Prophylactic and therapeutic efficacy of mAb treatment against MERS-CoV in common marmosets
- PMID: 29885377
- PMCID: PMC7113689
- DOI: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2018.06.006
Prophylactic and therapeutic efficacy of mAb treatment against MERS-CoV in common marmosets
Abstract
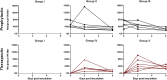
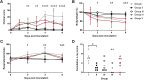
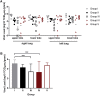
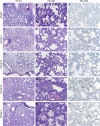
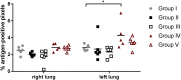
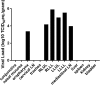
The high case-fatality rate of confirmed MERS-CoV infections underlines the urgent need for an effective treatment to reduce the disease severity and mortality. REGN3051 and REGN3048 are two fully human neutralizing monoclonal antibodies (mAb) against MERS-CoV that reduced virus replication in mice expressing human DPP4 upon prophylactic and therapeutic treatment. Here, we evaluated the prophylactic and therapeutic efficacy of REGN3048 and REGN3051 in the common marmoset model of MERS-CoV infection. Intravenous administration of mAb resulted in high levels of MERS-CoV-neutralizing activity in circulating blood. When animals were treated with mAbs one day before challenge, respiratory disease was less severe and, in animals treated with both REGN3048 and REGN3051, viral loads in the lungs were reduced. However, therapeutic treatment on day one after challenge was less efficacious as it did not prevent the development of severe respiratory disease and all treated animals developed bronchointerstitial pneumonia of similar severity as the control animals. Thus, mAb administration may be more effective in a prophylactic treatment regimen rather than treatment of MERS.
Keywords: Animal model; Common marmoset; MERS-CoV; Monoclonal antibody treatment; Neutralizing antibody.
Copyright © 2018 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Neutralizing Monoclonal Antibodies as Promising Therapeutics against Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus Infection.Viruses. 2018 Nov 30;10(12):680. doi: 10.3390/v10120680. Viruses. 2018. PMID: 30513619 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prophylactic efficacy of a human monoclonal antibody against MERS-CoV in the common marmoset.Antiviral Res. 2019 Mar;163:70-74. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2019.01.016. Epub 2019 Jan 24. Antiviral Res. 2019. PMID: 30684561 Free PMC article.
-
Human Neutralizing Monoclonal Antibody Inhibition of Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus Replication in the Common Marmoset.J Infect Dis. 2017 Jun 15;215(12):1807-1815. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jix209. J Infect Dis. 2017. PMID: 28472421 Free PMC article.
-
Treatment With Lopinavir/Ritonavir or Interferon-β1b Improves Outcome of MERS-CoV Infection in a Nonhuman Primate Model of Common Marmoset.J Infect Dis. 2015 Dec 15;212(12):1904-13. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiv392. Epub 2015 Jul 21. J Infect Dis. 2015. PMID: 26198719 Free PMC article.
-
Development of human neutralizing monoclonal antibodies for prevention and therapy of MERS-CoV infections.Microbes Infect. 2015 Feb;17(2):142-8. doi: 10.1016/j.micinf.2014.11.008. Epub 2014 Nov 29. Microbes Infect. 2015. PMID: 25456101 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Passive Immunity Should and Will Work for COVID-19 for Some Patients.Clin Hematol Int. 2021 Apr 16;3(2):47-68. doi: 10.2991/chi.k.210328.001. eCollection 2021 Jun. Clin Hematol Int. 2021. PMID: 34595467 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Marmosets as models of infectious diseases.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024 Feb 23;14:1340017. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2024.1340017. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38465237 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neutralizing Monoclonal Antibodies as Promising Therapeutics against Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus Infection.Viruses. 2018 Nov 30;10(12):680. doi: 10.3390/v10120680. Viruses. 2018. PMID: 30513619 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular Characteristics, Functions, and Related Pathogenicity of MERS-CoV Proteins.Engineering (Beijing). 2019 Oct;5(5):940-947. doi: 10.1016/j.eng.2018.11.035. Epub 2019 Jul 17. Engineering (Beijing). 2019. PMID: 32288963 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prevention and treatment of COVID-19 disease by controlled modulation of innate immunity.Eur J Immunol. 2020 Jul;50(7):932-938. doi: 10.1002/eji.202048693. Epub 2020 Jun 15. Eur J Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32438473 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Agrawal A.S., Ying T., Tao X., Garron T., Algaissi A., Wang Y., Wang L., Peng B.H., Jiang S., Dimitrov D.S., Tseng C.T. Passive Transfer of A Germline-like neutralizing human monoclonal antibody protects transgenic mice against lethal Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus infection. Sci. Rep. 2016;6:31629. - PMC - PubMed
-
- American Academy of Pediatrics Committee on Infectious, D, American Academy of Pediatrics Bronchiolitis Guidelines, C Updated guidance for palivizumab prophylaxis among infants and young children at increased risk of hospitalization for respiratory syncytial virus infection. Pediatrics. 2014;134:415–420. - PubMed
-
- Arabi Y.M., Hajeer A.H., Luke T., Raviprakash K., Balkhy H., Johani S., Al-Dawood A., Al-Qahtani S., Al-Omari A., Al-Hameed F., Hayden F.G., Fowler R., Bouchama A., Shindo N., Al-Khairy K., Carson G., Taha Y., Sadat M., Alahmadi M. Feasibility of using convalescent plasma immunotherapy for MERS-CoV infection, Saudi Arabia. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2016;22:1554–1561. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chan J.F., Yao Y., Yeung M.L., Deng W., Bao L., Jia L., Li F., Xiao C., Gao H., Yu P., Cai J.P., Chu H., Zhou J., Chen H., Qin C., Yuen K.Y. Treatment with lopinavir/ritonavir or interferon-beta1b improves outcome of MERS-CoV infection in a nonhuman primate model of common marmoset. J. infect. dis. 2015;212:1904–1913. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

