Alternagin-C binding to α2β1 integrin controls matrix metalloprotease-9 and matrix metalloprotease-2 in breast tumor cells and endothelial cells
- PMID: 29713337
- PMCID: PMC5917863
- DOI: 10.1186/s40409-018-0150-2
Alternagin-C binding to α2β1 integrin controls matrix metalloprotease-9 and matrix metalloprotease-2 in breast tumor cells and endothelial cells
Abstract
Background: Matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) are key players in tumor progression, helping tumor cells to modify their microenvironment, which allows cell migration to secondary sites. The role of integrins, adhesion receptors that connect cells to the extracellular matrix, in MMP expression and activity has been previously suggested. However, the mechanisms by which integrins control MMP expression are not completely understood. Particularly, the role of α2β1 integrin, one of the major collagen I receptors, in MMP activity and expression has not been studied. Alternagin-C (ALT-C), a glutamate-cysteine-aspartate-disintegrin from Bothrops alternatus venom, has high affinity for an α2β1 integrin. Herein, we used ALT-C as a α2β1 integrin ligand to study the effect of ALT-C on MMP-9 and MMP-2 expression as well as on tumor cells, fibroblats and endothelial cell migration.
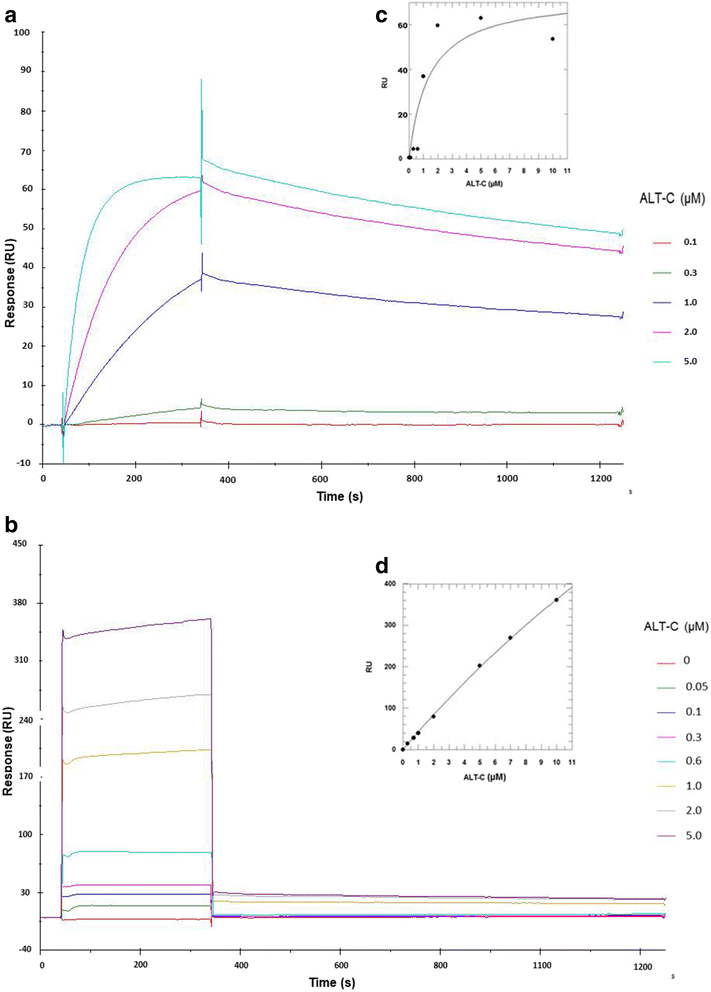
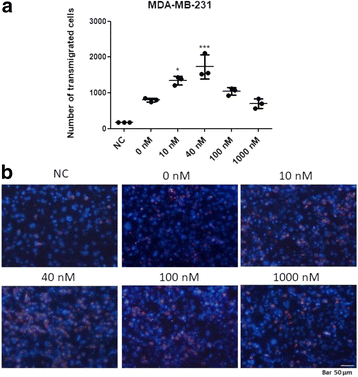
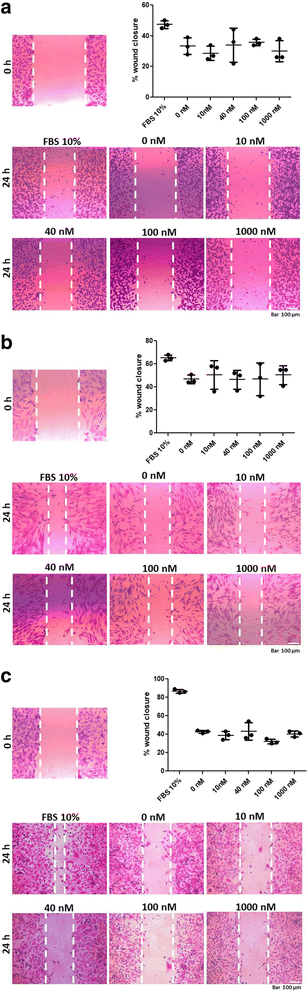
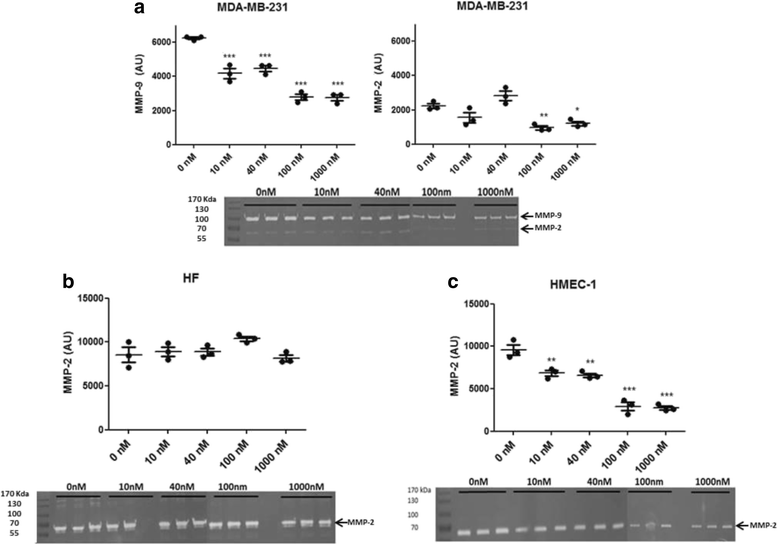
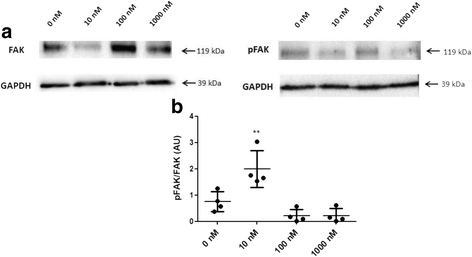
Methods: ALT-C was purified by two steps of gel filtration followed by anion exchange chromatography. The α2β1 integrin binding properties of ALT-C, its dissociation constant (Kd ) relative to this integrin and to collagen I (Col I) were determined by surface plasmon resonance. The effects of ALT-C (10, 40, 100 and 1000 nM) in migration assays were studied using three human cell lines: human fibroblasts, breast tumor cell line MDA-MB-231, and microvascular endothelial cells HMEC-1, considering cells found in the tumor microenvironment. ALT-C effects on MMP-9 and MMP-2 expression and activity were analyzed by quantitative PCR and gelatin zymography, respectively. Focal adhesion kinase activation was determined by western blotting.
