Activated dendritic cells modulate proliferation and differentiation of human myoblasts
- PMID: 29748534
- PMCID: PMC5945640
- DOI: 10.1038/s41419-018-0426-z
Activated dendritic cells modulate proliferation and differentiation of human myoblasts
Erratum in
-
Correction: Activated dendritic cells modulate proliferation and differentiation of human myoblasts.Cell Death Dis. 2022 Sep 22;13(9):811. doi: 10.1038/s41419-022-05278-7. Cell Death Dis. 2022. PMID: 36138001 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
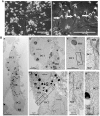
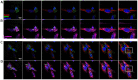
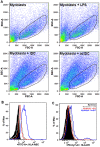
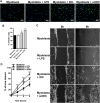
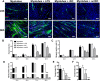
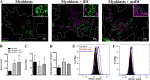
Idiopathic Inflammatory Myopathies (IIMs) are a heterogeneous group of autoimmune diseases affecting skeletal muscle tissue homeostasis. They are characterized by muscle weakness and inflammatory infiltration with tissue damage. Amongst the cells in the muscle inflammatory infiltration, dendritic cells (DCs) are potent antigen-presenting and key components in autoimmunity exhibiting an increased activation in inflamed tissues. Since, the IIMs are characterized by the focal necrosis/regeneration and muscle atrophy, we hypothesized that DCs may play a role in these processes. Due to the absence of a reliable in vivo model for IIMs, we first performed co-culture experiments with immature DCs (iDC) or LPS-activated DCs (actDC) and proliferating myoblasts or differentiating myotubes. We demonstrated that both iDC or actDCs tightly interact with myoblasts and myotubes, increased myoblast proliferation and migration, but inhibited myotube differentiation. We also observed that actDCs increased HLA-ABC, HLA-DR, VLA-5, and VLA-6 expression and induced cytokine secretion on myoblasts. In an in vivo regeneration model, the co-injection of human myoblasts and DCs enhanced human myoblast migration, whereas the absolute number of human myofibres was unchanged. In conclusion, we suggest that in the early stages of myositis, DCs may play a crucial role in inducing muscle-damage through cell-cell contact and inflammatory cytokine secretion, leading to muscle regeneration impairment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Functional KCa1.1 channels are crucial for regulating the proliferation, migration and differentiation of human primary skeletal myoblasts.Cell Death Dis. 2016 Oct 20;7(10):e2426. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2016.324. Cell Death Dis. 2016. PMID: 27763639 Free PMC article.
-
Nilotinib impairs skeletal myogenesis by increasing myoblast proliferation.Skelet Muscle. 2018 Feb 20;8(1):5. doi: 10.1186/s13395-018-0150-5. Skelet Muscle. 2018. PMID: 29463296 Free PMC article.
-
The changing AMPK expression profile in differentiating mouse skeletal muscle myoblast cells helps confer increasing resistance to apoptosis.Exp Physiol. 2007 Jan;92(1):207-17. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.2006.034736. Epub 2006 Aug 31. Exp Physiol. 2007. PMID: 16945942
-
Effects of type IV collagen on myogenic characteristics of IGF-I gene-engineered myoblasts.J Biosci Bioeng. 2015 May;119(5):596-603. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiosc.2014.10.008. Epub 2014 Nov 21. J Biosci Bioeng. 2015. PMID: 25454061
-
The immunoproteasomes are key to regulate myokines and MHC class I expression in idiopathic inflammatory myopathies.J Autoimmun. 2016 Dec;75:118-129. doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2016.08.004. Epub 2016 Aug 10. J Autoimmun. 2016. PMID: 27522114
Cited by
-
STING Is Required in Conventional Dendritic Cells for DNA Vaccine Induction of Type I T Helper Cell- Dependent Antibody Responses.Front Immunol. 2022 Apr 22;13:861710. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.861710. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35529875 Free PMC article.
-
Mapping the Immune Cell Microenvironment with Spatial Profiling in Muscle Tissue Injected with the Venom of Daboia russelii.Toxins (Basel). 2023 Mar 10;15(3):208. doi: 10.3390/toxins15030208. Toxins (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36977099 Free PMC article.
-
Cell type mapping of inflammatory muscle diseases highlights selective myofiber vulnerability in inclusion body myositis.Nat Aging. 2024 Jul;4(7):969-983. doi: 10.1038/s43587-024-00645-9. Epub 2024 Jun 4. Nat Aging. 2024. PMID: 38834884 Free PMC article.
-
Unveiling the emerging role of curcumin to alleviate ochratoxin A-induced muscle toxicity in grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella): in vitro and in vivo studies.J Anim Sci Biotechnol. 2024 May 12;15(1):72. doi: 10.1186/s40104-024-01023-6. J Anim Sci Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 38734645 Free PMC article.
-
NK/DC crosstalk-modulating antitumor activity via Sema3E/PlexinD1 axis for enhanced cancer immunotherapy.Immunol Res. 2024 Dec;72(6):1217-1228. doi: 10.1007/s12026-024-09536-y. Epub 2024 Sep 5. Immunol Res. 2024. PMID: 39235526 Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

