Leptin, cardiovascular diseases and type 2 diabetes mellitus
- PMID: 29877321
- PMCID: PMC6289384
- DOI: 10.1038/aps.2018.40
Leptin, cardiovascular diseases and type 2 diabetes mellitus
Abstract
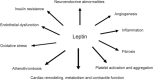
Leptin, an adipokine that is implicated in the control of food intake via appetite suppression, may also stimulate oxidative stress, inflammation, thrombosis, arterial stiffness, angiogenesis and atherogenesis. These leptin-induced effects may predispose to the development of cardiovascular diseases. In the present review we discuss the evidence linking leptin levels with the presence, severity and/or prognosis of both coronary artery disease and non-cardiac vascular diseases such as stroke, carotid artery disease, peripheral artery disease (PAD) and abdominal aortic aneurysms (AAA) as well as with chronic kidney disease (CKD) and type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). Leptin levels have been positively associated with the presence, severity, extent and lesion complexity of coronary atherosclerosis as well as with the presence, severity and poor clinical outcomes of both ischemic and hemorrhagic strokes. But conflicting results also exist. Furthermore, leptin was reported to independently predict common carotid intima-media thickness and carotid plaque instability. A link between hyperleptinemia and PAD has been reported, whereas limited data were available on the potential association between leptin and AAA. Elevated leptin concentrations have also been related to CKD incidence and progression as well as with insulin resistance, T2DM, micro- and macrovascular diabetic complications. Statins and antidiabetic drugs (including sitagliptin, metformin, pioglitazone, liraglutide and empagliflozin) may affect leptin levels. Further research is needed to establish the potential use (if any) of leptin as a therapeutic target in these diseases.
Keywords: abdominal aortic aneurysms; carotid artery disease; chronic kidney disease; coronary heart disease; leptin; obesity; peripheral artery disease; stroke.
Figures
Similar articles
-
EMPA-REG and Other Cardiovascular Outcome Trials of Glucose-lowering Agents: Implications for Future Treatment Strategies in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus.Clin Ther. 2016 Jun;38(6):1288-1298. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2016.04.037. Epub 2016 May 19. Clin Ther. 2016. PMID: 27210264
-
Clinical impact of the leptin to soluble leptin receptor ratio on subclinical carotid atherosclerosis in patients with type 2 diabetes.J Atheroscler Thromb. 2013;20(2):186-94. doi: 10.5551/jat.14662. Epub 2012 Oct 31. J Atheroscler Thromb. 2013. PMID: 23124060
-
Serum leptin levels are independently related to the incidence of ischemic heart disease in a prospective study of patients with type 2 diabetes.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2015 May 22;14:62. doi: 10.1186/s12933-015-0208-1. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2015. PMID: 25994184 Free PMC article.
-
The role of statins in the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus: an update.Curr Pharm Des. 2014;20(22):3665-74. doi: 10.2174/13816128113196660673. Curr Pharm Des. 2014. PMID: 24040875 Review.
-
What fans the fire: insights into mechanisms of leptin in metabolic syndrome-associated heart diseases.Curr Pharm Des. 2014;20(4):652-8. doi: 10.2174/138161282004140213160930. Curr Pharm Des. 2014. PMID: 23688014 Review.
Cited by
-
Editorial: Sedentary behaviour and cardiometabolic health.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2024 Oct 16;11:1498410. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2024.1498410. eCollection 2024. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2024. PMID: 39479390 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Leptin Is Associated with Testosterone, Nutritional Markers, and Vascular Muscular Dysfunction in Chronic Kidney Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jul 12;25(14):7646. doi: 10.3390/ijms25147646. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39062887 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of maternal advanced lipoxidation end products diet on the glycolipid metabolism and gut microbiota in offspring mice.Front Nutr. 2024 Jun 19;11:1421848. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2024.1421848. eCollection 2024. Front Nutr. 2024. PMID: 38962449 Free PMC article.
-
Physalis alkekengi L. Extract Reduces the Oxidative Stress, Inflammation and Apoptosis in Endothelial Vascular Cells Exposed to Hyperglycemia.Molecules. 2020 Aug 17;25(16):3747. doi: 10.3390/molecules25163747. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 32824505 Free PMC article.
-
Key Players in the Complex Pathophysiology of Obesity: A Cross-Talk Between the Obesogenic Genes and Unraveling the Metabolic Pathway of Action of Capsaicin and Orange Peel.Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2025 Jan;197(1):649-666. doi: 10.1007/s12010-024-04999-z. Epub 2024 Aug 5. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2025. PMID: 39102081 Review.
References
-
- Mechanick JI, Zhao S, Garvey WT. Leptin, An Adipokine With Central Importance in the Global Obesity Problem. Glob Heart. 2017 Dec 13. [Epub ahead of print] - PubMed
-
- Crujeiras AB, Carreira MC, Cabia B, Andrade S, Amil M, Casanueva FF. Leptin resistance in obesity: an epigenetic landscape. Life Sci. 2015;140:57–63. - PubMed
-
- Stepien M, Stepien A, Wlazel RN, Paradowski M, Rizzo M, Banach M, et al. Predictors of insulin resistance in patients with obesity: a pilot study. Angiology. 2014;65:22–30. - PubMed
-
- Stepien M, Stepien A, Banach M, Wlazel RN, Paradowski M, Rizzo M, et al. New obesity indices and adipokines in normotensive patients and patients with hypertension: comparative pilot analysis. Angiology. 2014;65:333–42. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical