Determination of the Membrane Environment of CD59 in Living Cells
- PMID: 29772810
- PMCID: PMC6023084
- DOI: 10.3390/biom8020028
Determination of the Membrane Environment of CD59 in Living Cells
Abstract
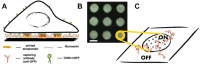
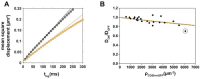
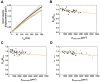
The organization and dynamics of proteins and lipids in the plasma membrane, and their role in membrane functionality, have been subject of a long-lasting debate. Specifically, it is unclear to what extent membrane proteins are affected by their immediate lipid environment and vice versa. Studies on model membranes and plasma membrane vesicles indicated preferences of proteins for lipid phases characterized by different acyl chain order; however, whether such phases do indeed exist in live cells is still not known. Here, we refine a previously developed micropatterning approach combined with single molecule tracking to quantify the influence of the glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchored (GPI-anchored) protein CD59 on its molecular environment directly in the live cell plasma membrane. We find that locally enriched and immobilized CD59 presents obstacles to the diffusion of fluorescently labeled lipids with a different phase-partitioning behavior independent of cell cholesterol levels and type of lipid. Our results give no evidence for either specific binding of the lipids to CD59 or the existence of nanoscopic ordered membrane regions associated with CD59.
Keywords: CD59; GPI-anchored protein; diffusion; lipid; membrane rafts; micropatterning; plasma membrane.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Depressing time: Waiting, melancholia, and the psychoanalytic practice of care.In: Kirtsoglou E, Simpson B, editors. The Time of Anthropology: Studies of Contemporary Chronopolitics. Abingdon: Routledge; 2020. Chapter 5. In: Kirtsoglou E, Simpson B, editors. The Time of Anthropology: Studies of Contemporary Chronopolitics. Abingdon: Routledge; 2020. Chapter 5. PMID: 36137063 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
Using Experience Sampling Methodology to Capture Disclosure Opportunities for Autistic Adults.Autism Adulthood. 2023 Dec 1;5(4):389-400. doi: 10.1089/aut.2022.0090. Epub 2023 Dec 12. Autism Adulthood. 2023. PMID: 38116059 Free PMC article.
-
Australia in 2030: what is our path to health for all?Med J Aust. 2021 May;214 Suppl 8:S5-S40. doi: 10.5694/mja2.51020. Med J Aust. 2021. PMID: 33934362
-
Qualitative evidence synthesis informing our understanding of people's perceptions and experiences of targeted digital communication.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019 Oct 23;10(10):ED000141. doi: 10.1002/14651858.ED000141. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019. PMID: 31643081 Free PMC article.
-
The effectiveness of abstinence-based and harm reduction-based interventions in reducing problematic substance use in adults who are experiencing homelessness in high income countries: A systematic review and meta-analysis: A systematic review.Campbell Syst Rev. 2024 Apr 21;20(2):e1396. doi: 10.1002/cl2.1396. eCollection 2024 Jun. Campbell Syst Rev. 2024. PMID: 38645303 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A Fast and Simple Contact Printing Approach to Generate 2D Protein Nanopatterns.Front Chem. 2019 Jan 24;6:655. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2018.00655. eCollection 2018. Front Chem. 2019. PMID: 30733939 Free PMC article.
-
Tunable DNA Hybridization Enables Spatially and Temporally Controlled Surface-Anchoring of Biomolecular Cargo.Langmuir. 2018 Dec 11;34(49):15021-15027. doi: 10.1021/acs.langmuir.8b01942. Epub 2018 Aug 30. Langmuir. 2018. PMID: 30160973 Free PMC article.
-
Measurement of FGFR3 signaling at the cell membrane via total internal reflection fluorescence microscopy to compare the activation of FGFR3 mutants.J Biol Chem. 2023 Feb;299(2):102832. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2022.102832. Epub 2022 Dec 27. J Biol Chem. 2023. PMID: 36581204 Free PMC article.
-
A micropatterning platform for quantifying interaction kinetics between the T cell receptor and an intracellular binding protein.Sci Rep. 2019 Mar 1;9(1):3288. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-39865-0. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 30824760 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

