New insights into apoptosome structure and function
- PMID: 29765111
- PMCID: PMC6030056
- DOI: 10.1038/s41418-017-0025-z
New insights into apoptosome structure and function
Abstract
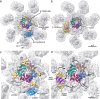
The apoptosome is a platform that activates apical procaspases in response to intrinsic cell death signals. Biochemical and structural studies in the past two decades have extended our understanding of apoptosome composition and structure, while illuminating the requirements for initiator procaspase activation. A number of studies have now provided high-resolution structures for apoptosomes from C. elegans (CED-4), D. melanogaster (Dark), and H. sapiens (Apaf-1), which define critical protein interfaces, including intra and interdomain interactions. This work also reveals interactions of apoptosomes with their respective initiator caspases, CED-3, Dronc and procaspase-9. Structures of the human apoptosome have defined the requirements for cytochrome c binding, which triggers the conversion of inactive Apaf-1 molecules to an extended, assembly competent state. While recent data have provided a detailed understanding of apoptosome formation and procaspase activation, they also highlight important evolutionary differences with functional implications for caspase activation. Comparison of the CARD/CARD disks and apoptosomes formed by CED-4, Dark and Apaf-1. Cartoons of the active states of the CARD-CARD disks, illustrating the two CED-4 CARD tetrameric ring layers (CED4a and CED4b; top row) and the binding of 8 Dronc CARDs and between 3-4 pc-9 CARDs, to the Dark and Apaf-1 CARD disk respectively (middle and lower rows). Ribbon diagrams of the active CED-4, Dark and Apaf-1 apoptosomes are shown (right column).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Apoptosome assembly.Methods Enzymol. 2008;442:141-56. doi: 10.1016/S0076-6879(08)01407-9. Methods Enzymol. 2008. PMID: 18662568
-
Apoptosome structure, assembly, and procaspase activation.Structure. 2013 Apr 2;21(4):501-15. doi: 10.1016/j.str.2013.02.024. Structure. 2013. PMID: 23561633 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structure of the apoptosome: mechanistic insights into activation of an initiator caspase from Drosophila.Genes Dev. 2015 Feb 1;29(3):277-87. doi: 10.1101/gad.255877.114. Genes Dev. 2015. PMID: 25644603 Free PMC article.
-
Structure of the Drosophila apoptosome at 6.9 å resolution.Structure. 2011 Jan 12;19(1):128-40. doi: 10.1016/j.str.2010.10.009. Structure. 2011. PMID: 21220123 Free PMC article.
-
Apoptosome: a platform for the activation of initiator caspases.Cell Death Differ. 2007 Jan;14(1):56-65. doi: 10.1038/sj.cdd.4402028. Epub 2006 Sep 15. Cell Death Differ. 2007. PMID: 16977332 Review.
Cited by
-
The actin nucleation factors JMY and WHAMM enable a rapid Arp2/3 complex-mediated intrinsic pathway of apoptosis.PLoS Genet. 2021 Apr 19;17(4):e1009512. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1009512. eCollection 2021 Apr. PLoS Genet. 2021. PMID: 33872315 Free PMC article.
-
Targeted hypermutation of putative antigen sensors in multicellular bacteria.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024 Feb 27;121(9):e2316469121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2316469121. Epub 2024 Feb 14. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024. PMID: 38354254 Free PMC article.
-
Structural Insight into KsBcl-2 Mediated Apoptosis Inhibition by Kaposi Sarcoma Associated Herpes Virus.Viruses. 2022 Mar 31;14(4):738. doi: 10.3390/v14040738. Viruses. 2022. PMID: 35458468 Free PMC article.
-
Intrinsic apoptosis is evolutionarily divergent among metazoans.Evol Lett. 2023 Nov 16;8(2):267-282. doi: 10.1093/evlett/qrad057. eCollection 2024 Apr. Evol Lett. 2023. PMID: 38525035 Free PMC article.
-
Output Regulation and Function Optimization of Mitochondria in Eukaryotes.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020 Nov 17;8:598112. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.598112. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020. PMID: 33330486 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

