Discrimination Between Human Leukocyte Antigen Class I-Bound and Co-Purified HIV-Derived Peptides in Immunopeptidomics Workflows
- PMID: 29780384
- PMCID: PMC5946011
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.00912
Discrimination Between Human Leukocyte Antigen Class I-Bound and Co-Purified HIV-Derived Peptides in Immunopeptidomics Workflows
Abstract
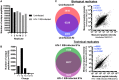
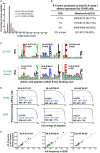
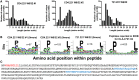
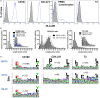
Elucidation of novel peptides presented by human leukocyte antigen (HLA) class I alleles by immunopeptidomics constitutes a powerful approach that can inform the rational design of CD8+ T cell inducing vaccines to control infection with pathogens such as human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) or to combat tumors. Recent advances in the sensitivity of liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry instrumentation have facilitated the discovery of thousands of natural HLA-restricted peptides in a single measurement. However, the extent of contamination of class I-bound peptides identified using HLA immunoprecipitation (IP)-based immunopeptidomics approaches with peptides from other sources has not previously been evaluated in depth. Here, we investigated the specificity of the IP-based immunopeptidomics methodology using HLA class I- or II-deficient cell lines and membrane protein-specific antibody IPs. We demonstrate that the 721.221 B lymphoblastoid cell line, widely regarded to be HLA class Ia-deficient, actually expresses and presents peptides on HLA-C*01:02. Using this cell line and the C8166 (HLA class I- and II-expressing) cell line, we show that some HLA class II-bound peptides were co-purified non-specifically during HLA class I and membrane protein IPs. Furthermore, IPs of "irrelevant" membrane proteins from HIV-1-infected HLA class I- and/or II-expressing cells revealed that unusually long HIV-1-derived peptides previously reported by us and other immunopeptidomics studies as potentially novel CD8+ T cell epitopes were non-specifically co-isolated, and so constitute a source of contamination in HLA class I IPs. For example, a 16-mer (FLGKIWPSYKGRPGNF), which was detected in all samples studied represents the full p1 segment of the abundant intracellular or virion-associated proteolytically-processed HIV-1 Gag protein. This result is of importance, as these long co-purified HIV-1 Gag peptides may not elicit CD8+ T cell responses when incorporated into candidate vaccines. These results have wider implications for HLA epitope discovery from abundant or membrane-associated antigens by immunopeptidomics in the context of infectious diseases, cancer, and autoimmunity.
Keywords: HIV; antigen presentation; epitope; human leukocyte antigen; immunopeptidomics; major histocompatibility complex; mass spectrometry.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Identification of Immunodominant HIV-1 Epitopes Presented by HLA-C*12:02, a Protective Allele, Using an Immunopeptidomics Approach.J Virol. 2019 Aug 13;93(17):e00634-19. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00634-19. Print 2019 Sep 1. J Virol. 2019. PMID: 31217245 Free PMC article.
-
HLA-E-restricted, Gag-specific CD8+ T cells can suppress HIV-1 infection, offering vaccine opportunities.Sci Immunol. 2021 Mar 25;6(57):eabg1703. doi: 10.1126/sciimmunol.abg1703. Sci Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33766848 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive screening for human immunodeficiency virus type 1 subtype-specific CD8 cytotoxic T lymphocytes and definition of degenerate epitopes restricted by HLA-A0207 and -C(W)0304 alleles.J Virol. 2002 May;76(10):4971-86. doi: 10.1128/jvi.76.10.4971-4986.2002. J Virol. 2002. PMID: 11967314 Free PMC article.
-
T Cell Epitope Discovery in the Context of Distinct and Unique Indigenous HLA Profiles.Front Immunol. 2022 May 6;13:812393. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.812393. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35603215 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Importance of Being Presented: Target Validation by Immunopeptidomics for Epitope-Specific Immunotherapies.Front Immunol. 2022 Apr 6;13:883989. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.883989. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35464395 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Immunopeptidomics-based design of mRNA vaccine formulations against Listeria monocytogenes.Nat Commun. 2022 Oct 14;13(1):6075. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-33721-y. Nat Commun. 2022. PMID: 36241641 Free PMC article.
-
Cloud Computing Based Immunopeptidomics Utilizing Community Curated Variant Libraries Simplifies and Improves Neo-Antigen Discovery in Metastatic Melanoma.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Jul 26;13(15):3754. doi: 10.3390/cancers13153754. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34359654 Free PMC article.
-
Critical Review of Existing MHC I Immunopeptidome Isolation Methods.Molecules. 2020 Nov 19;25(22):5409. doi: 10.3390/molecules25225409. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 33228004 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MARS an improved de novo peptide candidate selection method for non-canonical antigen target discovery in cancer.Nat Commun. 2024 Jan 22;15(1):661. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-44460-z. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 38253617 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of novel HIV-1-derived HLA-E-binding peptides.Immunol Lett. 2018 Oct;202:65-72. doi: 10.1016/j.imlet.2018.08.005. Epub 2018 Aug 30. Immunol Lett. 2018. PMID: 30172717 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

