Collagen type 1 promotes survival of human breast cancer cells by overexpressing Kv10.1 potassium and Orai1 calcium channels through DDR1-dependent pathway
- PMID: 29872495
- PMCID: PMC5973854
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.19065
Collagen type 1 promotes survival of human breast cancer cells by overexpressing Kv10.1 potassium and Orai1 calcium channels through DDR1-dependent pathway
Abstract
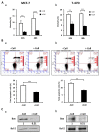
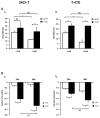
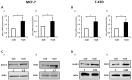
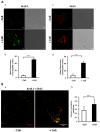
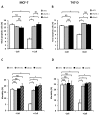
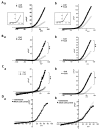
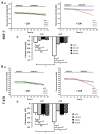
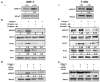
Collagen type 1 is among the tumor microenvironment (TM) factors, that regulates proliferation, survival, migration and invasion. Ion channels are key players in interactions between tumor cells and TM. Kv10.1 has been shown to play an essential role in breast cancer cell proliferation and migration by permitting Ca2+ influx notably via Orai1. Here, we show that human breast cancer (BC) cells growing, in culture media completely devoid of the serum and seeded on collagen 1 coating, exhibited less apoptotic rate and a decrease in Bax expression when compared to those grown on plastic. The survival conferred by collagen 1 was completely abolished by removing extracellular Ca2+ from the culture medium. In addition, Ca2+ entry was increased in collagen 1 condition along with increased Kv10.1 and Orai1 expressions. Moreover, collagen 1 was able to increase co-localization of Kv10.1 and Orai1 on the plasma membrane. Interestingly, silencing of Kv10.1 and Orai1 reduced survival and Ca2+influx without any additive effect. This calcium-dependent survival is accompanied by the activation of ERK1/2, and its pharmacological inhibition completely abolished the increase in Kv10.1 and Orai1 expressions, activities, and the cell survival induced by collagen 1. Moreover, both Kv10.1 and Orai1 knockdown reduced ERK1/2 activation but not Akt. Finally, DDR1 silencing but not β1-integrin reduced the collagen induced survival, ERK1/2 phosphorylation and the expression of Kv10.1 and Orai1. Together these data show that the Kv10.1/Orai1 complex is involved in BC cell survival and this is dependent on collagen 1/DDR1 pathway. Therefore, they represent a checkpoint of tumor progression induced by the tumor microenvironment.
Keywords: Kv10.1; Orai1; breast cancer; survival; tumour microenvironment.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST The authors declare that they have no interest of any kind affecting this study.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Original association of ion transporters mediates the ECM-induced breast cancer cell survival: Kv10.1-Orai1-SPCA2 partnership.Sci Rep. 2019 Feb 4;9(1):1175. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-37602-7. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 30718673 Free PMC article.
-
Human ether à-gogo K(+) channel 1 (hEag1) regulates MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cell migration through Orai1-dependent calcium entry.J Cell Physiol. 2012 Dec;227(12):3837-46. doi: 10.1002/jcp.24095. J Cell Physiol. 2012. PMID: 22495877
-
The N and C-termini of SPCA2 regulate differently Kv10.1 function: role in the collagen 1-induced breast cancer cell survival.Am J Cancer Res. 2021 Jan 1;11(1):251-263. eCollection 2021. Am J Cancer Res. 2021. PMID: 33520372 Free PMC article.
-
Kv10.1 K(+) channel: from physiology to cancer.Pflugers Arch. 2016 May;468(5):751-62. doi: 10.1007/s00424-015-1784-3. Epub 2016 Jan 8. Pflugers Arch. 2016. PMID: 26743871 Review.
-
Kv10.1 potassium channel: from the brain to the tumors.Biochem Cell Biol. 2017 Oct;95(5):531-536. doi: 10.1139/bcb-2017-0062. Epub 2017 Jul 14. Biochem Cell Biol. 2017. PMID: 28708947 Review.
Cited by
-
Store-Operated Ca2+ Entry in Breast Cancer Cells: Remodeling and Functional Role.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Dec 14;19(12):4053. doi: 10.3390/ijms19124053. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30558192 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Calcium-Signaling Toolkit in Cancer: Remodeling and Targeting.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2019 Aug 1;11(8):a035204. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a035204. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2019. PMID: 31088826 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Original association of ion transporters mediates the ECM-induced breast cancer cell survival: Kv10.1-Orai1-SPCA2 partnership.Sci Rep. 2019 Feb 4;9(1):1175. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-37602-7. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 30718673 Free PMC article.
-
Age-related modifications of type I collagen impair DDR1-induced apoptosis in non-invasive breast carcinoma cells.Cell Adh Migr. 2018;12(4):335-347. doi: 10.1080/19336918.2018.1472182. Epub 2018 Jun 28. Cell Adh Migr. 2018. PMID: 29733741 Free PMC article.
-
Store-Independent Calcium Entry and Related Signaling Pathways in Breast Cancer.Genes (Basel). 2021 Jun 29;12(7):994. doi: 10.3390/genes12070994. Genes (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34209733 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Liotta LA, Kohn EC. The microenvironment of the tumour-host interface. Nature. 2001;411:375–9. - PubMed
-
- Di Lullo GA, Sweeney SM, Körkkö J, Ala-Kokko L, San Antonio JD. Mapping the ligand-binding sites and disease-associated mutations on the most abundant protein in the human, type I collagen. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:4223–31. - PubMed
-
- Maquoi E, Assent D, Detilleux J, Pequeux C, Foidart JM, Noel A. MT1-MMP protects breast carcinoma cells against type I collagen-induced apoptosis. Oncogene. 2012;31:480–93. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

