Reversal of memory and neuropsychiatric symptoms and reduced tau pathology by selenium in 3xTg-AD mice
- PMID: 29691439
- PMCID: PMC5915484
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-018-24741-0
Reversal of memory and neuropsychiatric symptoms and reduced tau pathology by selenium in 3xTg-AD mice
Abstract
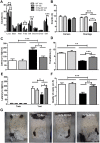
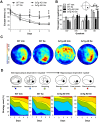
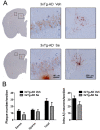
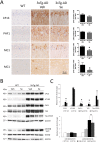
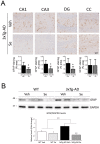
Accumulation of amyloid-β plaques and tau contribute to the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease (AD), but it is unclear whether targeting tau pathology by antioxidants independently of amyloid-β causes beneficial effects on memory and neuropsychiatric symptoms. Selenium, an essential antioxidant element reduced in the aging brain, prevents development of neuropathology in AD transgenic mice at early disease stages. The therapeutic potential of selenium for ameliorating or reversing neuropsychiatric and cognitive behavioral symptoms at late AD stages is largely unknown. Here, we evaluated the effects of chronic dietary sodium selenate supplementation for 4 months in female 3xTg-AD mice at 12-14 months of age. Chronic sodium selenate treatment efficiently reversed hippocampal-dependent learning and memory impairments, and behavior- and neuropsychiatric-like symptoms in old female 3xTg-AD mice. Selenium significantly decreased the number of aggregated tau-positive neurons and astrogliosis, without globally affecting amyloid plaques, in the hippocampus of 3xTg-AD mice. These results indicate that selenium treatment reverses AD-like memory and neuropsychiatric symptoms by a mechanism involving reduction of aggregated tau and/or reactive astrocytes but not amyloid pathology. These results suggest that sodium selenate could be part of a combined therapeutic approach for the treatment of memory and neuropsychiatric symptoms in advanced AD stages.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Sex Differences in Neuropathology and Cognitive Behavior in APP/PS1/tau Triple-Transgenic Mouse Model of Alzheimer's Disease.Neurosci Bull. 2018 Oct;34(5):736-746. doi: 10.1007/s12264-018-0268-9. Epub 2018 Aug 11. Neurosci Bull. 2018. PMID: 30099679 Free PMC article.
-
Selenomethionine Mitigates Cognitive Decline by Targeting Both Tau Hyperphosphorylation and Autophagic Clearance in an Alzheimer's Disease Mouse Model.J Neurosci. 2017 Mar 1;37(9):2449-2462. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3229-16.2017. Epub 2017 Jan 30. J Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 28137967 Free PMC article.
-
Ultrasound with microbubbles improves memory, ameliorates pathology and modulates hippocampal proteomic changes in a triple transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer's disease.Theranostics. 2020 Sep 26;10(25):11794-11819. doi: 10.7150/thno.44152. eCollection 2020. Theranostics. 2020. PMID: 33052247 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of CX3CR1 and Fractalkine Chemokines in Amyloid Beta Clearance and p-Tau Accumulation in Alzheimer's Disease (AD) Rodent Models: Is Fractalkine a Systemic Biomarker for AD?Curr Alzheimer Res. 2016;13(4):403-12. doi: 10.2174/1567205013666151116125714. Curr Alzheimer Res. 2016. PMID: 26567742 Review.
-
Alcohol drinking exacerbates neural and behavioral pathology in the 3xTg-AD mouse model of Alzheimer's disease.Int Rev Neurobiol. 2019;148:169-230. doi: 10.1016/bs.irn.2019.10.017. Epub 2019 Oct 23. Int Rev Neurobiol. 2019. PMID: 31733664 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Selective ferroptosis vulnerability due to familial Alzheimer's disease presenilin mutations.Cell Death Differ. 2022 Nov;29(11):2123-2136. doi: 10.1038/s41418-022-01003-1. Epub 2022 Apr 21. Cell Death Differ. 2022. PMID: 35449212 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Selenium Treatment on Central Insulin Sensitivity: A Proteomic Analysis in β-Amyloid Precursor Protein/Presenilin-1 Transgenic Mice.Front Mol Neurosci. 2022 Jul 7;15:931788. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2022.931788. eCollection 2022. Front Mol Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35875664 Free PMC article.
-
Selenoprotein W modulates tau homeostasis in an Alzheimer's disease mouse model.Commun Biol. 2024 Jul 17;7(1):872. doi: 10.1038/s42003-024-06572-0. Commun Biol. 2024. PMID: 39020075 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Fish Oil Combined with Selenium and Zinc on Learning and Memory Impairment in Aging Mice and Amyloid Precursor Protein Processing.Biol Trace Elem Res. 2021 May;199(5):1855-1863. doi: 10.1007/s12011-020-02280-y. Epub 2020 Jul 14. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2021. PMID: 32666432
-
Sodium selenate as a disease-modifying treatment for mild-moderate Alzheimer's disease: an open-label extension study.BMJ Neurol Open. 2021 Dec 16;3(2):e000223. doi: 10.1136/bmjno-2021-000223. eCollection 2021. BMJ Neurol Open. 2021. PMID: 34988458 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

