Genomic atlas of the human plasma proteome
- PMID: 29875488
- PMCID: PMC6697541
- DOI: 10.1038/s41586-018-0175-2
Genomic atlas of the human plasma proteome
Abstract
Although plasma proteins have important roles in biological processes and are the direct targets of many drugs, the genetic factors that control inter-individual variation in plasma protein levels are not well understood. Here we characterize the genetic architecture of the human plasma proteome in healthy blood donors from the INTERVAL study. We identify 1,927 genetic associations with 1,478 proteins, a fourfold increase on existing knowledge, including trans associations for 1,104 proteins. To understand the consequences of perturbations in plasma protein levels, we apply an integrated approach that links genetic variation with biological pathway, disease, and drug databases. We show that protein quantitative trait loci overlap with gene expression quantitative trait loci, as well as with disease-associated loci, and find evidence that protein biomarkers have causal roles in disease using Mendelian randomization analysis. By linking genetic factors to diseases via specific proteins, our analyses highlight potential therapeutic targets, opportunities for matching existing drugs with new disease indications, and potential safety concerns for drugs under development.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
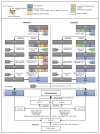
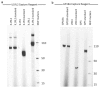
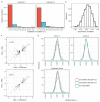
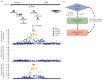
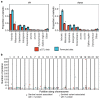
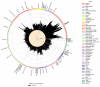
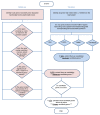
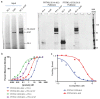
Similar articles
-
Large-scale integration of the plasma proteome with genetics and disease.Nat Genet. 2021 Dec;53(12):1712-1721. doi: 10.1038/s41588-021-00978-w. Epub 2021 Dec 2. Nat Genet. 2021. PMID: 34857953
-
High-Throughput Characterization of Blood Serum Proteomics of IBD Patients with Respect to Aging and Genetic Factors.PLoS Genet. 2017 Jan 27;13(1):e1006565. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1006565. eCollection 2017 Jan. PLoS Genet. 2017. PMID: 28129359 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic-informed proteome-wide scan reveals potential causal plasma proteins for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis.Thorax. 2024 Aug 19;79(9):878-882. doi: 10.1136/thorax-2024-221398. Thorax. 2024. PMID: 38871465
-
Plasma proteomic associations with genetics and health in the UK Biobank.Nature. 2023 Oct;622(7982):329-338. doi: 10.1038/s41586-023-06592-6. Epub 2023 Oct 4. Nature. 2023. PMID: 37794186 Free PMC article.
-
Genetics' Piece of the PI: Inferring the Origin of Complex Traits and Diseases from Proteome-Wide Protein-Protein Interaction Dynamics.Bioessays. 2020 Feb;42(2):e1900169. doi: 10.1002/bies.201900169. Epub 2019 Dec 18. Bioessays. 2020. PMID: 31854021 Review.
Cited by
-
Causal associations between the insulin-like growth factor family and sarcopenia: a bidirectional Mendelian randomization study.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024 Oct 23;15:1422472. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1422472. eCollection 2024. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 39507055 Free PMC article.
-
Integrative analysis of transcriptome and proteome wide association studies prioritized functional genes for obesity.Hum Genet. 2024 Nov 4. doi: 10.1007/s00439-024-02714-w. Online ahead of print. Hum Genet. 2024. PMID: 39495296
-
Mendelian Randomization Estimates the Effects of Plasma and Cerebrospinal Fluid Proteins on Intelligence, Fluid Intelligence Score, and Cognitive Performance.Mol Neurobiol. 2024 Nov 4. doi: 10.1007/s12035-024-04542-5. Online ahead of print. Mol Neurobiol. 2024. PMID: 39495227
-
PD-1/PD-L1 and coronary heart disease: a mendelian randomization study.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2024 Oct 18;11:1424770. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2024.1424770. eCollection 2024. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2024. PMID: 39494235 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Albert FW, Kruglyak L. The role of regulatory variation in complex traits and disease. Nat Rev Genet. 2015;16:197–212. - PubMed
-
- Yao C, et al. Genome-wide association study of plasma proteins identifies putatively causal genes, proteins, and pathways for cardiovascular disease. 2017 Preprint at https://www.biorxiv.org/content/early/2017/05/12/136523.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- MR/L003120/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- RG/13/13/30194/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- MR/S004068/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MR/S003746/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- SP/12/12/29836/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- SP/08/007/23628/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- MC_UU_00002/7/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- 1508647/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- RG/16/4/32218/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- MR/P02811X/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MR/P013880/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- CH/12/2/29428/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- MC_QA137933/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- 204623/Z/16/Z/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

