Knockdown of KPNA2 inhibits autophagy in oral squamous cell carcinoma cell lines by blocking p53 nuclear translocation
- PMID: 29781035
- PMCID: PMC6059741
- DOI: 10.3892/or.2018.6451
Knockdown of KPNA2 inhibits autophagy in oral squamous cell carcinoma cell lines by blocking p53 nuclear translocation
Abstract
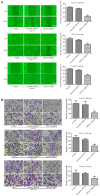
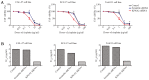
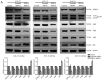
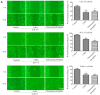
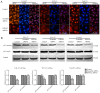
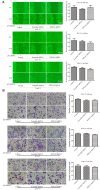
Oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC), one of the 10 most common types of neoplasms in the US, constitutes ~90% of all cases of oral malignancies. Chemoresistance and metastasis are difficult to avoid during the course of treatment, leading to a poor prognosis and a high mortality rate for patients with OSCC. Autophagy, a critical conserved cellular process, has been reported to be highly associated with the regulation of chemoresistance and metastasis of cancer cells. The present study investigated the role of karyopherin α2 (KPNA2), a member of the importin α family, which may serve an important role in p53 nucleocytoplasmic transport in the process of OSCC autophagy. In the CAL‑27, SCC‑15 and Tca8113 OSCC cell lines, we observed that the downregulation of KPNA2 suppressed cell migration and cisplatin resistance, using wound‑healing, Transwell and CCK‑8 assays. Additionally, the results of western blot analysis and transmission electron microscopy (TEM) analysis indicated that the knockdown of KPNA2 inhibited autophagy. We confirmed that the inhibition of autophagy with anti‑autophagy agents decreased the migration and cisplatin resistance of OSCC cells. We hypothesized that the suppression of cell migration and cisplatin resistance induced by KPNA2 knockdown may be associated with the inhibition of autophagy. To identify the underlying mechanism, further experiments determined that KPNA2 affects the level of autophagy via regulating the p53 nuclear import. Thus, the present study demonstrated that the function of KPNA2 in the process of autophagy may be p53‑dependent, and by regulating the translocation of p53, KPNA2 can support autophagy to promote the chemoresistance and metastasis of OSCC cells.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Exosomes containing miR-21 transfer the characteristic of cisplatin resistance by targeting PTEN and PDCD4 in oral squamous cell carcinoma.Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2017 Sep 1;49(9):808-816. doi: 10.1093/abbs/gmx078. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2017. PMID: 28910982
-
CerS6 regulates cisplatin resistance in oral squamous cell carcinoma by altering mitochondrial fission and autophagy.J Cell Physiol. 2018 Dec;233(12):9416-9425. doi: 10.1002/jcp.26815. Epub 2018 Jul 27. J Cell Physiol. 2018. PMID: 30054909
-
LncRNA HOXA11-AS Promotes Proliferation and Cisplatin Resistance of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma by Suppression of miR-214-3p Expression.Biomed Res Int. 2019 May 28;2019:8645153. doi: 10.1155/2019/8645153. eCollection 2019. Biomed Res Int. 2019. PMID: 31275988 Free PMC article.
-
Novel roles of karyopherin subunit alpha 2 in hepatocellular carcinoma.Biomed Pharmacother. 2023 Jul;163:114792. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2023.114792. Epub 2023 Apr 28. Biomed Pharmacother. 2023. PMID: 37121148 Review.
-
The emerging roles of KPNA2 in cancer.Life Sci. 2020 Jan 15;241:117140. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2019.117140. Epub 2019 Dec 6. Life Sci. 2020. PMID: 31812670 Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of Potential Biomarkers Using Integrative Approach: A Case Study of ESCC.SN Comput Sci. 2023;4(2):114. doi: 10.1007/s42979-022-01492-4. Epub 2022 Dec 21. SN Comput Sci. 2023. PMID: 36573207 Free PMC article.
-
The regulation of long non-coding RNA 00958 (LINC00958) for oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) cells death through absent in melanoma 2 (AIM2) depending on microRNA-4306 and Sirtuin1 (SIRT1) in vitro.Bioengineered. 2021 Dec;12(1):5085-5098. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2021.1955561. Bioengineered. 2021. PMID: 34384029 Free PMC article.
-
Analyses of DNA Methylation Involved in the Activation of Nuclear Karyopherin Alpha 2 Leading to Identify the Progression and Prognostic Significance Across Human Breast Cancer.Cancer Manag Res. 2020 Aug 3;12:6665-6677. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S261290. eCollection 2020. Cancer Manag Res. 2020. PMID: 32801900 Free PMC article.
-
Long non-coding RNA HAGLROS facilitates tumorigenesis and progression in hepatocellular carcinoma by sponging miR-26b-5p to up-regulate karyopherin α2 (KPNA2) and inactivate p53 signaling.Bioengineered. 2022 Mar;13(3):7829-7846. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2022.2049472. Bioengineered. 2022. PMID: 35291921 Free PMC article.
-
Overexpression of Karyopherin Subunit alpha 2 (KPNA2) Predicts Unfavorable Prognosis and Promotes Bladder Cancer Tumorigenicity via the P53 Pathway.Med Sci Monit. 2020 Mar 9;26:e921087. doi: 10.12659/MSM.921087. Med Sci Monit. 2020. PMID: 32147666 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

