Multiple roles of epithelial heparan sulfate in stomach morphogenesis
- PMID: 29700203
- PMCID: PMC6031332
- DOI: 10.1242/jcs.210781
Multiple roles of epithelial heparan sulfate in stomach morphogenesis
Abstract
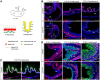
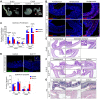
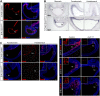
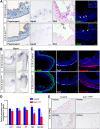
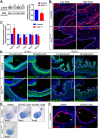
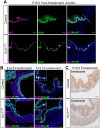
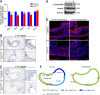
Heparan sulfate proteoglycans (HSPGs) have been shown to regulate various developmental processes. However, the function of heparan sulfate (HS) during the development of mammalian stomach has not been characterized yet. Here, we investigate the role of epithelial HS in embryonic stomach by examining mice deficient in the glycosyltransferase gene Ext1 We show that HS exhibits a specific and dynamic expression pattern in mouse embryonic stomach. Depletion of the epithelial HS leads to stomach hypoplasia, with phenotypic differences in the gastric mucosa between the forestomach and hindstomach. In the posterior stomach, HS depletion disrupts glandular stomach patterning and cytodifferentiation via attenuation of Fgf signaling activity. Inhibition of Fgf signaling in vitro recapitulates the patterning defect. Ligand and carbohydrate engagement assay (LACE) reveals a diminished assembly of Fgf10 and Fgfr2b in the mutant. In the anterior stomach, loss of epithelial HS leads to stratification and differentiation defects of the multilayered squamous epithelium, along with reduced Hh and Bmp signaling activity. Our data demonstrate that epithelial HS plays multiple roles in regulating mammalian stomach morphogenesis in a regional-specific manner.
Keywords: Ext1; Fgf; Glandular development; Heparan sulfate; Hh-Bmp; Stratification.
© 2018. Published by The Company of Biologists Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interestsThe authors declare no competing or financial interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Specific heparan sulfate structures modulate FGF10-mediated submandibular gland epithelial morphogenesis and differentiation.J Biol Chem. 2008 Apr 4;283(14):9308-17. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M709995200. Epub 2008 Jan 28. J Biol Chem. 2008. PMID: 18230614 Free PMC article.
-
Stomach development is dependent on fibroblast growth factor 10/fibroblast growth factor receptor 2b-mediated signaling.Gastroenterology. 2006 Apr;130(4):1233-44. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2006.02.018. Gastroenterology. 2006. PMID: 16618415
-
Epithelial heparan sulfate regulates Sonic Hedgehog signaling in lung development.PLoS Genet. 2017 Aug 31;13(8):e1006992. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1006992. eCollection 2017 Aug. PLoS Genet. 2017. PMID: 28859094 Free PMC article.
-
FGF10: A multifunctional mesenchymal-epithelial signaling growth factor in development, health, and disease.Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2016 Apr;28:63-9. doi: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2015.10.001. Epub 2015 Oct 31. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2016. PMID: 26559461 Review.
-
Tinkering with heparan sulfate sulfation to steer development.Trends Cell Biol. 2007 Apr;17(4):173-7. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2007.02.006. Epub 2007 Feb 21. Trends Cell Biol. 2007. PMID: 17320398 Review.
Cited by
-
The Balance between Differentiation and Terminal Differentiation Maintains Oral Epithelial Homeostasis.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Oct 13;13(20):5123. doi: 10.3390/cancers13205123. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34680271 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Physiology and Pathophysiology of Heparan Sulfate in Animal Models: Its Biosynthesis and Degradation.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Feb 10;23(4):1963. doi: 10.3390/ijms23041963. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35216081 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of FGF10 Signaling in Development and Disease.Front Genet. 2018 Oct 23;9:500. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2018.00500. eCollection 2018. Front Genet. 2018. PMID: 30405705 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Aubin J., Dery U., Lemieux M., Chailler P. and Jeannotte L. (2002). Stomach regional specification requires Hoxa5-driven mesenchymal-epithelial signaling. Development 129, 4075-4087. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

