The Novel Roles of Connexin Channels and Tunneling Nanotubes in Cancer Pathogenesis
- PMID: 29695070
- PMCID: PMC5983846
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms19051270
The Novel Roles of Connexin Channels and Tunneling Nanotubes in Cancer Pathogenesis
Abstract
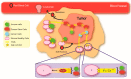
Neoplastic growth and cellular differentiation are critical hallmarks of tumor development. It is well established that cell-to-cell communication between tumor cells and "normal" surrounding cells regulates tumor differentiation and proliferation, aggressiveness, and resistance to treatment. Nevertheless, the mechanisms that result in tumor growth and spread as well as the adaptation of healthy surrounding cells to the tumor environment are poorly understood. A major component of these communication systems is composed of connexin (Cx)-containing channels including gap junctions (GJs), tunneling nanotubes (TNTs), and hemichannels (HCs). There are hundreds of reports about the role of Cx-containing channels in the pathogenesis of cancer, and most of them demonstrate a downregulation of these proteins. Nonetheless, new data demonstrate that a localized communication via Cx-containing GJs, HCs, and TNTs plays a key role in tumor growth, differentiation, and resistance to therapies. Moreover, the type and downstream effects of signals communicated between the different populations of tumor cells are still unknown. However, new approaches such as artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) could provide new insights into these signals communicated between connected cells. We propose that the identification and characterization of these new communication systems and their associated signaling could provide new targets to prevent or reduce the devastating consequences of cancer.
Keywords: gap junctions; glioblastoma; hemichannels; intercellular communication; tumor microtubes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Connexin-dependent intercellular stress signaling in tissue homeostasis and tumor development.Acta Biochim Pol. 2017;64(3):377-389. doi: 10.18388/abp.2017_1592. Epub 2017 May 17. Acta Biochim Pol. 2017. PMID: 28510614 Review.
-
Recruitment of RNA molecules by connexin RNA-binding motifs: Implication in RNA and DNA transport through microvesicles and exosomes.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 2017 Apr;1864(4):728-736. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2017.02.001. Epub 2017 Feb 4. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 2017. PMID: 28167212 Review.
-
Connexins in Cancer: Jekyll or Hyde?Biomolecules. 2020 Dec 10;10(12):1654. doi: 10.3390/biom10121654. Biomolecules. 2020. PMID: 33321749 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Communication of Ca(2+) signals via tunneling membrane nanotubes is mediated by transmission of inositol trisphosphate through gap junctions.Cell Calcium. 2016 Oct;60(4):266-72. doi: 10.1016/j.ceca.2016.06.004. Epub 2016 Jun 20. Cell Calcium. 2016. PMID: 27388952 Free PMC article.
-
Gap junctional communication promotes apoptosis in a connexin-type-dependent manner.Cell Death Dis. 2013 Apr 11;4(4):e584. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2013.105. Cell Death Dis. 2013. PMID: 23579271 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
TNTdetect.AI: A Deep Learning Model for Automated Detection and Counting of Tunneling Nanotubes in Microscopy Images.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Oct 10;14(19):4958. doi: 10.3390/cancers14194958. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36230881 Free PMC article.
-
Perspective on nanochannels as cellular mediators in different disease conditions.Cell Commun Signal. 2018 Nov 8;16(1):76. doi: 10.1186/s12964-018-0281-7. Cell Commun Signal. 2018. PMID: 30409198 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prospective Approach to Deciphering the Impact of Intercellular Mitochondrial Transfer from Human Neural Stem Cells and Brain Tumor-Initiating Cells to Neighboring Astrocytes.Cells. 2024 Jan 23;13(3):204. doi: 10.3390/cells13030204. Cells. 2024. PMID: 38334595 Free PMC article.
-
Spatial Arrangements of Connexin43 in Cancer Related Cells and Re-Arrangements under Treatment Conditions: Investigations on the Nano-Scale by Super-Resolution Localization Light Microscopy.Cancers (Basel). 2019 Mar 4;11(3):301. doi: 10.3390/cancers11030301. Cancers (Basel). 2019. PMID: 30836676 Free PMC article.
-
Gap junction protein connexin43 and tunneling nanotubes in human trabecular meshwork cells.Int J Physiol Pathophysiol Pharmacol. 2019 Oct 15;11(5):212-219. eCollection 2019. Int J Physiol Pathophysiol Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31777645 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

