Applications of RNA Indexes for Precision Oncology in Breast Cancer
- PMID: 29753129
- PMCID: PMC6112337
- DOI: 10.1016/j.gpb.2018.03.002
Applications of RNA Indexes for Precision Oncology in Breast Cancer
Abstract
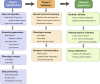
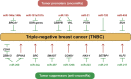
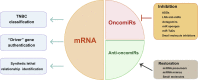
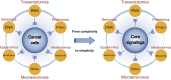
Precision oncology aims to offer the most appropriate treatments to cancer patients mainly based on their individual genetic information. Genomics has provided numerous valuable data on driver mutations and risk loci; however, it remains a formidable challenge to transform these data into therapeutic agents. Transcriptomics describes the multifarious expression patterns of both mRNAs and non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs), which facilitates the deciphering of genomic codes. In this review, we take breast cancer as an example to demonstrate the applications of these rich RNA resources in precision medicine exploration. These include the use of mRNA profiles in triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) subtyping to inform corresponding candidate targeted therapies; current advancements and achievements of high-throughput RNA interference (RNAi) screening technologies in breast cancer; and microRNAs as functional signatures for defining cell identities and regulating the biological activities of breast cancer cells. We summarize the benefits of transcriptomic analyses in breast cancer management and propose that unscrambling the core signaling networks of cancer may be an important task of multiple-omic data integration for precision oncology.
Keywords: Breast cancer; Precision oncology; RNA interference; Transcriptomics; microRNA.
Copyright © 2018 The Authors. Production and hosting by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
High-throughput «Omics» technologies: New tools for the study of triple-negative breast cancer.Cancer Lett. 2016 Nov 1;382(1):77-85. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2016.03.001. Epub 2016 Mar 7. Cancer Lett. 2016. PMID: 26965997 Review.
-
Molecular subtyping and genomic profiling expand precision medicine in refractory metastatic triple-negative breast cancer: the FUTURE trial.Cell Res. 2021 Feb;31(2):178-186. doi: 10.1038/s41422-020-0375-9. Epub 2020 Jul 27. Cell Res. 2021. PMID: 32719455 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Identification of Potential Long Non-Coding RNA Candidates that Contribute to Triple-Negative Breast Cancer in Humans through Computational Approach.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Nov 16;22(22):12359. doi: 10.3390/ijms222212359. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34830241 Free PMC article.
-
Genomic Alterations Affecting Competitive Endogenous RNAs (ceRNAs) and Regulatory Networks (ceRNETs) with Clinical Implications in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer (TNBC).Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Feb 23;25(5):2624. doi: 10.3390/ijms25052624. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38473871 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Long non-coding RNAs: implications in targeted diagnoses, prognosis, and improved therapeutic strategies in human non- and triple-negative breast cancer.Clin Epigenetics. 2018 Jun 27;10:88. doi: 10.1186/s13148-018-0514-z. eCollection 2018. Clin Epigenetics. 2018. PMID: 29983835 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
New Biomarkers and Treatment Advances in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer.Diagnostics (Basel). 2023 Jun 2;13(11):1949. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics13111949. Diagnostics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37296801 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinical Evidence of Circulating Tumor DNA Application in Aggressive Breast Cancer.Diagnostics (Basel). 2023 Jan 27;13(3):470. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics13030470. Diagnostics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36766575 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RNA-sequence-based microRNA expression signature in breast cancer: tumor-suppressive miR-101-5p regulates molecular pathogenesis.Mol Oncol. 2020 Feb;14(2):426-446. doi: 10.1002/1878-0261.12602. Epub 2019 Dec 29. Mol Oncol. 2020. PMID: 31755218 Free PMC article.
-
Insight Into the Prospects for RNAi Therapy of Cancer.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Mar 16;12:644718. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.644718. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33796026 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Overexpression of Tumor Protein p53-regulated Apoptosis-inducing Protein 1 Regulates Proliferation and Apoptosis of Breast Cancer Cells through the PI3K/Akt Pathway.J Breast Cancer. 2019 Jun;22(2):172-184. doi: 10.4048/jbc.2019.22.e21. J Breast Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31281721 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hunter D.J. Uncertainty in the era of precision medicine. N Engl J Med. 2016;375:711–713. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

