Combined application of Embelin and tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand inhibits proliferation and invasion in osteosarcoma cells via caspase-induced apoptosis
- PMID: 29731867
- PMCID: PMC5921233
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2018.8209
Combined application of Embelin and tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand inhibits proliferation and invasion in osteosarcoma cells via caspase-induced apoptosis
Abstract
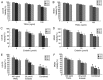
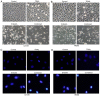
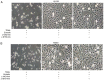
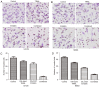
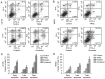
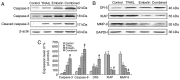
Embelin, as an inhibitor of the X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein (XIAP), may induce apoptosis in various types of cancer cells. The present study aimed to determine the effect of Embelin on the tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL)-induced apoptosis of osteosarcoma cells. Embelin and TRAIL were applied to U2OS and MG63 cells, respectively or in combination. MTT was initially used to detect the difference in survival rates between the group receiving combined application of 100 ng/ml TRAIL and 20 µmol/l Embelin and the individual application groups. Light microscopic quantification was used to detect the morphology of the osteosarcoma cells in each group. Determination of cell apoptosis was subsequently performed using flow cytometry. The invasive ability of the cells was detected by a Transwell assay, prior to relative protein expression being determined by western blot analysis. Based on all the test data, it was revealed that the survival rates and the invasive ability were significantly lower following the combined application of 100 ng/ml TRAIL and 20 µmol/l Embelin than following the individual application of either (P<0.01). Additionally, upregulating expression of caspases, as well as death receptor 5, and downregulating expression of XIAP and matrix metalloproteinase 9 (MMP-9), had more significant effects in the combined group compared with the individual group and the control group. All these results suggested that Embelin may enhance TRAIL-induced apoptosis and inhibit the invasion of human osteosarcoma cells.
Keywords: Embelin; TRAIL; apoptosis; invasion; osteosarcoma.
Figures
Similar articles
-
X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein inhibitor Embelin induces apoptosis via PI3K/Akt pathway and inhibits invasion in osteosarcoma cells.J Cancer Res Ther. 2018 Sep;14(Supplement):S648-S655. doi: 10.4103/0973-1482.203599. J Cancer Res Ther. 2018. PMID: 30249882
-
Effect of Embelin on TRAIL receptor 2 mAb-induced apoptosis of TRAIL-resistant A549 non-small cell lung cancer cells.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2013;14(10):6115-20. doi: 10.7314/apjcp.2013.14.10.6115. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2013. PMID: 24289635
-
Proteasome inhibitor MG132 enhances TRAIL-induced apoptosis and inhibits invasion of human osteosarcoma OS732 cells.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2013 Sep 20;439(2):179-86. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2013.08.066. Epub 2013 Aug 29. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2013. PMID: 23994633
-
Anti-tumor Effects of IL-1β Induced TRAIL-Expressing hUCMSCs on Embelin Treated Breast Cancer Cell Lines.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2023 Apr 1;24(4):1297-1305. doi: 10.31557/APJCP.2023.24.4.1297. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2023. PMID: 37116152 Free PMC article.
-
Embelin and Its Derivatives: Design, Synthesis, and Potential Delivery Systems for Cancer Therapy.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022 Sep 9;15(9):1131. doi: 10.3390/ph15091131. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36145352 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Apoptosis-related factors are relevant to progression of pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors.World J Surg Oncol. 2023 Dec 12;21(1):381. doi: 10.1186/s12957-023-03267-4. World J Surg Oncol. 2023. PMID: 38082268 Free PMC article.
-
CAR-engineered NK cells; a promising therapeutic option for treatment of hematological malignancies.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021 Jul 2;12(1):374. doi: 10.1186/s13287-021-02462-y. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021. PMID: 34215336 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Polyphyllin I enhances tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand-induced inhibition of human osteosarcoma cell growth downregulating the Wnt/β-catenin pathway.J Tradit Chin Med. 2024 Apr;44(2):251-259. doi: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.2024.02.002. J Tradit Chin Med. 2024. PMID: 38504531 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gillissen B, Richter A, Richter A, Overkamp T, Essmann F, Hemmati PG, Preissner R, Belka C, Daniel PT. Targeted therapy of the XIAP/proteasome pathway overcomes TRAIL-resistance in carcinoma by switching apoptosis signaling to a Bax/Bak-independent ‘type I’ mode. Cell Death Dis. 2013;4:e643. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2013.67. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
