Amentoflavone Inhibits ERK-modulated Tumor Progression in Hepatocellular Carcinoma In Vitro
- PMID: 29695559
- PMCID: PMC6000793
- DOI: 10.21873/invivo.11274
Amentoflavone Inhibits ERK-modulated Tumor Progression in Hepatocellular Carcinoma In Vitro
Abstract
Background/aim: A previous study indicated that amentoflavone inhibits tumor growth of breast cancer. However, the anti-cancer effects and mechanism of amentoflavone in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) have not been elucidated. The aim of the present study was to verify the effect of amentoflavone on tumor progression in HCC.
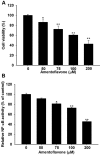
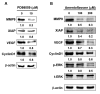
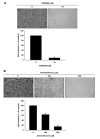
Materials and methods: HCC SK-Hep1 cells were treated with different concentrations of amentoflavone or 10 μM PD98059 (extracellular signal-regulated kinases (ERK) inhibitor) for 48 h, respectively, and then cell viability, NF-κB activation, levels of tumor progression-associated proteins, and cell invasion were evaluated with 3-(4,5-Dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT), NF-κB reporter gene assay, western blotting, and cell invasion assay.
Results: The results demonstrated that both amentoflavone and PD98059 not only significantly reduced cell viability, NF-κB activation, and cell invasion, but also inhibited the expression of tumor progression-associated proteins. In addition, we found that amentoflavone suppresses ERK phosphorylation.
Conclusion: The results of the present study suggest that amentoflavone down-regulates ERK-modulated tumor progression in HCC.
Keywords: Amentoflavone; ERK; NF-κB; hepatocellular carcinoma.
Copyright© 2018, International Institute of Anticancer Research (Dr. George J. Delinasios), All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Chemopreventive mechanisms of amentoflavone: recent trends and advancements.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2023 May;396(5):865-876. doi: 10.1007/s00210-023-02416-6. Epub 2023 Feb 11. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36773053 Review.
-
Amentoflavone Inhibits Hepatocellular Carcinoma Progression Through Blockage of ERK/NF-ĸB Activation.In Vivo. 2018 Sep-Oct;32(5):1097-1103. doi: 10.21873/invivo.11351. In Vivo. 2018. PMID: 30150431 Free PMC article.
-
Amentoflavone Inhibits Metastatic Potential Through Suppression of ERK/NF-κB Activation in Osteosarcoma U2OS Cells.Anticancer Res. 2017 Sep;37(9):4911-4918. doi: 10.21873/anticanres.11900. Anticancer Res. 2017. PMID: 28870912
-
Fluoxetine Induces Apoptosis through Extrinsic/Intrinsic Pathways and Inhibits ERK/NF-κB-Modulated Anti-Apoptotic and Invasive Potential in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells In Vitro.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Feb 11;20(3):757. doi: 10.3390/ijms20030757. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 30754643 Free PMC article.
-
Insights Into Amentoflavone: A Natural Multifunctional Biflavonoid.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Dec 22;12:768708. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.768708. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 35002708 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Natural Products as Inducers of Non-Canonical Cell Death: A Weapon against Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Jan 15;13(2):304. doi: 10.3390/cancers13020304. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33467668 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Induction of Apoptosis and Inhibition of EGFR/NF-κB Signaling Are Associated With Regorafenib-sensitized Non-small Cell Lung Cancer to Cisplatin.In Vivo. 2021 Sep-Oct;35(5):2569-2576. doi: 10.21873/invivo.12539. In Vivo. 2021. PMID: 34410944 Free PMC article.
-
ERK/AKT Inactivation and Apoptosis Induction Associate With Quetiapine-inhibited Cell Survival and Invasion in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells.In Vivo. 2020 Sep-Oct;34(5):2407-2417. doi: 10.21873/invivo.12054. In Vivo. 2020. PMID: 32871766 Free PMC article.
-
Amentoflavone maintaining extracellular matrix homeostasis and inhibiting subchondral bone loss in osteoarthritis by inhibiting ERK, JNK and NF-κB signaling pathways.J Orthop Surg Res. 2024 Oct 15;19(1):662. doi: 10.1186/s13018-024-05075-2. J Orthop Surg Res. 2024. PMID: 39407273 Free PMC article.
-
Chemopreventive mechanisms of amentoflavone: recent trends and advancements.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2023 May;396(5):865-876. doi: 10.1007/s00210-023-02416-6. Epub 2023 Feb 11. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36773053 Review.
References
-
- Roberts PJ, Der CJ. Targeting the Raf-MEK-ERK mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade for the treatment of cancer. Oncogene. 2007;26:3291–3310. - PubMed
-
- Schmitz KJ, Wohlschlaeger J, Lang H, Sotiropoulos GC, Malago M, Steveling K, Reis H, Cicinnati VR, Schmid KW, Baba HA. Activation of the ERK and AKT signalling pathway predicts poor prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma and ERK activation in cancer tissue is associated with hepatitis C virus infection. J Hepatol. 2008;48:83–90. - PubMed
-
- Tsai JJ, Pan PJ, Hsu FT. Regorafenib induces extrinsic and intrinsic apoptosis through inhibition of ERK/NF-ĸB activation in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Oncol Rep. 2017;37:1036–1044. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
