SMCHD1 Merges Chromosome Compartments and Assists Formation of Super-Structures on the Inactive X
- PMID: 29887375
- PMCID: PMC6475921
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2018.05.007
SMCHD1 Merges Chromosome Compartments and Assists Formation of Super-Structures on the Inactive X
Abstract
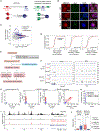
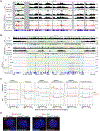
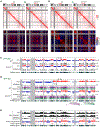
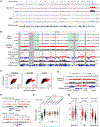
Mammalian chromosomes are partitioned into A/B compartments and topologically associated domains (TADs). The inactive X (Xi) chromosome, however, adopts a distinct conformation without evident compartments or TADs. Here, through exploration of an architectural protein, structural-maintenance-of-chromosomes hinge domain containing 1 (SMCHD1), we probe how the Xi is reconfigured during X chromosome inactivation. A/B compartments are first fused into "S1" and "S2" compartments, coinciding with Xist spreading into gene-rich domains. SMCHD1 then binds S1/S2 compartments and merges them to create a compartment-less architecture. Contrary to current views, TADs remain on the Xi but in an attenuated state. Ablating SMCHD1 results in a persistent S1/S2 organization and strengthening of TADs. Furthermore, loss of SMCHD1 causes regional defects in Xist spreading and erosion of heterochromatic silencing. We present a stepwise model for Xi folding, where SMCHD1 attenuates a hidden layer of Xi architecture to facilitate Xist spreading.
Keywords: Polycomb complexes; SMCHD1; TADs; X chromosome inactivation; Xist RNA; chromosome conformation; compartments; long noncoding RNAs; nuclear organization; topologically associating domains.
Copyright © 2018. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
PRC1 collaborates with SMCHD1 to fold the X-chromosome and spread Xist RNA between chromosome compartments.Nat Commun. 2019 Jul 3;10(1):2950. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-10755-3. Nat Commun. 2019. PMID: 31270318 Free PMC article.
-
Structural organization of the inactive X chromosome in the mouse.Nature. 2016 Jul 28;535(7613):575-9. doi: 10.1038/nature18589. Epub 2016 Jul 18. Nature. 2016. PMID: 27437574 Free PMC article.
-
The non-canonical SMC protein SmcHD1 antagonises TAD formation and compartmentalisation on the inactive X chromosome.Nat Commun. 2019 Jan 3;10(1):30. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-07907-2. Nat Commun. 2019. PMID: 30604745 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamic interplay and function of multiple noncoding genes governing X chromosome inactivation.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016 Jan;1859(1):112-20. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2015.07.015. Epub 2015 Aug 7. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016. PMID: 26260844 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel players in X inactivation: insights into Xist-mediated gene silencing and chromosome conformation.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2017 Mar 3;24(3):197-204. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.3370. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2017. PMID: 28257137 Review.
Cited by
-
3D mapping and accelerated super-resolution imaging of the human genome using in situ sequencing.Nat Methods. 2020 Aug;17(8):822-832. doi: 10.1038/s41592-020-0890-0. Epub 2020 Jul 27. Nat Methods. 2020. PMID: 32719531 Free PMC article.
-
Role of the Chromosome Architectural Factor SMCHD1 in X-Chromosome Inactivation, Gene Regulation, and Disease in Humans.Genetics. 2019 Oct;213(2):685-703. doi: 10.1534/genetics.119.302600. Epub 2019 Aug 16. Genetics. 2019. PMID: 31420322 Free PMC article.
-
Extensive cellular heterogeneity of X inactivation revealed by single-cell allele-specific expression in human fibroblasts.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018 Dec 18;115(51):13015-13020. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1806811115. Epub 2018 Dec 3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018. PMID: 30510006 Free PMC article.
-
Xist-mediated silencing requires additive functions of SPEN and Polycomb together with differentiation-dependent recruitment of SmcHD1.Cell Rep. 2022 May 17;39(7):110830. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2022.110830. Cell Rep. 2022. PMID: 35584662 Free PMC article.
-
Early-life stress and ovarian hormones alter transcriptional regulation in the nucleus accumbens resulting in sex-specific responses to cocaine.Cell Rep. 2023 Oct 31;42(10):113187. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2023.113187. Epub 2023 Sep 29. Cell Rep. 2023. PMID: 37777968 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bickmore WA, and van Steensel B (2013). Genome architecture: domain organization of interphase chromosomes. Cell 152, 1270–1284. - PubMed
-
- Blewitt ME, Gendrel AV, Pang Z, Sparrow DB, Whitelaw N, Craig JM, Apedaile A, Hilton DJ, Dunwoodie SL, Brockdorff N, et al. (2008). SmcHD1, containing a structural-maintenance-of-chromosomes hinge domain, has a critical role in X inactivation. Nature genetics 40, 663–669. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

