Differential Mobility Spectrometry-Mass Spectrometry (DMS-MS) in Radiation Biodosimetry: Rapid and High-Throughput Quantitation of Multiple Radiation Biomarkers in Nonhuman Primate Urine
- PMID: 29736597
- PMCID: PMC6287943
- DOI: 10.1007/s13361-018-1977-z
Differential Mobility Spectrometry-Mass Spectrometry (DMS-MS) in Radiation Biodosimetry: Rapid and High-Throughput Quantitation of Multiple Radiation Biomarkers in Nonhuman Primate Urine
Abstract
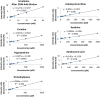
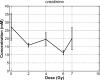
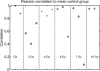
High-throughput methods to assess radiation exposure are a priority due to concerns that include nuclear power accidents, the spread of nuclear weapon capability, and the risk of terrorist attacks. Metabolomics, the assessment of small molecules in an easily accessible sample, is the most recent method to be applied for the identification of biomarkers of the biological radiation response with a useful dose-response profile. Profiling for biomarker identification is frequently done using an LC-MS platform which has limited throughput due to the time-consuming nature of chromatography. We present here a chromatography-free simplified method for quantitative analysis of seven metabolites in urine with radiation dose-response using urine samples provided from the Pannkuk et al. (2015) study of long-term (7-day) radiation response in nonhuman primates (NHP). The stable isotope dilution (SID) analytical method consists of sample preparation by strong cation exchange-solid phase extraction (SCX-SPE) to remove interferences and concentrate the metabolites of interest, followed by differential mobility spectrometry (DMS) ion filtration to select the ion of interest and reduce chemical background, followed by mass spectrometry (overall SID-SPE-DMS-MS). Since no chromatography is used, calibration curves were prepared rapidly, in under 2 h (including SPE) for six simultaneously analyzed radiation biomarkers. The seventh, creatinine, was measured separately after 2500× dilution. Creatinine plays a dual role, measuring kidney glomerular filtration rate (GFR), and indicating kidney damage at high doses. The current quantitative method using SID-SPE-DMS-MS provides throughput which is 7.5 to 30 times higher than that of LC-MS and provides a path to pre-clinical radiation dose estimation. Graphical Abstract.
Keywords: Biomarkers; DMS-MS; Differential mobility spectrometry; FAIMS-MS; Field asymmetric waveform ion mobility spectrometry; Metabolomics; Nonhuman primate; Quantitation; Radiation exposure.
Figures



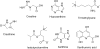
Similar articles
-
Rapid and High-Throughput Detection and Quantitation of Radiation Biomarkers in Human and Nonhuman Primates by Differential Mobility Spectrometry-Mass Spectrometry.J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2016 Oct;27(10):1626-36. doi: 10.1007/s13361-016-1438-5. Epub 2016 Jul 8. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2016. PMID: 27392730 Free PMC article.
-
Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry-Based Metabolomics of Nonhuman Primates after 4 Gy Total Body Radiation Exposure: Global Effects and Targeted Panels.J Proteome Res. 2019 May 3;18(5):2260-2269. doi: 10.1021/acs.jproteome.9b00101. Epub 2019 Mar 18. J Proteome Res. 2019. PMID: 30843397 Free PMC article.
-
Differential mobility spectrometry (DMS) reveals the elevation of urinary acetylcarnitine in non-human primates (NHPs) exposed to radiation.J Mass Spectrom. 2018 Jul;53(7):548-559. doi: 10.1002/jms.4085. J Mass Spectrom. 2018. PMID: 29596720 Free PMC article.
-
Mass spectrometric based approaches in urine metabolomics and biomarker discovery.Mass Spectrom Rev. 2017 Mar;36(2):115-134. doi: 10.1002/mas.21455. Epub 2015 Apr 16. Mass Spectrom Rev. 2017. PMID: 25881008 Review.
-
Radiation metabolomics and its potential in biodosimetry.Int J Radiat Biol. 2011 Aug;87(8):802-23. doi: 10.3109/09553002.2011.556177. Epub 2011 Jun 22. Int J Radiat Biol. 2011. PMID: 21692691 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Combined hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography-scanning field asymmetric waveform ion mobility spectrometry-time-of-flight mass spectrometry for untargeted metabolomics.Anal Bioanal Chem. 2019 Sep;411(24):6309-6317. doi: 10.1007/s00216-019-01790-6. Epub 2019 Apr 23. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2019. PMID: 31011786 Free PMC article.
-
A Systematic Review of Metabolomic and Lipidomic Candidates for Biomarkers in Radiation Injury.Metabolites. 2020 Jun 20;10(6):259. doi: 10.3390/metabo10060259. Metabolites. 2020. PMID: 32575772 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metabolomics in Radiation Biodosimetry: Current Approaches and Advances.Metabolites. 2020 Aug 11;10(8):328. doi: 10.3390/metabo10080328. Metabolites. 2020. PMID: 32796693 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Metabolomics Workflow for Analyzing Complex Biological Samples Using a Combined Method of Untargeted and Target-List Based Approaches.Metabolites. 2020 Aug 25;10(9):342. doi: 10.3390/metabo10090342. Metabolites. 2020. PMID: 32854199 Free PMC article.
-
Biofluid Metabolomics of Mice Exposed to External Low-Dose Rate Radiation in a Novel Irradiation System, the Variable Dose-Rate External 137Cs Irradiator.J Proteome Res. 2021 Nov 5;20(11):5145-5155. doi: 10.1021/acs.jproteome.1c00638. Epub 2021 Sep 29. J Proteome Res. 2021. PMID: 34585931 Free PMC article.
References
-
- International Atomic Energy Agency. Incident and Emergency Preparedness and Response - 2016. 2017 https://www.iaea.org/sites/default/files/publications/reports/2016/gc61-....
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