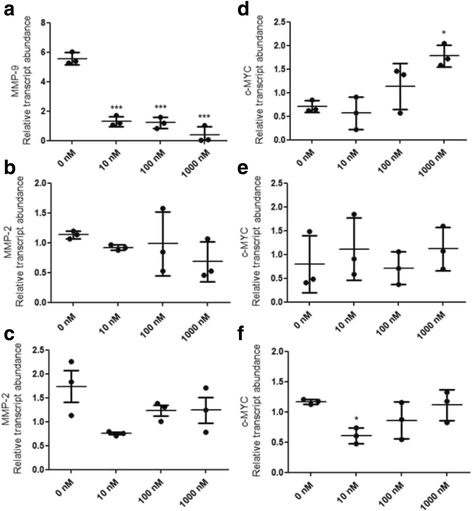
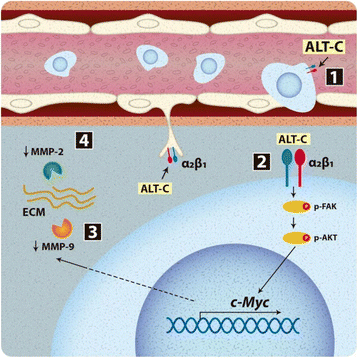
Results: Our data demonstrate that ALT-C, after binding to α2β1 integrin, acts by two distinct mechanisms against tumor progression, depending on the cell type: in tumor cells, ALT-C decreases MMP-9 and MMP-2 contents and activity, but increases focal adhesion kinase phosphorylation and transmigration; and in endothelial cells, ALT-C inhibits MMP-2, which is necessary for tumor angiogenesis. ALT-C also upregulates c-Myc mRNA level, which is related to tumor suppression.
Conclusion: These results demonstrate that α2β1 integrin controls MMP expression and reveal this integrin as a target for the development of antiangiogenic and antimetastatic therapies.
Keywords: ALT-C; C-Myc; Cancer; MMP; Tumor microenvironment; α2β1 integrin.
Conflict of interest statement
Not applicable.The authors declare that they have no competing interests.Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Alternagin-C, an alpha2beta1 integrin ligand, attenuates collagen-based adhesion, stimulating the metastasis suppressor 1 expression in triple-negative breast tumor cells.Toxicon. 2022 Apr 30;210:1-10. doi: 10.1016/j.toxicon.2022.02.001. Epub 2022 Feb 9. Toxicon. 2022. PMID: 35149005
-
Alternagin-C, a disintegrin-like protein from the venom of Bothrops alternatus, modulates alpha2beta1 integrin-mediated cell adhesion, migration and proliferation.Braz J Med Biol Res. 2005 Oct;38(10):1505-11. doi: 10.1590/s0100-879x2005001000007. Epub 2005 Sep 6. Braz J Med Biol Res. 2005. PMID: 16172743 Review.
-
Alternagin-C (ALT-C), a disintegrin-like protein, attenuates alpha2beta1 integrin and VEGF receptor 2 signaling resulting in angiogenesis inhibition.Biochimie. 2020 Jul;174:144-158. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2020.04.023. Epub 2020 Apr 30. Biochimie. 2020. PMID: 32360415
-
The disintegrin-like domain of the snake venom metalloprotease alternagin inhibits alpha2beta1 integrin-mediated cell adhesion.Arch Biochem Biophys. 2000 Dec 15;384(2):341-50. doi: 10.1006/abbi.2000.2120. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2000. PMID: 11368322
-
Altered integrin expression and the malignant phenotype: the contribution of multiple integrated integrin receptors.J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 1998 Apr;3(2):191-200. doi: 10.1023/a:1018798907544. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 1998. PMID: 10819527 Review.
Cited by
-
Snake venom disintegrins update: insights about new findings.J Venom Anim Toxins Incl Trop Dis. 2023 Sep 18;29:e20230039. doi: 10.1590/1678-9199-JVATITD-2023-0039. eCollection 2023. J Venom Anim Toxins Incl Trop Dis. 2023. PMID: 37818211 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Integrin β1 in breast cancer: mechanisms of progression and therapy.Breast Cancer. 2025 Jan;32(1):43-59. doi: 10.1007/s12282-024-01635-w. Epub 2024 Sep 30. Breast Cancer. 2025. PMID: 39343856 Review.
-
Breast Cancer Tumor Stroma: Cellular Components, Phenotypic Heterogeneity, Intercellular Communication, Prognostic Implications and Therapeutic Opportunities.Cancers (Basel). 2019 May 13;11(5):664. doi: 10.3390/cancers11050664. Cancers (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31086100 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cell migration inhibition activity of a non-RGD disintegrin from Crotalus durissus collilineatus venom.J Venom Anim Toxins Incl Trop Dis. 2018 Oct 20;24:28. doi: 10.1186/s40409-018-0167-6. eCollection 2018. J Venom Anim Toxins Incl Trop Dis. 2018. PMID: 30377432 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Geiger TR, Peeper DS. Metastasis mechanisms. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2009;1796(2):293–308. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

