PDE4 and mAKAPβ are nodal organizers of β2-ARs nuclear PKA signalling in cardiac myocytes
- PMID: 29733383
- PMCID: PMC6106106
- DOI: 10.1093/cvr/cvy110
PDE4 and mAKAPβ are nodal organizers of β2-ARs nuclear PKA signalling in cardiac myocytes
Abstract
Aims: β1- and β2-adrenergic receptors (β-ARs) produce different acute contractile effects on the heart partly because they impact on different cytosolic pools of cAMP-dependent protein kinase (PKA). They also exert different effects on gene expression but the underlying mechanisms remain unknown. The aim of this study was to understand the mechanisms by which β1- and β2-ARs regulate nuclear PKA activity in cardiomyocytes.
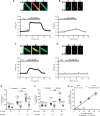
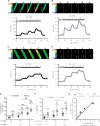
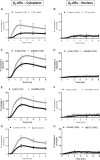
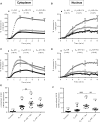
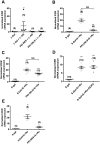
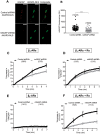
Methods and results: We used cytoplasmic and nuclear targeted biosensors to examine cAMP signals and PKA activity in adult rat ventricular myocytes upon selective β1- or β2-ARs stimulation. Both β1- and β2-AR stimulation increased cAMP and activated PKA in the cytoplasm. Although the two receptors also increased cAMP in the nucleus, only β1-ARs increased nuclear PKA activity and up-regulated the PKA target gene and pro-apoptotic factor, inducible cAMP early repressor (ICER). Inhibition of phosphodiesterase (PDE)4, but not Gi, PDE3, GRK2 nor caveolae disruption disclosed nuclear PKA activation and ICER induction by β2-ARs. Both nuclear and cytoplasmic PKI prevented nuclear PKA activation and ICER induction by β1-ARs, indicating that PKA activation outside the nucleus is required for subsequent nuclear PKA activation and ICER mRNA expression. Cytoplasmic PKI also blocked ICER induction by β2-AR stimulation (with concomitant PDE4 inhibition). However, in this case nuclear PKI decreased ICER up-regulation by only 30%, indicating that other mechanisms are involved. Down-regulation of mAKAPβ partially inhibited nuclear PKA activation upon β1-AR stimulation, and drastically decreased nuclear PKA activation upon β2-AR stimulation in the presence of PDE4 inhibition.
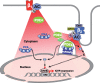
Conclusions: β1- and β2-ARs differentially regulate nuclear PKA activity and ICER expression in cardiomyocytes. PDE4 insulates a mAKAPβ-targeted PKA pool at the nuclear envelope that prevents nuclear PKA activation upon β2-AR stimulation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Control of cytoplasmic and nuclear protein kinase A by phosphodiesterases and phosphatases in cardiac myocytes.Cardiovasc Res. 2014 Apr 1;102(1):97-106. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvu029. Epub 2014 Feb 18. Cardiovasc Res. 2014. PMID: 24550350 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of type 5 phosphodiesterase counteracts β2-adrenergic signalling in beating cardiomyocytes.Cardiovasc Res. 2015 Jun 1;106(3):408-20. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvv123. Epub 2015 Apr 7. Cardiovasc Res. 2015. PMID: 25852085
-
Heterologous desensitization of cardiac β-adrenergic signal via hormone-induced βAR/arrestin/PDE4 complexes.Cardiovasc Res. 2017 May 1;113(6):656-670. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvx036. Cardiovasc Res. 2017. PMID: 28339772 Free PMC article.
-
AKAP12 Signaling Complex: Impacts of Compartmentalizing cAMP-Dependent Signaling Pathways in the Heart and Various Signaling Systems.J Am Heart Assoc. 2020 Jul 7;9(13):e016615. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.120.016615. Epub 2020 Jun 23. J Am Heart Assoc. 2020. PMID: 32573313 Free PMC article. Review.
-
cAMP-specific phosphodiesterase-4D5 (PDE4D5) provides a paradigm for understanding the unique non-redundant roles that PDE4 isoforms play in shaping compartmentalized cAMP cell signalling.Biochem Soc Trans. 2007 Nov;35(Pt 5):938-41. doi: 10.1042/BST0350938. Biochem Soc Trans. 2007. PMID: 17956250 Review.
Cited by
-
PDE4 Phosphodiesterases in Cardiovascular Diseases: Key Pathophysiological Players and Potential Therapeutic Targets.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Nov 30;24(23):17017. doi: 10.3390/ijms242317017. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38069339 Free PMC article. Review.
-
AKAP6 and phospholamban colocalize and interact in HEK-293T cells and primary murine cardiomyocytes.Physiol Rep. 2019 Jul;7(14):e14144. doi: 10.14814/phy2.14144. Physiol Rep. 2019. PMID: 31325238 Free PMC article.
-
Nuclear Calcium in Cardiac (Patho)Physiology: Small Compartment, Big Impact.Biomedicines. 2023 Mar 21;11(3):960. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11030960. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 36979939 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Physiological and pathological roles of protein kinase A in the heart.Cardiovasc Res. 2022 Jan 29;118(2):386-398. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvab008. Cardiovasc Res. 2022. PMID: 33483740 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Status of β1-Adrenoceptor Signal Transduction System in Cardiac Hypertrophy and Heart Failure.Rev Cardiovasc Med. 2023 Sep 21;24(9):264. doi: 10.31083/j.rcm2409264. eCollection 2023 Sep. Rev Cardiovasc Med. 2023. PMID: 39076390 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Xiao RP, Lakatta EG.. Beta 1-adrenoceptor stimulation and beta 2-adrenoceptor stimulation differ in their effects on contraction, cytosolic Ca2+, and Ca2+ current in single rat ventricular cells. Circ Res 1993;73:286–300. - PubMed
-
- Milano CA, Allen LF, Rockman HA, Dolber PC, McMinn TR, Chien KR, Johnson TD, Bond RA, Lefkowitz RJ.. Enhanced myocardial function in transgenic mice overexpressing the beta 2-adrenergic receptor. Science 1994;264:582–586. - PubMed
-
- Communal C, Singh K, Sawyer DB, Colucci WS.. Opposing effects of beta(1)- and beta(2)-adrenergic receptors on cardiac myocyte apoptosis: role of a pertussis toxin-sensitive G protein. Circulation 1999;100:2210–2212. - PubMed
-
- Xiao RP. Beta-adrenergic signaling in the heart: dual coupling of the beta2-adrenergic receptor to G(s) and G(i) proteins. Sci STKE 2001;2001:re15. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

