Characterization of a non-nudix pyrophosphatase points to interplay between flavin and NAD(H) homeostasis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae
- PMID: 29902190
- PMCID: PMC6002036
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0198787
Characterization of a non-nudix pyrophosphatase points to interplay between flavin and NAD(H) homeostasis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae
Abstract
The flavin cofactors FMN and FAD are required for a wide variety of biological processes, however, little is known about their metabolism. Here, we report the cloning and biochemical characterization of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae pyrophosphatase Fpy1p. Genetic and functional studies suggest that Fpy1p may play a key role in flavin metabolism and is the first-reported non-Nudix superfamily enzyme to display FAD pyrophosphatase activity. Characterization of mutant yeast strains found that deletion of fpy1 counteracts the adverse effects that are caused by deletion of flx1, a known mitochondrial FAD transporter. We show that Fpy1p is capable of hydrolyzing FAD, NAD(H), and ADP-ribose. The enzymatic activity of Fpy1p is dependent upon the presence of K+ and divalent metal cations, with similar kinetic parameters to those that have been reported for Nudix FAD pyrophosphatases. In addition, we report that the deletion of fpy1 intensifies the FMN-dependence of null mutants of the riboflavin kinase Fmn1p, demonstrate that fpy1 mutation abolishes the decreased fitness resulting from the deletion of the flx1 ORF, and offer a possible mechanism for the genetic interplay between fpy1, flx1 and fmn1.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

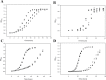
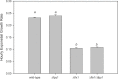
Similar articles
-
Evidence for the presence of a FAD pyrophosphatase and a FMN phosphohydrolase in yeast mitochondria: a possible role in flavin homeostasis.Yeast. 2011 Oct;28(10):693-705. doi: 10.1002/yea.1897. Epub 2011 Sep 13. Yeast. 2011. PMID: 21915900
-
A regulatory role of NAD redox status on flavin cofactor homeostasis in S. cerevisiae mitochondria.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2013;2013:612784. doi: 10.1155/2013/612784. Epub 2013 Sep 1. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2013. PMID: 24078860 Free PMC article.
-
FLX1 codes for a carrier protein involved in maintaining a proper balance of flavin nucleotides in yeast mitochondria.J Biol Chem. 1996 Mar 29;271(13):7392-7. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.13.7392. J Biol Chem. 1996. PMID: 8631763
-
Role of NUDIX Hydrolases in NAD and ADP-Ribose Metabolism in Mammals.Biochemistry (Mosc). 2020 Aug;85(8):883-894. doi: 10.1134/S0006297920080040. Biochemistry (Mosc). 2020. PMID: 33045949 Review.
-
Mitochondrial NUDIX hydrolases: A metabolic link between NAD catabolism, GTP and mitochondrial dynamics.Neurochem Int. 2017 Oct;109:193-201. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2017.03.009. Epub 2017 Mar 14. Neurochem Int. 2017. PMID: 28302504 Review.
Cited by
-
Development of Novel Experimental Models to Study Flavoproteome Alterations in Human Neuromuscular Diseases: The Effect of Rf Therapy.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jul 26;21(15):5310. doi: 10.3390/ijms21155310. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32722651 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Alteration of Flavin Cofactor Homeostasis in Human Neuromuscular Pathologies.Methods Mol Biol. 2021;2280:275-295. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-1286-6_18. Methods Mol Biol. 2021. PMID: 33751442 Review.
-
Mechanism of enhanced salt tolerance in Saccharomyces cerevisiae by CRZ1 overexpression.Sci Rep. 2024 Oct 2;14(1):22875. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-74174-1. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39358483 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Massey V (1995) Flavoprotein Structure and Mechanism Bethesda, MD, ETATS-UNIS: Federation of American Societies for Experimental Biology. 3 p. - PubMed
-
- Fraaije MW, Mattevi A (2000) Flavoenzymes: diverse catalysts with recurrent features. Trends in Biochemical Sciences 25: 126–132. - PubMed
-
- De Colibus L, Mattevi A (2006) New frontiers in structural flavoenzymology. Curr Opin Struct Biol 16: 722–728. doi: 10.1016/j.sbi.2006.10.003 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Roje S (2007) Vitamin B biosynthesis in plants. Phytochemistry 68: 1904–1921. doi: 10.1016/j.phytochem.2007.03.038 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

