Management of chickenpox in pregnant women: an Italian perspective
- PMID: 29802481
- PMCID: PMC7101639
- DOI: 10.1007/s10096-018-3286-7
Management of chickenpox in pregnant women: an Italian perspective
Abstract
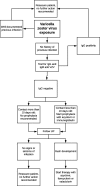
Chickenpox is a highly contagious disease caused by primary infection of varicella zoster virus (VZV). The disease is spread worldwide and is usually benign but, in some groups of population like pregnant women, can have a severe outcome. Due to a not optimal vaccination coverage, a relatively high number of childbearing-aged women in a European country such as Italy tested seronegative for VZV and so are currently at risk of acquiring chickenpox during pregnancy, especially if they live in contact with children for family or work reasons. Only few data are available about the risk of infection in this setting: the incidence of chickenpox may range from 1.5 to 4.6 cases/1000 childbearing females and from 1.21 to 6 cases/10,000 pregnant women, respectively. This review is aimed to focus on the epidemiology and the clinical management of exposure to chickenpox during pregnancy. Particular emphasis is given to the accurate screening of childbearing women at the time of the first gynecological approach - the females who tested susceptible to infection can be counseled about the risks and instructed on procedure should contact occur - and to the early prophylaxis of the at-risk exposure. Lastly, the achievement of adequate vaccination coverage of the Italian population remains a cornerstone in the prevention of chickenpox in pregnancy.
Keywords: Chickenpox; Management; Pregnancy; Prophylaxis; Vaccine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
VZV infection in pregnancy: a retrospective review over 5 years in Sheffield and discussion on the potential utilisation of varicella vaccine in prevention.J Infect. 2007 Jul;55(1):64-7. doi: 10.1016/j.jinf.2007.02.003. Epub 2007 Apr 5. J Infect. 2007. PMID: 17418420
-
Long -term persistence of antibodies against varicella in fully immunized healthcare workers: an Italian retrospective cohort study.BMC Infect Dis. 2021 May 25;21(1):475. doi: 10.1186/s12879-021-06180-x. BMC Infect Dis. 2021. PMID: 34034659 Free PMC article.
-
[Modelling the impact of vaccination on the epidemiology of varicella zoster virus].Rev Epidemiol Sante Publique. 2008 Oct;56(5):323-31. doi: 10.1016/j.respe.2008.07.087. Epub 2008 Oct 31. Rev Epidemiol Sante Publique. 2008. PMID: 18951741 French.
-
[Summary of the multidisciplinary guideline 'Varicella'].Ned Tijdschr Geneeskd. 2011;155(51):A3511. Ned Tijdschr Geneeskd. 2011. PMID: 22200141 Review. Dutch.
-
Varicella and the pregnant woman: prevention and management.Aust N Z J Obstet Gynaecol. 2008 Feb;48(1):26-33. doi: 10.1111/j.1479-828X.2007.00797.x. Aust N Z J Obstet Gynaecol. 2008. PMID: 18275568 Review.
Cited by
-
Seroprevalence Assessment of Anti-Varicella Antibodies among Adults in the Province of Florence (Italy).Vaccines (Basel). 2024 Sep 16;12(9):1056. doi: 10.3390/vaccines12091056. Vaccines (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39340086 Free PMC article.
-
Seroprevalence of Varicella in Pregnant Women and Newborns in a Region of Colombia.Vaccines (Basel). 2021 Dec 31;10(1):52. doi: 10.3390/vaccines10010052. Vaccines (Basel). 2021. PMID: 35062713 Free PMC article.
-
Epidemiological Characteristics of Varicella under Different Immunisation Strategies in Suzhou Prefecture, Jiangsu Province.Vaccines (Basel). 2022 Oct 19;10(10):1745. doi: 10.3390/vaccines10101745. Vaccines (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36298610 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pinkbook | Varicella | Epidemiology of Vaccine Preventable Diseases | CDC. https://www.cdc.gov/vaccines/pubs/pinkbook/varicella.html. Accessed 5 Apr 2018
-
- (2014) Varicella and herpes zoster vaccines: WHO position paper
-
- Lolekha S, Tanthiphabha W, Sornchai P, Kosuwan P, Sutra S, Warachit B, Chup-Upprakarn S, Hutagalung Y, Weil J, Bock HL Effect of climatic factors and population density on varicella zoster virus epidemiology within a tropical country. Am J Trop Med Hyg 64:131–136 - PubMed
-
- Maretic Z, Cooray MP. Comparisons between chickenpox in a tropical and a European country. J Trop Med Hyg. 1963;66:311–315. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical