Modulation of the expression of genes related to the system of amyloid-beta metabolism in the brain as a novel mechanism of ceftriaxone neuroprotective properties
- PMID: 29745864
- PMCID: PMC5998892
- DOI: 10.1186/s12868-018-0412-5
Modulation of the expression of genes related to the system of amyloid-beta metabolism in the brain as a novel mechanism of ceftriaxone neuroprotective properties
Abstract
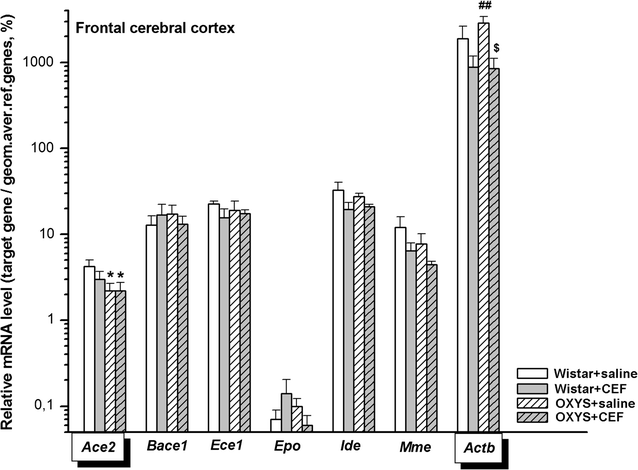
Background: The dominant hypothesis about the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease (AD) is the "amyloid cascade" concept and modulating the expression of proteins involved in the metabolism of amyloid-beta (Aβ) is proposed as an effective strategy for the prevention and therapy of AD. Recently, we found that an antibiotic ceftriaxone (CEF), which possesses neuroprotective activity, reduced cognitive deficits and neurodegenerative changes in OXYS rats, a model of sporadic AD. The molecular mechanisms of this effect are not completely clear, we suggested that the drug might serve as the regulator of the expression of the genes involved in the metabolism of Aβ and the pathogenesis of AD. The study was aimed to determine the effects of CEF on mRNA levels of Bace1 (encoding β-secretase BACE1 involved in Aβ production), Mme, Ide, Ece1, Ace2 (encoding enzymes involved in Aβ degradation), Epo (encoding erythropoietin related to endothelial function and clearance of Aβ across the blood brain barrier) in the frontal cortex, hippocampus, striatum, hypothalamus, and amygdala of OXYS and Wistar (control strain) male rats. Starting from the age of 14 weeks, animals received CEF (100 mg/kg/day, i.p., 36 days) or saline. mRNA levels were evaluated with RT-qPCR method. Biochemical parameters of plasma were measured for control of system effects of the treatment.
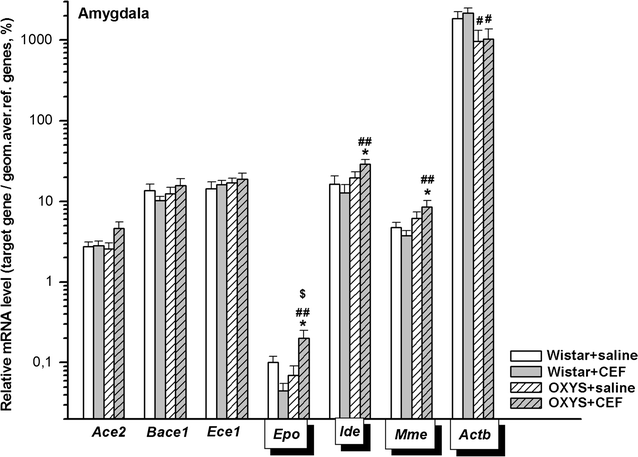
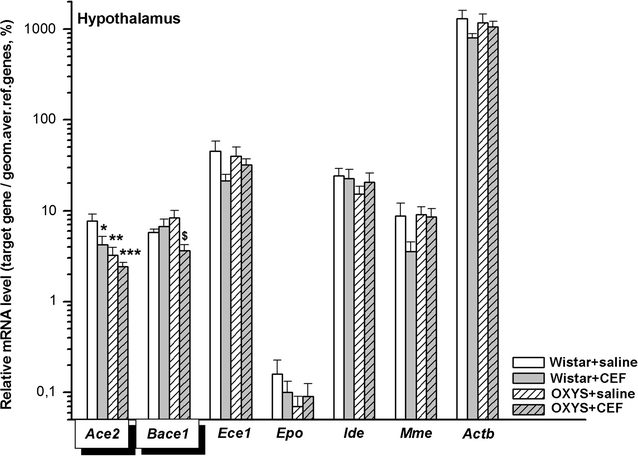
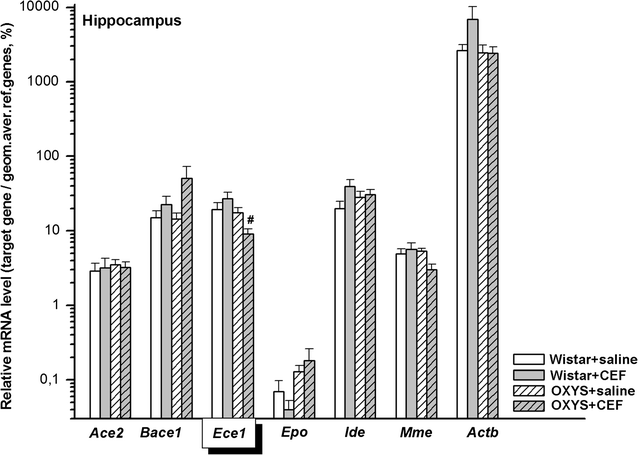
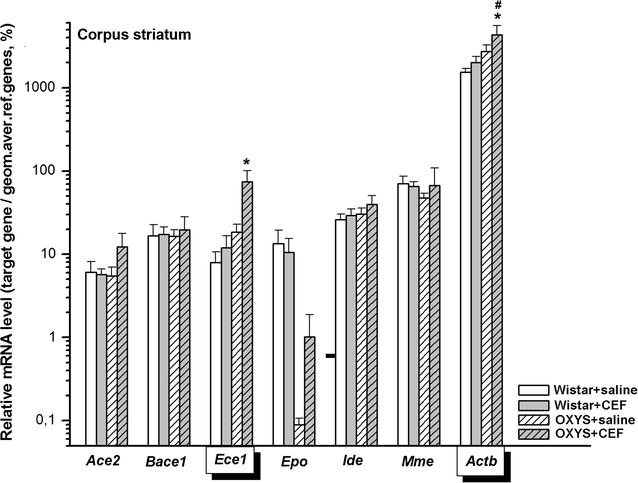
Results: To better understand strain variations studied here, we compared the gene expression between untreated OXYS and Wistar rats. This comparison showed a significant decrease in mRNA levels of Ace2 in the frontal cortex and hypothalamus, and of Actb in the amygdala of untreated OXYS rats. Analysis of potential effects of CEF revealed its novel targets. In the compound-treated OXYS cohort, CEF diminished mRNA levels of Bace1 and Ace2 in the hypothalamus, and Aktb in the frontal cortex. Furthermore, CEF augmented Mme, Ide, and Epo mRNA levels in the amygdala as well as the levels of Ece1 and Aktb in the striatum. Finally, CEF also attenuated the activity of ALT and AST in plasma of OXYS rats.
Conclusion: Those findings disclosed novel targets for CEF action that might be involved into neuroprotective mechanisms at early, pre-plaque stages of AD-like pathology development.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; Amyloid metabolism; Ceftriaxone; Gene expression; Neuroprotection; Rats; mRNA.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Neuroprotective effects of ceftriaxone treatment on cognitive and neuronal deficits in a rat model of accelerated senescence.Behav Brain Res. 2017 Jul 14;330:8-16. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2017.05.002. Epub 2017 May 6. Behav Brain Res. 2017. PMID: 28487222
-
Cerebrolysin decreases amyloid-beta production by regulating amyloid protein precursor maturation in a transgenic model of Alzheimer's disease.J Neurosci Res. 2006 May 15;83(7):1252-61. doi: 10.1002/jnr.20818. J Neurosci Res. 2006. PMID: 16511867
-
Neuroprotective Effects of Ceftriaxone Involve the Reduction of Aβ Burden and Neuroinflammatory Response in a Mouse Model of Alzheimer's Disease.Front Neurosci. 2021 Sep 29;15:736786. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2021.736786. eCollection 2021. Front Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34658774 Free PMC article.
-
Senescence-accelerated OXYS rats: a model of age-related cognitive decline with relevance to abnormalities in Alzheimer disease.Cell Cycle. 2014;13(6):898-909. doi: 10.4161/cc.28255. Epub 2014 Feb 17. Cell Cycle. 2014. PMID: 24552807 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Melatonin regulates Aβ production/clearance balance and Aβ neurotoxicity: A potential therapeutic molecule for Alzheimer's disease.Biomed Pharmacother. 2020 Dec;132:110887. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2020.110887. Epub 2020 Nov 2. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020. PMID: 33254429 Review.
Cited by
-
Selective toxicity of antibacterial agents-still a valid concept or do we miss chances and ignore risks?Infection. 2021 Feb;49(1):29-56. doi: 10.1007/s15010-020-01536-y. Epub 2020 Dec 23. Infection. 2021. PMID: 33367978 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multifunctional angiotensin converting enzyme 2, the SARS-CoV-2 entry receptor, and critical appraisal of its role in acute lung injury.Biomed Pharmacother. 2021 Apr;136:111193. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2020.111193. Epub 2021 Jan 5. Biomed Pharmacother. 2021. PMID: 33461019 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neuroprotective Effect of Ceftriaxone on MPTP-Induced Parkinson's Disease Mouse Model by Regulating Inflammation and Intestinal Microbiota.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021 Dec 13;2021:9424582. doi: 10.1155/2021/9424582. eCollection 2021. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021. PMID: 34938384 Free PMC article.
-
Editorial: Experimental and Innovative Approaches to Multi-Target Treatment of Parkinson's and Alzheimer's Diseases.Front Neurosci. 2022 May 16;16:910020. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2022.910020. eCollection 2022. Front Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35651630 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Convergence of Neuroinflammation, Microbiota, and Parkinson's Disease: Therapeutic Insights and Prospects.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Oct 29;25(21):11629. doi: 10.3390/ijms252111629. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39519181 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

