicity; Radiotherapy; Redox system.
Conflict of interest statement
No
Figures
Similar articles
-
Targeting of cellular redox metabolism for mitigation of radiation injury.Life Sci. 2020 Jun 1;250:117570. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2020.117570. Epub 2020 Mar 20. Life Sci. 2020. PMID: 32205088 Review.
-
Reduction-oxidation (redox) system in radiation-induced normal tissue injury: molecular mechanisms and implications in radiation therapeutics.Clin Transl Oncol. 2018 Aug;20(8):975-988. doi: 10.1007/s12094-017-1828-6. Epub 2018 Jan 9. Clin Transl Oncol. 2018. PMID: 29318449 Review.
-
NADPH Oxidase as a Target for Modulation of Radiation Response; Implications to Carcinogenesis and Radiotherapy.Curr Mol Pharmacol. 2019;12(1):50-60. doi: 10.2174/1874467211666181010154709. Curr Mol Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 30318012 Review.
-
Targeting of Inflammation for Radiation Protection and Mitigation.Curr Mol Pharmacol. 2018;11(3):203-210. doi: 10.2174/1874467210666171108165641. Curr Mol Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29119941 Review.
-
Quercetin-3-Rutinoside alleviates radiation-induced lung inflammation and fibrosis via regulation of NF-κB/TGF-β1 signaling.Phytomedicine. 2022 May;99:154004. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2022.154004. Epub 2022 Feb 18. Phytomedicine. 2022. PMID: 35219007
Cited by
-
Adipose-derived stem cells repair radiation-induced chronic lung injury via inhibiting TGF-β1/Smad 3 signaling pathway.Open Med (Wars). 2023 Nov 9;18(1):20230850. doi: 10.1515/med-2023-0850. eCollection 2023. Open Med (Wars). 2023. PMID: 38025537 Free PMC article.
-
Targets for protection and mitigation of radiation injury.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2020 Aug;77(16):3129-3159. doi: 10.1007/s00018-020-03479-x. Epub 2020 Feb 18. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2020. PMID: 32072238 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The protective role of short-chain fatty acids acting as signal molecules in chemotherapy- or radiation-induced intestinal inflammation.Am J Cancer Res. 2020 Nov 1;10(11):3508-3531. eCollection 2020. Am J Cancer Res. 2020. PMID: 33294252 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lung Pneumonitis and Fibrosis in Cancer Therapy: A Review on Cellular and Molecular Mechanisms.Curr Drug Targets. 2022;23(16):1505-1525. doi: 10.2174/1389450123666220907144131. Curr Drug Targets. 2022. PMID: 36082868 Review.
-
Mitochondrial Translocator Protein (TSPO) Expression in the Brain After Whole Body Gamma Irradiation.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Oct 25;9:715444. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.715444. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34760884 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ameziane-El-Hassani R, Talbot M, de Souza Dos Santos MC, Al Ghuzlan A, Hartl D, Bidart J-M, De Deken X, Miot F, Diallo I, De Vathaire F, Schlumberger M, Dupuy C. NADPH oxidase DUOX1 promotes long-term persistence of oxidative stress after an exposure to irradiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015;112:5051–5056. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Anscher MS, Thrasher B, Rabbani Z, Teicher B, Vujaskovic Z. Antitransforming growth factor-beta antibody 1D11 ameliorates normal tissue damage caused by high-dose radiation. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2006;65:876–881. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

