Large-scale Isolation, Expansion and Characterization of Human Amniotic Epithelial Cells
- PMID: 29843193
- PMCID: PMC5984062
- DOI: 10.15283/ijsc18001
Large-scale Isolation, Expansion and Characterization of Human Amniotic Epithelial Cells
Abstract
Background and objectives: The human Amniotic epithelial cells (AME) derived from amniotic membrane of placenta have been considered as the potential fetal stem cell source with minimal or no ethical concerns and are important therapeutic tool for anti-fibrotic and regenerative therapies.
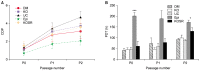
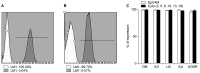
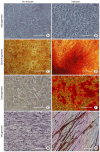
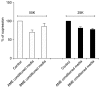
Methods and results: Here, we evaluated the isolation, media screening, scale-up and characterization of AME cells. The isolation, expansion of AMEs were performed by sequential passaging and growth kinetics studies. The AMEs were characterized using immunocytochemistry, immunophenotyping, In-vitro differentiation, and anti-fibrotic assays. The growth kinetics study revealed that the AME cultured in Ultraculture (UC) and DMEM knockout (DMEM-KO) have prominently higher growth rate compared to others. Overall, the AMEs cultured from 5 different media retained basic morphological characteristics and the functional characteristics.
Conclusions: Our result suggests that the AMEs can be successfully cultured in UC based complete media without losing its epithelial cell characteristics even after passaging for passage 2 (P2). However, a careful and methodical pre-clinical and clinical translation studies need to be conducted to show its safety and efficacy.
Keywords: Amniotic epithelial cells; Cell therapy; Cryopreservation; Growth kinetics; Stability; Tissue engineering.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicting financial interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comparative study of isolation, expansion and characterization of epithelial cells.Cytotherapy. 2017 Feb;19(2):263-271. doi: 10.1016/j.jcyt.2016.10.008. Epub 2016 Nov 25. Cytotherapy. 2017. PMID: 27894881
-
Are serum-free and xeno-free culture conditions ideal for large scale clinical grade expansion of Wharton's jelly derived mesenchymal stem cells? A comparative study.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2014 Jul 28;5(4):88. doi: 10.1186/scrt477. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2014. PMID: 25069491 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of umbilical cord tissue-derived mesenchymal stromal cells isolated from cryopreserved material and extracted by explantation and digestion methods utilizing a split manufacturing model.Cytotherapy. 2020 Oct;22(10):581-591. doi: 10.1016/j.jcyt.2020.06.002. Epub 2020 Jul 25. Cytotherapy. 2020. PMID: 32718875
-
The Bottlenecks in Translating Placenta-Derived Amniotic Epithelial and Mesenchymal Stromal Cells Into the Clinic: Current Discrepancies in Marker Reports.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2020 Mar 13;8:180. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2020.00180. eCollection 2020. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2020. PMID: 32232037 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Amniotic membrane and its epithelial and mesenchymal stem cells as an appropriate source for skin tissue engineering and regenerative medicine.Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 2018;46(sup2):431-440. doi: 10.1080/21691401.2018.1458730. Epub 2018 Apr 24. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 2018. PMID: 29687742 Review.
Cited by
-
DNA Microarray-Based Global Gene Expression Profiling in Human Amniotic Epithelial Cells Predicts the Potential of Microalgae-Derived Squalene for the Nervous System and Metabolic Health.Biomedicines. 2021 Dec 27;10(1):48. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10010048. Biomedicines. 2021. PMID: 35052729 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Isorhamnetin on Diabetes and Its Associated Complications: A Review of In Vitro and In Vivo Studies and a Post Hoc Transcriptome Analysis of Involved Molecular Pathways.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jan 9;23(2):704. doi: 10.3390/ijms23020704. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35054888 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biphasic Calcium Phosphate Biomaterials: Stem Cell-Derived Osteoinduction or In Vivo Osteoconduction? Novel Insights in Maxillary Sinus Augmentation by Advanced Imaging.Materials (Basel). 2021 Apr 23;14(9):2159. doi: 10.3390/ma14092159. Materials (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33922799 Free PMC article.
-
A Survey and Critical Evaluation of Isolation, Culture, and Cryopreservation Methods of Human Amniotic Epithelial Cells.Cell Cycle. 2022 Apr;21(7):655-673. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2021.2020015. Epub 2022 Mar 15. Cell Cycle. 2022. PMID: 35289707 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Human Amniotic Epithelial Cells as a Tool to Investigate the Effects of Cyanidin 3-O-Glucoside on Cell Differentiation.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Apr 5;22(7):3768. doi: 10.3390/ijms22073768. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33916494 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mason C, Brindley DA, Culme-Seymour EJ, Davie NL. Cell therapy industry: billion dollar global business with unlimited potential. Regen Med. 2011;6:265–272. - PubMed
-
- Ackermann K, Borgia SL, Korting HC, Mewes KR, Schäfer-Korting M. The Phenion full-thickness skin model for percutaneous absorption testing. Skin Pharmacol Physiol. 2010;23:105–112. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

